Everything posted by ResidentialBusiness
-
Labour unveils disability benefits reforms that aim to save more than £5bn
Move risks stoking biggest backbench rebellion of Sir Keir Starmer’s premiershipView the full article
-
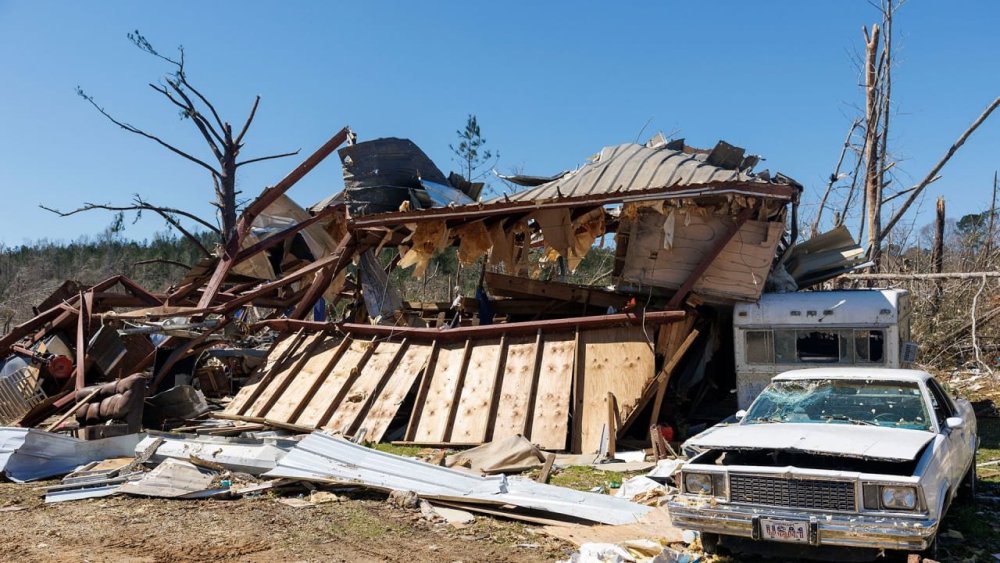
3-day outbreak of severe weather leaves hundreds displaced in U.S. South and Midwest
Kim Atchison was hunkered down in her grandmother’s storm shelter with her 5-year-old grandson Saturday night in their tiny Alabama hometown of Plantersville when her husband and son raced in. “Get down; get all the way down to the bottom of the cellar,” they told her, saying they could see a twister coming. Atchison said she remembers first the “dead silence” and then hearing the wind that felt like a funnel and things outside hitting against each other. “All was quiet after that because it was that fast,” she said. “Like a snap of a finger and it was gone.” Atchison and her family were among the fortunate ones to avoid being killed in the three-day outbreak of severe weather across eight states that kicked up a devastating combination of wildfires, dust storms, and tornadoes—claiming at least 42 lives since Friday. Two people were killed by a twister in Plantersville. One of the lives lost was that of 82-year-old Annie Free, who “just looked out for everyone,” Atchison’s husband said. The tornado struck Free’s home, leaving only the front patio behind. Darren Atchison spent Monday delivering granola bars and sports drinks to the pummeled neighborhood, driving his all-terrain vehicle around downed trees. More than a half-dozen houses were destroyed while others were left in rough shape, some with walls peeled clean off. The tornado flipped a trailer onto its roof and toppled trees in every direction. When Heidi Howland emerged from her home after hiding in her bedroom underneath a mattress with her husband, kids and grandkids as the twister approached, she found fallen trees and broken car windows. Many of her neighbors whose houses were damaged came to her front porch to take refuge from the rain after the storm passed Saturday night. One was Free’s daughter, who Howland said cried late into the night because the first responders couldn’t find her mother. Free’s body wasn’t found until the morning. Also killed was Dunk Pickering, a fixture in the community who often hosted live music events and helped neighbors during tough times. Neighbor John Green found Pickering’s body in the wreckage of a building just across the street from Green’s home. “Whether he knew you or not, he would help anyone,” Green said. “I’ve known him for 20 years. He’s been like that ever since the day I first met him.” Green and other neighbors spent at least five hours Saturday night pulling people from the rubble and carrying them to paramedics who were unable to reach the area because roads were blocked by debris. Wildfires in Oklahoma Wind-driven wildfires across the state destroyed more than 400 homes over the weekend and will continue to be a threat in the coming days because of high winds. Dozens of fires were still burning across the state on Monday, said Keith Merckx at Oklahoma Forestry Services, and much of the state including the Oklahoma City area remained under fire warnings. While conditions over the weekend allowed crews to get a handle on most wildfires across Texas and Oklahoma, forecasters at the National Weather Service said extremely critical fire weather conditions were expected Tuesday over an area spanning from southeastern New Mexico through the Texas Panhandle and into western Oklahoma. “These fires, once they get started, become really hard to stop. They move more quickly than our resources can keep up with,” Merckx said. Four deaths so far were blamed on the fires or high winds, according to the Oklahoma Department of Emergency Management. More than 70 homes were destroyed by wildfire outbreaks Friday in and around Stillwater, home to Oklahoma State University. Tornadoes and high winds across the South In Mississippi, six people died and more than 200 were displaced by a string of tornadoes across three counties, the governor said. Within about an hour of each other on Saturday, two big tornadoes tore through Walthall County, Mississippi, according to the National Weather Service. The strongest one packed winds of 170 mph (274 kph) when it swept a well-built home from its foundation, leaving a pile of debris behind, the agency said in an updated report late Monday. Three people died in the county, including 7-year-old Carter Young, who was in a mobile home, Walthall County Coroner Chris Blackwell said. The other two people killed—Gabrielle Pierre, 34, and Jeffery Irvin, 42—were in a mobile home next door to the one where Young was found, Blackwell said. Scattered twisters and storm damage led to the deaths of at least 13 people in Missouri, including a 30-year-old man who along with his dog was found dead from carbon monoxide poisoning after he was using a generator indoors during the storm, authorities said. In Arkansas, officials confirmed three deaths. As the storm headed east, two boys ages 11 and 13 were killed when a tree fell on their home in western North Carolina early Sunday, firefighters in Transylvania County said. Firefighters found them amid the uprooted three-foot-wide tree after relatives said they had been trapped in their bedroom, officials said. A tornado touched down at about 3 a.m. Monday in a neighborhood in Perquimans County, North Carolina, destroying three mobile homes and damaging several others, according to the National Weather Service. Eight people were injured in the community, with no reported deaths, the weather service said. The community is about 50 miles (80 kilometers) south of Norfolk, Virginia. Dust storms in Kansas and Texas High winds spurred dust storms that led to almost a dozen deaths in car crashes Friday. Eight people died in a Kansas highway pileup involving at least 50 vehicles, according to the state highway patrol. Authorities said three people also were killed in car crashes during a dust storm in Amarillo in the Texas Panhandle. Seewer reported from Toledo, Ohio. Associated Press writers Jamie Stengle in Dallas, Sara Cline in Tylertown, Mississippi, Jeff Martin in Atlanta, Nadia Lathan in Austin, Texas; Rebecca Reynolds in Louisville, Kentucky, and Jeff Roberson in Wayne County, Missouri, contributed. —Safiyah Riddle and John Seewer, Associated Press View the full article
-
TikTok Has a New Security Checkup Dashboard
Social media apps aren't exactly known for their privacy and security features, but TikTok users are getting a little bit of help with a built-in tool to monitor their account security and keep their information safe. The new Security Checkup dashboard shows you where your TikTok security is lacking with step-by-step guidance to update your settings. How to use TikTok's Security CheckupTo get to your security dashboard on TikTok, go to your profile and tap Settings and privacy > Security and permissions. Security Checkup will show you which settings have been completed and which need attention, with guidance on how to update each: Adding an email and/or phone number for account recovery Enabling two-step verification Creating a passkey with device-based authentication like Face ID or Touch Unlock Checking which devices are logged into your account (and removing any that are unauthorized or aren't in use) TikTok will also flag "unusual account behavior" and log it in your Security Checkup for you to review. TikTok isn't the only social media platform with this kind of security feature. Meta, for example, has a Security Checkup on Instagram that guides users through improving their password strength, enabling two-factor authentication, and adding account recovery information. You can find this in your profile settings (tap the three vertical lines) and go to Accounts Center > Password and Security > Security Checkup to select the account you want to evaluate. Google has a similar dashboard that shows you where you are signed in with your Google account, apps and services you've connected, recent security activity, sign-in and recovery settings, and recommendations for improving your account security. View the full article
-
NCAA March Madness 2025 livestream: How to watch the men’s and women’s First Four games
Now that the last pint of green beer has been poured, it’s time to move on to the next reason to celebrate March: college basketball. The National Collegiate Athletic Association’s (NCAA) annual single-elimination tournament, more commonly known as March Madness, kicked things off over the weekend with Selection Sunday. Here’s what you need to know heading into the First Four games and how to tune in. A very brief history of March Madness On the men’s side, the tournament dates back to 1939. Eight teams competed for the Division 1 Championship title, with Oregon taking home the inaugural trophy. The women got in on the action in 1982. Since then, the Tennessee Lady Volunteers have competed in every edition of the tournament. What happened during Selection Sunday? These days, the playing field has expanded to 68 teams on both sides of the tournament. Thirty-one of the teams are picked because they automatically qualify after winning their own Division 1 conference. The other 37 are picked by the NCAA Selection Committee, who takes factors such as the team’s overall season record into consideration. After the teams are chosen, that same committee grants each one a seed or ranking. This helps ensure the playing schedule is fair and balanced. It’s hard not to be an armchair critic when the teams and seeds are announced. Almost every year has some controversy, and 2025 is no exception. Men’s fans were shocked to see the University of North Carolina included in the tournament after its 22–13 record in the 2024–25 season. Bubba Cunningham, the UNC athletic director who also sits on the Selection Committee, assured CBS that he recused himself from the process. “All the policies and procedures were followed, and Keith [Gill, the commissioner of the Sun Belt Conference] can address exactly how North Carolina was discussed because I was not in the room for any of that,” he explained, as cited by CNN. Meanwhile, women’s fans were surprised to see the UCLA Bruins take the No. 1 seed from South Carolina. This is the first time since 2021 that the Gamecocks were not given the honors. Head Coach Dawn Stanley would like to have more insight into the decision-making process. “Obviously, it’s disappointing. It really is. I’d like to get some feedback on how they came to that conclusion because we put together, we manufactured a schedule that if done right it should produce an overall number one seed,” she said, according to CBS Sports. How can I watch or stream the First Four March Madness games? Now that the beginning of the brackets are ready to go, let’s watch some hoops. The action-packed tournament starts out with the lowest seeded teams facing off in what’s known as the First Four. For the first men’s game, St. Francis will take on Alabama State on Tuesday at 6:40 p.m. ET. Here’s the full First Four men’s schedule: Tuesday, March 18: Alabama State vs. Saint Francis: 6:40 p.m. (truTV) San Diego State vs. North Carolina: 9:10 p.m. (truTV) Wednesday, March 19: American University vs. Mount St. Mary’s: 6:40 p.m. (truTV) Texas vs. Xavier: 9:10 p.m. (truTV) For the first women’s game, Iowa State and Princeton will battle it out on Wednesday at 7 p.m. ET. Here’s the full First Four women’s schedule: Wednesday, March 19: Iowa State vs. Princeton: 7 p.m. (ESPNU) UC San Diego vs. Southern U: 9 p.m. (ESPNU) Thursday, March 20: High Point vs. William & Mary: 9 p.m. (ESPNU) Columbia vs. Washington: 7 p.m. (ESPN2) Every moment of the NCAA men’s and women’s tournament will be broadcast live. Because there are numerous games, it takes multiple channels to broadcast them all. This year the First Four men’s games will be on the TruTV channel. This lesser-known cable channel is included in most traditional cable subscriptions. The women’s First Four games will be on ESPNU and ESPN2. Cord-cutters should be able to find these channels on the following streaming services, but double check your local offerings before signing up: Hulu + Live TV YouTube TV Sling TV What about the rest of the tournament? The rest of the men’s games will be spread out on CBS, TBS, and TNT, and their streaming platforms, such as Paramount+. The women’s tournament will call ESPN’s networks and ABC home. For a printable men’s bracket and full schedule click here. For a printable women’s bracket and full schedule click here. View the full article
-
UK offers bumper pay package for new national armaments guru
Salary will be up to £400,000 per year, plus an annual bonus of up to 60%View the full article
-
How to Add Your Passport to Google Wallet
Airport security will probably always be somewhat of a hassle, but one friction point you can potentially minimize is utilizing a digital ID in place of a physical one—and if you're an Android user, your passport added to Google Wallet's ID pass is officially accepted by TSA. It's certainly convenient to not have to carry or keep track of your physical passport when you travel, and a digital passport in ID pass can get you through security screening if you don't have a REAL ID after the requirements take effect on May 7. That said, your digital passport doesn't completely replace your physical document, which you'll still need when traveling internationally and in situations where you have to present identification outside of TSA. Here's how to digitize your passport and other forms of identification for the next time you fly. How to add your passport to Google WalletTo add your passport to ID pass, open Google Wallet on your Android device and tap the + icon. Tap ID > ID pass, then hit the Get Started button. The app will guide you through a series of instructions to scan your passport and your face, which will take several minutes to complete and approve. You can also add a state-issued ID (like your driver's license) to Google Wallet using this same process—just select ID > Driver's license or state ID instead of ID pass. How to use other digital IDs for travelAt the time of writing, Apple Wallet and Samsung Wallet do not support passports, and ID pass for Google Wallet is the only digital passport accepted at TSA for domestic travel. However, your driver's license or identification card stored in Apple Wallet, Google Wallet, Samsung Wallet, or a state-specific mobile app can also get you through security screening if issued by one of the following states: Arizona California Colorado Georgia Hawaii Iowa Louisiana Maryland New Mexico New York Ohio Puerto Rico Utah Virginia West Virginia To add an ID to Apple Wallet, tap the + icon in the app and hit Driver's License or State ID. Select your eligible state, and follow the prompts. For Samsung Wallet, click the + icon, tap Digital IDs > Driver's License/State ID, and follow the instructions to scan your ID and face and authenticate with your fingerprint or a PIN. Note that some of the states listed (like New York and Utah) require you to use a state-specific app for digital IDs instead of your device's digital wallet. Even if you have a digital ID, don't count on being able to use it at every airport. Check TSA's digital ID map before you leave home to make sure any airport you are traveling through accepts eligible digital IDs. (On the flip side, TSA PreCheck members traveling on Delta Airlines, United Airlines, and Alaska Airlines out of a select number of airports can clear security solely on facial recognition—no physical or digital documents required.) View the full article
-
Google PMax: Inside The Negative Keyword Limit Increase & What’s Next via @sejournal, @adsliaison
Explore the reasons behind the negative keyword limit increase in Google Ads and what it means for your advertising strategy. The post Google PMax: Inside The Negative Keyword Limit Increase & What’s Next appeared first on Search Engine Journal. View the full article
-
How to use Google Search Console for keyword research
When it comes to keyword research, SEO professionals often rely on expensive tools to find the right keywords. However, Google Search Console (GSC) provides a completely free way to access insights straight from Google itself. GSC is a powerful and often underused tool that shows exactly what is working on a site and where improvements can be made. Unlike other keyword research tools that provide generic suggestions and estimated data, GSC delivers real-life search data based on actual searches leading to a website. It can often uncover interesting insights. Here’s how to use GSC to find valuable keyword opportunities and improve rankings. Why use Google Search Console for keyword research? Google Search Console is a goldmine for keyword insights. Here’s why you should use it. Free and requires no subscriptions: Many SEO tools require costly subscriptions, but GSC is completely free, making it accessible to businesses of all sizes. Provides real keyword performance data: Most keyword research tools provide estimated search volumes, but GSC shows actual data on searches that lead users to your site, ensuring accuracy. Helps identify keywords with high optimization potential: Analyzing existing keyword rankings allows you to optimize content and improve visibility with small tweaks. Uncovers content gaps and new topic opportunities: GSC reveals queries that may not have been intentionally targeted but are already driving traffic, providing ideas for new content. Tracks keyword performance over time: You can monitor how rankings fluctuate, which keywords are growing in importance, and how search behavior is evolving. Helps understand search intent: By analyzing query data, you can refine content to better match user intent and increase engagement. Provides device-specific insights: Performance can vary between desktop and mobile users, and GSC helps fine-tune SEO strategies accordingly. Dig deeper: 6 vital lenses for effective keyword research 5-step process for using Google Search Console Step 1: Discover what you’re already ranking for Rather than focusing solely on new keywords, GSC helps identify keywords that are already ranking but could perform better with some optimization. How to find ranking keywords Log into Google Search Console and select a website. Click on Performance > Search Results. Scroll down to the Queries section to see the search terms leading visitors to the site. What to look for Keywords ranking in positions 11-30 (Pages 2-3 of Google). These have potential to break into Page 1 with slight optimizations. Unexpected keywords that weren’t intentionally targeted but are ranking anyway, presenting new content opportunities. High-impression, low-CTR keywords, indicating that page titles or meta descriptions may need optimization to improve click-through rates. Seasonal search trends, allowing content to be optimized ahead of high-traffic periods. Queries with declining CTRs, which may indicate changing search intent or increased competition. Dig deeper: Why traditional keyword research is failing and how to fix it with search intent Step 2: Find new blog topics GSC is useful for content ideation by revealing long-tail search queries that are ideal for blog topics. How to do it Navigate to the Performance report and look for long-tail search queries. Identify keywords that are not well-covered on the site. Create dedicated blog posts answering those exact queries. Optimize existing content by incorporating these new long-tail keywords naturally. Cross-link between related blog posts to build topical authority. Get the newsletter search marketers rely on. Business email address Sign me up! Processing... See terms. Step 3: Identify and manage irrelevant keywords GSC can also reveal irrelevant search terms bringing traffic to a site. Some queries may drive traffic that does not align with the intended audience, leading to vanity traffic that skews reports. How to manage irrelevant search terms Identify keywords bringing in non-relevant traffic that do not contribute to conversions or engagement. Adjust on-page content and metadata to clarify the intent of the page. Use negative keywords in paid search campaigns if these terms are also appearing in PPC reports. Monitor engagement rates and session duration for traffic from these terms to assess engagement levels. Example If a bathroom renovation site ranks for “how to clean a kitchen splashback,” that traffic is unlikely to convert into meaningful engagement. Identifying and minimizing such cases ensures that a site is optimized for relevant search terms. Step 4: Track overall keyword performance GSC provides detailed performance tracking without the need for a paid keyword tracking tool. Key metrics to check Total clicks: The number of visitors coming from search results. Total impressions: The number of times a site appears in search results. Click-through rate (CTR): The percentage of users who click after seeing a result. Average position: The ranking in Google search results. Branded vs. non-branded search terms: Understanding the balance between brand visibility and new audience acquisition. Device-specific performance: Identifying whether certain keywords perform better on mobile vs. desktop. Unlike most SEO tools that limit the number of keywords tracked, GSC offers unlimited data on how a site is performing. Step 5: Monitor and adjust regularly SEO requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments. Google’s algorithms evolve, competitors optimize, and search trends change. Regularly checking GSC data helps refine content strategies over time. Quick SEO wins using GSC Find and optimize underperforming pages with high impressions but low CTR. Prioritize content updates for topics already driving traffic. Fix technical SEO issues flagged in Search Console, such as slow-loading pages or mobile usability errors. Create new content based on keyword discoveries. Identify and address keyword cannibalization by ensuring the right page is ranking for a given query. Use internal linking strategically to strengthen authority for key landing pages. Dig deeper: How to use Google Search Console to unlock easy SEO wins More advanced strategies While not strictly related to keyword research, ensuring that any errors are dealt with can help with achieving a deeper understanding of keywords. After all, if a page isn’t indexed due to a technical issue, then no amount of tweaking to the content will help. Identifying errors The URL Inspection tool in GSC is invaluable for understanding how Google views and indexes a specific page. You can use it to troubleshoot indexing problems and ensure that pages are properly crawled. How to use it Open Google Search Console and navigate to the URL Inspection Tool. Enter the URL of the page you want to inspect. Click Enter to see the latest indexing status. Review key insights, including: Indexing status: Is the page indexed or not? Crawl errors: Identifies issues preventing the page from appearing in search results. Canonical URL: Ensures that Google recognizes the correct version of the page. Last crawl date: Shows when Google last crawled the page. Rendered page view: Displays how Googlebot sees the page. If the page is not indexed, click Request Indexing to prompt Google to crawl it again. If there are errors, follow the recommendations provided and resolve issues such as robots.txt blocking, noindex tags, or canonical conflicts. By regularly inspecting URLs, you can ensure that critical pages are properly indexed and visible in search results. Dig deeper: How to fix ‘Crawled – Currently not indexed’ error in Google Search Console International SEO For websites targeting multiple countries, understanding geographic search performance can help refine international SEO strategies and localize content for different markets. How to use it In Google Search Console, navigate to Performance > Search Results. Click on the Countries tab to see a breakdown of traffic by region. Identify which countries are driving the most organic traffic and how search trends vary between locations. Dig deeper: Advanced SEO: How to level up your keyword strategy Harness Google Search Console for SEO wins Google Search Console is a powerful and often overlooked tool for keyword research. It provides real data directly from Google, showing exactly how a site is performing in search. Use it to find quick-win keyword opportunities. Identify new content ideas based on real user searches. Eliminate vanity traffic that does not convert. Track performance trends and adjust SEO strategies accordingly. By using GSC effectively, you can uncover high-impact opportunities, refine strategies, and drive meaningful improvements in search performance – all without spending a penny on keyword research tools. View the full article
-
Google Tests Links In AI Overviews To More Search Results
While Google keeps saying it values publishers and knows how important it is to link to publishers and site owners from Search and AI Overviews, well, it is just as important for Google to link to their own search results for AI Overviews. Google is testing adding links, more visible and clickable links, right in the AI Overviews, to its own search results.View the full article
-
Google Ads Images Double Expand Swipe Carousel
Google Ads is testing the ability to not just expand the images in the ad carousel but expand it again. So you can double expand the images and swipe through them either as smaller images or as larger images.View the full article
-
First Order Discount Label On Google Shopping Ads
In December, Google Merchant Center introduced a new field for "first order" discount. Now, we are seeing "First order" labels in the Google Shopping Ads within the Google Search results.View the full article
-
Google Tests Three Rows Of Google Shopping Ads
To be honest, this seems more like a quirk than a test, but Sachin Patel spotted Google showing three rows of Google Shopping Ads in the Google Search results. We've seen two rows on mobile search previously and now three rows on desktop search.View the full article
-
Google Business Profile Good For Kids Icon
Labeling your Google Business Profile as kid-friendly is not new, but I don't believe I have ever seen an icon that represents that within the Google Business Profile listing within Google Search. The icon is a pack of crayons that says "Good for Kids."View the full article
-
Google Education Q&A Gains Spanish and Vietnamese Support
Google launched education Q&A carousel back in 2022 for English languages only. Now, Google has expanded support to include also Spanish and Vietnamese language. Spanish is supported in Mexico while Vietnamese is supported in all Google regions.View the full article
-
The most innovative companies in education in 2025
This year, the most innovative companies in the education sector are tackling a dizzying array of challenges facing students and schools alike—not to mention parents. As a teletherapy platform, Parallel Learning enables schools and special education providers to counsel students and track their progress. Promova, whose mission is to make language learning more accessible to people who are neurodivergent, is the first language learning app to build a dedicated setting for those with dyslexia—a specialized typeface and adjustments to font size and brightness help mitigate some of the most common reading challenges that people with dyslexia experience. EdSights uses AI chatbots to help colleges and universities identify students who might be at risk of dropping out, in part by increasing student engagement. And then there’s Good Inside, which has become a go-to resource for parents seeking guidance and advice from expert coaches, along with a robust online community. Meanwhile, other education companies are using artificial intelligence to train both our youngest learners and working professionals who are looking to upskill and adapt to evolving technologies. Generative AI continues to fuel growth at online learning platforms like Coursera, which has doubled down on micro-credentials and now offers more than 80 professional certificates with AI courses that are intended to prepare job candidates for entry-level roles without a college degree. Amira Learning is helping young students improve their reading literacy with an AI-powered tutor, while CodeSignal has built a platform for tech workers to pick up new technical skills and practice soft skills through AI-powered simulations. 1. Amira LearningFor empowering students to read more fluently As AI-powered tutors have flooded the market, Amira Learning has drawn special attention for its success in using the technology to help young students become better readers. The six-year-old company, which has raised upwards of $40 million in venture funding and served over 2 million students, is now being used across more than 1,800 districts and in 3,000 schools. In 2024, Amira—which charges schools per student and is also available as a subscription service for families—launched a new version of its AI tutor that goes beyond reading fluency to improve reading comprehension for elementary school students. The company has inked deals to bring its product to school districts in Louisiana, where Amira is now used by 100,000 students across 25 school districts, as well as Mississippi and Iowa. Early studies have already captured its impact in other states: In Utah, students who used Amira for just 30 minutes a week saw the equivalent of 1.5 years of improvement in their reading abilities over the course of one school year. Another study, in Louisiana, showed a marked improvement in oral reading fluency among first graders who had used Amira for six weeks. This June, Amira merged with 27-year-old digital learning company Istation, whose gamified educational content was being used in more than 1,000 school districts. Now Amira’s AI tutor can be paired with content from Istation’s vast library, making its lessons even more effective. 2. CodeSignalFor helping new tech workers brush up on their technical and soft skills CodeSignal is a popular skills assessment platform to evaluate candidates used by recruiters and hiring teams at major companies like Meta and Uber. In 2024, the company expanded beyond just helping employers with interviews and assessments by introducing a new platform, CodeSignal Learn, which gives tech workers the ability to acquire new technical skills and keep up with industry needs. Through free and paid tiers, the platform is catering to both tech workers who are looking to advance their careers and those who are trying to find a new job, as well as recruiters who already use CodeSignal for screening candidates but are interested in addressing skills gaps among their existing employee base. CodeSignal Learn emphasizes practice-based learning over a more didactic approach, and an AI-powered coach called Cosmo helps guide users and can step in if they get stuck on anything. Since rolling out CodeSignal Learn in February 2024, the company has added more than 198,000 users who have completed over a million practices; on average, the platform draws about 8,500 active users each week. Over the last year, CodeSignal also launched a product called Conversation Practice to help engineers and developers who are newer to the job market improve their soft skills. Through AI simulations, users can practice real-world communication and work on their leadership skills. 3. Good InsideFor teaching parenting as a skill you can hone Clinical psychologist Becky Kennedy has made a career of offering guidance to parents on how they can set firm boundaries while fostering strong connections with their children. She has channeled her “sturdy parenting” approach—and vast following (she boasts 3 million followers on Instagram)—into a subscription-based online community and parenting resource called Good Inside, which now has 80,000 paid members across more than 100 countries. In 2024, Good Inside launched an AI-powered app to help subscribers more effectively navigate day-to-day parenting challenges. The app gives busy parents on-demand access to scripts and other personalized guidance, drawing on Kennedy’s expertise and advice from other parenting coaches. An emotional-reset feature gives parents a nudge to decompress when they need it most, and a private community of like-minded parents promises moral support. 4. PromovaFor enabling neurodivergent people to learn languages Promova launched in 2019 with the intent of making language learning more accessible to people who are neurodivergent. In late 2023, the company became the first language learning app to introduce a dedicated setting for people with dyslexia, which is the most common learning disability. Dyslexia Mode uses a specialized typeface called Dysfont that helps address the most common reading challenges experienced by those with dyslexia. Promova has since updated Dyslexia Mode to incorporate feedback from users; the app now allows users to increase font size, remove all-caps text, and adjust color brightness to reduce the contrast between the text and the background. In 2024, the company also launched a free ASL class and a white noise feature that caters to neurodivergent learners. Promova has also updated the app’s interface to help mitigate focus and attention issues for users, particularly those with cognitive disabilities. In 2024, Promova saw significant growth: Overall downloads jumped from 11 million to 15 million, and the app’s monthly user base more than doubled from 800,000 to 1.8 million. 5. CourseraFor enabling workers to reskill through micro-credentials and partnerships with leading employers In response to demand for professional certificates and other upskilling opportunities, Coursera has doubled down on micro-credentials, adding 40 new programs in the last year—nearly double the number launched in 2023. The online learning company now offers well over 80 professional certificates, which can prepare job candidates for entry-level roles without a college degree. Coursera’s micro-credentials are sought after in part because of partnerships with leading tech companies; in 2024, employers like Epic Games, Adobe, and Unilever also started offering their own programs. The company has also made the majority of its professional certificates accessible to non-English speakers, offering those courses in 21 languages through AI-powered translation. Coursera also expanded its partnership with the University of Texas System, a micro-credential program launched in 2023 that offers students, faculty, staff, and alumni free access to upskilling. Through Coursera’s Career Academy, learners can invest in professional certificates from tech employers like Google, IBM, Microsoft, and Salesforce. This investment in micro-credentials has already boosted revenue: In Q4 2024, Coursera’s consumer revenue crossed $101 million, a 5% year-over-year increase, in part due to interest in entry-level professional certificates and GenAI offerings. Over the past year, Coursera saw more than 3 million enrollments in entry-level professional certificates. The company continues to see plenty of demand for AI courses: Coursera partnered with Google to launch one that’s now the most popular GenAI course on the platform. In fact, some of the new professional certificates that Coursera introduced in 2024 feature GenAI content from companies like Meta, Microsoft, and IBM. Coursera also worked with New York State’s Department of Labor last year to provide free access to certificate programs for displaced workers. 6. EdSightsFor keeping college students in school Nearly 40% of first-time college students in the U.S. don’t complete their degree within eight years after enrolling. EdSights wants to help academic institutions pinpoint people who are at risk of dropping out by using its AI-powered chatbots to engage with students and offer rapid response support for any number of challenges they may face—be it financial assistance or academic struggles. One of the key metrics EdSights uses to evaluate students is the Student Voice Score, an annual survey of student satisfaction and sentiment that enables academic institutions to compare their overall performance with that of their peers. As of 2024, EdSights serves more than a million students across 140 colleges. At Southern New Hampshire University, which claims to be the country’s largest nonprofit college, the company increased retention by 4% among first-year students and 12% for underrepresented students. On average, universities that use EdSights see a 4% increase in student retention, with some citing rates as high as 14%. This year, the company also introduced new AI-driven features designed to identify students who are facing mental health issues—and help them get the support they need. 7. SpheroFor taking its STEM robots into the classroom For over a decade, Sphero has built interactive robots and STEM educational tools that students of all ages can use in the classroom. To date, the company has activated 5 million robots, and its products are employed by more than 40,000 educators in 20,000-plus schools. In 2024, Sphero launched a new and improved version of its bestselling product for budding programmers. The Bolt+ coding robot is more immersive and open-ended than its predecessor and has already elicited positive feedback from teachers. This past year, Sphero also introduced Blueprint Engineering kits, which expose middle and high school students to mechanical and electrical engineering concepts. Both products are intended to be easily incorporated into the classroom, and Sphero’s new education resource hub makes it easier for teachers to compile lesson plans. In addition to the Bolt+ and Blueprint kits, Sphero debuted an interactive coding mat and literacy cards that pair with the Indi, a robot designed for kids as young as four. 8. SmaltFor tackling a shortage of climate workers across Europe To meet renewable energy goals, Europe has plans to add more than 3 million new jobs across the climate sector by 2030. But there’s a shortage of workers who can fill those positions. That’s where Smalt comes in: Founded in 2023, the Berlin-based company is training workers across Europe to address the growing skills gap in the climate industry, armed with a $8 million seed round backed by General Catalyst and Owl Ventures. Smalt is looking to bring more workers into the solar industry using its tech-enabled training platform, with a particular focus on reaching immigrants. In 2024, the company sourced and trained more than 20 immigrant workers for their first jobs. Smalt also created an app for workers to help mitigate installation mistakes and troubleshoot issues while out in the field; the app has already reduced installation errors by 15%. The company launched a B2B commercial business in 2024 as well, along with a customer dashboard that gives clients regular updates on their projects and facilitates streamlined communication. Smalt also boosted average revenue for workers, up 20% compared to 2023. 9. ResultantFor enabling states to make data-driven decisions about childcare and schools The data analytics consulting firm Resultant partners with state education agencies to help improve outcomes for kids and families. Across many states, childcare providers are only required to report vacancies once a year, which means the data is often no longer actionable or up to date. In 2024, Resultant worked with the state of Iowa to create a database of childcare providers called Child Care Connect—not unlike a restaurant reservation system—that updates daily and allows families to check their availability in real time. Resultant also built multiple programs in Indiana to tackle absenteeism in schools and high school graduation rates. (The rate of chronic absenteeism in the state was nearly 18% for the 2023-2024 school year, up from just 11% pre-pandemic.) Through the Attendance Insights Dashboard—which collects data on excused and unexcused absences by school and grade level, alongside demographic information—schools and districts can track attendance on a weekly basis and keep tabs on students whose academic performance might suffer. Beyond that, Resultant piloted the Early Warning Indicator System—which uses state-specific data to pinpoint students who might not graduate on time—across 11 school districts before rolling it out statewide for the 2024-2025 school year. Since the platform looks at a number of factors, it can distinguish a student who might have attendance issues but isn’t necessarily at risk of dropping out. 10. Parallel LearningFor expanding access to special education services Since 2021, Parallel Learning has been on a mission to augment special education services in schools across the country, whether in rural areas that are underserved or urban regions where educators are stretched too thin. The company offers a wide variety of special education services that can help address staff shortages and reduce barriers to care. After closing a $20 million Series A funding round in 2024, the company formally launched its proprietary teletherapy platform, Pathway, which gives special education providers the ability to conduct virtual therapy and keep tabs on how students are performing against the goals of their Individualized Education Program. In 2024, Parallel Learning served 6,000 students and saw 200x revenue growth, and its offerings are now used by more than 80 school districts. Students have reported high levels of satisfaction with both the providers and their own progress after using Parallel Learning’s services. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The most innovative companies in economic development for 2025
If a job is about more than the title or even the pay—but also a chance to find a deeper meaning and sense of purpose—the honorees in the inaugural class of most innovative companies in economic development are chasing a similar ideal, just on a larger scale. These accelerators, city agencies, and public-private partnerships are working to cultivate innovation economies in their regions—and in a sector that often (and understandably) focuses on the headline numbers—jobs created, dollars invested—these honorees did more than just stoke the economic engine; they afforded spaces for new narratives and creative communities. Some are working on reinvention: Huntsville, the Alabama town famous for its history with NASA’s rocketry program, has remarketed itself as a music, arts, and cultural destination; while Hilliard, an Ohio city of less than 40,000 in the Columbus area, continues to build out infrastructure to incubate innovative startups. Others found ways to expand the opportunities within existing hometown industries: NCBiotech built pathways to bring more local residents into the Research Triangle’s booming life sciences sector. Michigan Central, an old train station converted into a 30-acre innovation campus in Detroit, opened its doors last July. STACKT’s small-business incubation concept, comprised of repurposed shipping containers, is breathing new life into Toronto’s street life. And PIDC, a public-private investment group in Philadelphia, is redeveloping the centuries-old U.S. Naval Shipyard with a $1 billion diversity pledge. Illinois Quantum and Microelectronics Park, seeks to build out the future of cutting-edge quantum computing on the site of a former steel plant site in Chicago. Of course, crafting entirely new narrative works, too. Timbuktoo Initiative, launched last year by the UN Development Program, is working to improve venture capital pipelines to entrepreneurs across the continent. Sustainability has also been a driver for development: Bristol City Leap, in the UK, is a citywide decarbonization program that will create hundreds of local green jobs; while Lamu Blue Carbon Project, a blue carbon credit program, will preserve mangrove habitats in coastal Kenya. 1. City of HuntsvilleFor making music, and supporting musicians, a centerpiece of a city’s business growth For many years, Alabama’s “Rocket City,” so called due to its long history with NASA’s rocketry program, has been more like Rock City. Huntsville has made music a key focus of economic growth, starting with a 2018 city musical audit championed by Mayor Tommy Battle, that quickly grew into a larger effort to build a creative ecosystem. While this past year’s marquee event, the inaugural South Star Music Festival, was partially canceled due to bad weather, the changes wrought by this effort are visible—and vocal. 2024 marked the conclusion of the city’s five-year plan, passed in 2019, to focus on music-related development, including hiring a music board and full-time music officer and investing in music programs and facilities in school and libraries. Across town, a constellation of new, smaller venues, such the-middle-school-turned-event-center Campus No. 805 and the multistage retail space Stovehouse—not to mention the Music Ambassador Program, which started in 2023 as a way to promote local musicians’ touring efforts and so far has provided support to more than 40 tours—have continued to attract more creative talent. The city’s locally owned Orion Amphitheater, the nexus of the $2.2 billion Midcity development, has become a strong tourist draw. Huntsville has always seen this investment as not just a quality-of-life improvement, but as an economically advantageous way to attract a young workforce. As evidence for its appeal, the city points to its growing population, which has added 10,000 people a year since 2020; a 2.8% unemployment rate; and 2,500 new jobs added in the past year. 2. Michigan CentralFor turning a Midwest architectural icon into a startup hub for 21st century mobility The redevelopment of a formerly vibrant train station into a $1 billion innovation campus has become the latest symbol of Detroit’s efforts to resurge. A walkable, 30-acre district in the Corktown neighborhood, Michigan Central repurposed decades-old buildings from the city’s heyday to contribute to its current renaissance. Ford Motor Co. purchased and rehabbed an abandoned railway station and 18-story tower, restoring a decrepit shell to its original Art Deco sheen, while an unused book depository reopened as a startup hub, Newlab, which attracted more than 100 startups and over $700 million in funding in just over a year after its 2023 opening. The tech from one startup, Electreon, is embedded in the nation’s first EV charging road. But Michigan Central doesn’t just offer an architecturally striking space to incubate ideas; it provides a test bed. The mix of startups, mobility innovations, and a multinational corporation in the form of Ford fosters a varied ecosystem of talent, while the campus mobility lab and Advanced Aerial Innovation Region designation allow startups to test and iterate on their ideas in real world situations. Fast-track permitting from the city is accelerating the path to innovation, with the goal of turning the once-busy station into a hub of a different sort. 3. Bristol City LeapFor turning a blueprint for a more sustainable city into an economic engine Bristol, in southwest England, became the first city in the U.K. to adopt a net zero goal back in 2019. But the challenging road required to hit that target inspired the city government to seek out new kinds of partnerships to meet that bold pledge. In 2023, city council announced Bristol City Leap, a substantial initiative to decarbonize local businesses and develop 1,000-plus jobs by leveraging $1 billion in investments to make the city a testing ground for community change. City leaders engaged the decarbonization company Ameresco and Vattenfall Heat UK, which supplies district heating systems, to help transform Bristol’s energy system. Over the next five years, investments in the seaside city will create an EV charging network, add heat pumps and solar panels to schools, refurbish city-owned housing, and deploy renewables in tandem with partners like the Bristol Energy Cooperative. Last year, the initiative picked up momentum, distributing $350 million in grants and building to two sections of Bristol’s heat network, a district heating system that will pipe hot water warmed by heat pumps around the city. The initiative will also benefit local industry by slashing energy costs. Bristol has a reputation for climate action and community support for renewables; this city-scale move shows that it is raising its own bar. 4. STACKTFor giving small Canadian businesses the community, and boost, they need to succeed Toronto’s STACKT market, an outdoor bazaar built from repurposed shipping containers, has fostered a unique commercial community since 2019. In 2024, the founders decided to expand on that vision with a new platform and digital strategy designed to support budding entrepreneurs. The STACKTx network seeks to help small stores and thrive, with the goal of supporting the growth of 11,000 small businesses across Canada in the first year. STACKTx’s strategy starts with a free digital platform that includes digital resources, mentorship, information about grants and community partnerships, and discounts on marketing and product development services. 5,000 businesses have joined so far. In November, the organization hosted a social conference, featuring opening remarks from the country’s minister of small business, Rechie Valdez. STACKTx will help retail concepts take a low-cost test run with monthly storefront grants, which will give entrepreneurs a month-long retail lease in Toronto, and hopes eventually to expand to Ottawa, Calgary, and Vancouver. These grants aim to give storefront space to new businesses without the burden of long-term rent agreements and high overhead. 5. Illinois Quantum and Microelectronics ParkFor turning a 20th-century steel plant into a center for 21st-century quantum computing Once compared to the ruins of the Colosseum and Roman aqueducts, the former U.S. Steel plant South Works, in South Side, Chicago, presents a gargantuan urban void. Home to factory complexes that once employed 20,000 workers, the site has been the focus of several redevelopment crusades. A new plan, to build a quantum computing center there that will tap into the site’s generous electrical hookups, hopes to once again make this campus a central economic driver. After a successful push by Chicago Quantum Exchange, a group founded to advance the industry’s growth, Illinois economic development officials agreed to provide $500 million in investments and grants to build the 128-acre Illinois Quantum and Microelectronics Park. Flagship firm PsiQuantum will install numerous quantum computing systems onsite, including a 300,000-square-foot Quantum Computer Operations Center, and the announcement has already attracted additional high-tech firms like Eero-Q as well as DARPA, the Defense Department’s investment arm for defense technologies, which will build a national testing ground for quantum technologies. 6. Lamu Blue Carbon ProjectFor turning coastal carbon credits into a scheme for local revitalization Preserving trees and forests through carbon credits has been an effort rife with mixed results. But the new Go Blue initiative, which seeks to preserve vital mangrove forests and revitalize the rural economy of Kenya’s northernmost coastal county, Lamu, offers a new vision of positive environmental and economic development. The effort, launched in 2023, aims to preserve nearly 10,000 acres of mangroves, considered to be one of the most effective carbon sinks on the planet, and funnel sales of the resulting credits back to villagers in the country’s northern coastal communities. The effort represents an expansion of similar programs in the country, like Vanga Blue Forest. The successful Mikoko Pamoja Project, the world’s first-ever blue carbon effort to fund the preservation of marine carbon sinks, generated $130,000 annually to local villagers. With more than half of the planet’s mangrove forests at risk, programs that meld local, sustainable growth and conservation offer a new way to achieve green economic engines. 7. Philadelphia’sFor prioritizing equity in Philadelphia’s real estate projects When Philadelphia’s public-private investment corporation, PIDC, acquired the 1,200-acre Navy Yard property in 2000, the former military site offered myriad possibilities. PIDC determined that regardless of the direction development took, it needed to be equitable. As part of the vast transformation of the site to support the region’s burgeoning life sciences industry, the organization approved an ambitious joint venture with Ensemble Investments and Mosaic Development Partners on a project with a $1 billion diversity pledge, including using 20% of its equity investments on minority- and women-owned enterprises and funding extensive local hiring and workforce development initiatives. PIDC leadership at the time called it “one of the most intentional and inclusive economic opportunity initiatives in the history of this city.” Local architecture and design firms have greatly benefited from this approach; minority-owned businesses designed and constructed the 2500 League Island Blvd life sciences development, a rarity in the real estate world. 8. NCBiotechFor making sure the benefits of the biotech boom ripple across more of the workforce North Carolina’s booming biotech sector, which now employs 75,000 people and has $88 billion in annual economic impact, has been one of the nation’s biggest economic development success stories, turning the state into a science powerhouse. But in recent years, life sciences expansion has struggled to employ more North Carolinians. Local companies, desperate to hire trained staff, are poaching from each other, or bringing in new hires from out-of-state. To help bolster the workforce with more local talent, NCBiotech launched the Accelerate NC Life Sciences Manufacturing coalition, with funding from the U.S. Commerce Department’s Build Back Better Regional Challenge, launched a multi-pronged campaign in September 2022 to break down local barriers to employment. Between starting new programs withuniversities statewide, investing in infrastructure to bring labs and manufacturing sites to underserved communities, and kickstarting ambassador, apprenticeship, and awareness-raising campaigns, the Research Triangle has helped hundreds enter the industry. Unique biomanufacturing courses at historically Black universities across the state offer quicker, accredited means of providing training to diverse talent pools. More importantly, the campaign is creating a blueprint of how to build up a high-tech industry while shrinking, rather than expanding, issues of inequity. 9. Timbuktoo InitiativeFor accelerating a startup boom across Africa It can often seem like the bulk of venture capital flows to the companies and founders who need it the least. To capitalize on Africa’s nascent tech industry, the UN Development Program launched Timbuktoo last year, an effort to raise $1 billion in the next decade to fund startup hubs and support 10,000 new companies. The continent has experienced rapid growth in startup venture funding, which has grown six times faster than the global average since 2022, as well as an explosion in tech savviness among younger populations. But the funding hasn’t kept pace with the needs of new firms and ideas, nor expanded beyond the four countries leading Africa’s startup scene, Kenya, Egypt, South Africa and Nigeria. To remedy that, this initiative blends commercial and government capital, leveraging support from the UN as well as universities, corporations, investors, and development partners. Timbuktoo has so far launched a fintech hub in Lagos, Nigeria, that brings together 42 companies from 31 countries, and is planning similar spaces across the continent, including a healthcare hub in Rwanda and a green-tech hub in Kenya. 10. City of HilliardFor proving that a small Columbus, Ohio, suburb can build a high-tech innovation ecosystem A small Ohio suburb of less than 40,000 people doesn’t sound like the most likely site for a startup hub. But Hilliard City Lab, a savvy buildout of the infrastructure and expertise that innovative firms need to thrive, has become a key incubator in the region. The city isn’t swarming with VCs, so the program made targeted investments and partnerships count, including the construction of a 60-mile-long fiber optic network, the building of Ohio Manufacturing Innovation Center, and partnerships with local firms like Converge Technologies to provide space and expertise. The city also set up an AI sandbox, a testing site that lets firms evaluate artificial intelligence services without the need to spend hefty sums on cloud servers. Hilliard gives innovators another important form of support: cash. The city has awarded nearly $1 million in grants to 32 projects in the last four years to help seed small startups, half of which set up shop in 2024. This new test bed has already created results and new innovations, such as a first responder drone for 911 calls, a sewer overflow detector, an algae boat to clean ponds and lakes, and a virtual scoreboard for watching local sporting events. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The most innovative design companies of 2025
Design is in a time of transition. Whether it’s the influx of generative AI tools, Gen Z shaking off their post-COVID haze to drive new aesthetics, the practice of graphic design adding clarity to tight elections and challenging our meat consumption, or even the sudden viability of technologies ranging from environmentally friendly A/C to exoskeletons that are turning sci-fi dreams into practical realities, design is in a position to face an uncertain world of scarcity with an unprecedented abundance of innovation. Our honorees for the most innovative companies in design for 2025 span the gamut of product, architecture, and UX. But they are all united in pushing the consumer discourse through design and challenging the status quo to make the world better—or, at least, make it a little more brat. 1. OnFor building faster shoes faster Like all sneaker brands, On has carefully seeded its sought-after demographics into its marketing—Zendaya, FKA Twigs—but most of its collabs, which on paper are great (Loewe! Beams!) are actually relatively forgettable on their own, barely drifting from their approach to circular foamy Swiss minimalism. Its StockX listings sell for list. But On is selling all the same. Net sales were up 27% in 2024. It’s built up to a certain quiet, cross-culture ubiquity. Think of it like the performance comfort statement of Lululemon in 2015, but not so bougie that cool kids in Europe and Asia won’t wear it. No doubt being a young company helps here (On was founded in 2010). There’s a bring-your-own-meaning to it all that seemingly allows it to fit anywhere without the same cultural weight of donning a Dunk or a Samba. And that meaning is anchored in one of those ideas that make Nike so revolutionary: performance advertised in design. With a new technology called Lightspray, we’re seeing On’s ambitions grow. Despite a decade of experiments in additive manufacturing and circular products by competitors like Adidas, no sneaker brand has really cracked the code on balancing high performance, sustainable life cycle, and production efficiency. Lightspray is a promising approach to all three of these goals. A robot holds an outsole (produced in a traditional injection mold) and spins it around, all while a nozzle sprays the entire upper of the shoe into existence. That process takes just three minutes (while it takes another three for it to set). Lightspray requires no extra glues and can be colored with the most minimal spray of dye. On has simplified its sneaker to just a handful of components and a bare minimum of material, already reducing its carbon imprint by 75% on the upper alone. But because it’s made of just five parts, a Lightspray shoe can (theoretically) be more recyclable long term, as On promised to me earlier this year. Lightspray shoes have already been worn in multiple marathons (19 athletes wore them at the latest NYC marathon, including Hellen Obiri, who came in second place). This is a long-term bet on core design/manufacturing/performance tech from On, and will be something to watch for years to come. Read more about On, honored as No. 18 on Fast Company’s list of the World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies of 2025. 2. SharkNinjaFor building irresistible home appliances The SharkNinja brand has come a long way since its vacuum infomercial days of the mid-aughts. The company—and its 1,100-person global design and engineering team—has become one of the most sophisticated manufacturers of domestic appliances on the planet, packaging advanced engineering into novel, easy-to-use, affordable products. SharkNinja more than doubled its product portfolio in 2024 as part of a massive brand expansion involving categories ranging from outdoor gear (with a Yeti-like cooler) to beauty (Dyson-inspired hairstyling tools) to home (with a battery-powered fan that moves with you). But its runaway hit last year was in a category entirely of its own: the Ninja Slushi, an at-home frozen drink maker that allows customers to whip up a margarita in their kitchens or a perfect frozen Coke, à la the 7-Eleven Slurpee. Before launching online in July, the $300 Slushi amassed a 200,000-person waitlist and garnered more than 200 million impressions across social media, and it has since sold out 15 times. This success is a result of the company’s obsessive, value-grounded approach to innovation, which involves testing out its products in up to 750 homes before launch to ensure its customers feel competent trying their products the first time—and don’t mind cleaning them up on the twentieth. “If your cellphone’s not working, you blame the phone,” says SharkNinja chief design officer Ross Richardson. “If you can’t cook a steak properly, or you’re not able to dry your hair, most people will then blame themselves.” SharkNinja wants to change that, ensuring that its products are not just well engineered and easy to use but also allow for creative exploration (which helps them go viral on social media). In the case of the Slushi, the 6.5-inch-wide machine fits onto your counter better than you’d expect, and its prominent tap on the front requires no instruction manual to understand. Even the recipe booklet that comes with Slushi is less about the recipes than understanding basic ratios of, say, sugar and alcohol. “It’s a product that you can experiment with,” says Richardson. “When the consumer is not narrowed into ‘You have to do it this way!’ they want to share. And as soon as they share, we’ve got virality.” SharkNinja’s engineering team keeps the innovations flowing by developing products in a 24-hour global relay, passing work from its Massachusetts headquarters to London to China (where manufacturing previously had been taking place) each day. For the FrostVault cooler—which costs $250 and features drawers to keep your food dry from condensation—the Needham, Massachusetts, development team shoveled three tons of sand inside their studio to ensure that the drawers could open and close on a beach without jamming. SharkNinja can now build just about any product it can imagine—from the popular $370 Woodfire electric grill and smoker to the $350 FlexFusion ceramic hair straightener—at a price most consumers can afford. That formula helped SharkNinja grow revenue 30% in 2024, breaking $5.5 billion for the first time. “We’re the fastest-growing outdoor cooking company in the world, and we’re also the fastest-growing hair tools company in the world,” says CEO Mark Barrocas. “Who would have thought that would be under the same umbrella?” Read more about SharkNinja, honored as No. 27 on Fast Company’s list of the World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies of 2025. 3. JKRFor creating beautiful, high-impact rebrands Most rebrands tend to be either completely cringe or vastly underwhelming. But branding agency JKR spent 2024 pushing clients outside their comfort zones to launch a series of bold rebrands that breathed fresh life into legacy clients. With Impossible, JKR transformed the alt meat pioneer’s strangely greenwashed packaging into a blood red celebration of plant meat. Brand awareness jumped 25% in the first three months after release. For the Kosher food staple Manischewitz, the firm swapped dull white packaging for eye-popping orange, pushing sales by 7% in what the brand anticipates will equate to 10% YOY growth. At RSPCA, the largest animal welfare charity in the world, JKR drove a 200% boost in donations through the brand’s first makeover in 50 years, which swapped stoic typography for cute animal icons. And while it’s too soon to know how JKR’s work will impact Mozilla, the company’s new funky, pixel-loving makeover vows to “reclaim the internet” with dinosaurs and rainbow gradients. 4. Foster + PartnersFor refreshing an icon and reviving a city in the process An icon is back in San Francisco, thanks to a $1 billion project between the real estate developer SVHO and the architecture firm Foster + Partners. The duo reimagined the Transamerica Pyramid Center as a luxe modern workspace to reinvigorate the struggling downtown. Foster + Partners took the renovations all the way back to the studs. Drop ceilings and superfluous cladding were removed, increasing headspace by 10 full feet in the entrance. Clearer windows embrace unparalleled views across the Bay, which can be enjoyed from opulent casual meeting spaces in the center of the tower and top floor. But despite the lease prices that are 3x competitors in the area, it’s celebrating 70% occupancy in its first year of release and multiyear partnership with TED AI. As for the redwood park planted outside in 1930? That’s not only still open to the public with more seating than before, but it hosts biweekly concerts open to the community. 5. Special OfferFor turning a color into a cultural moment It was Brat summer, and we were all just living in it. But Charli XCX’s cultural movement owes some of its success to the NYC design studio Special Offer. The firm developed Brat‘s iconic, arresting green brand seen on the album and merch, with its almost lazily, stubbornly printed typeface. In a world full of brands that try too hard, it’s an aesthetic that’s difficult to describe in any other way than . . . so brat. But the brand’s greatest success was how fans made it their own. Not only was #brat used 1.4 million times on TikTok and 2.7 million times on Instagram, but a “Brat Generator” was visited more than 5 million times as fans built their own brat memes for the season. With apologies to all things demure, 2024 belonged to the brats. Into 2025, Special Offer is collaborating with several unannounced brands. Its newest project is building the exhibition identity for the Louis Vuitton Visionary Journeys installation in Bangkok. 6. CactusFor redesigning the entire experience of healthcare In a world full of design consultancies, Cactus has distinguished itself as a leader in rethinking every touch point of healthcare—be it hospital design or digital workflows—with clients that include Mayo Clinic, Advent Health, and Wellstar. One landmark project will begin construction in March. It’s a new oncology bay for USC’s Norris Center. Inspired by a first-class airline cabin, these modular rooms will offer comfortable, private spaces to cancer patients who are undergoing transfusions. Experimental treatments, in particular, can require patients to be connected to machinery for up to 12 hours. The new bays allow them to rest in a reclining chair or bed complete with amenities like music and a screen. In addition to offering the patient a cozier environment, the bays are nested together, making them space efficient and increasing the Norris Center’s capacity by 50%, while being easy for healthcare professionals to monitor. Norris Center will also test moving these bays outside of the clinic, given that their modular design can essentially create a pop-up clinic anywhere. 7. Code and TheoryFor building interfaces that offer clarity during uncertainty Digital agency Code and Theory is building the best data visualization tool in broadcast today. Following the firm’s success rebuilding CNN’s touchscreen Magic Wall in 2018, NBC recruited Code and Theory to re-create its competing Big Board for live news broadcasts. The new board, which debuted for the presidential primaries last year, became the focus on MSNBC’s election night coverage. Data guru Steve Kornacki used it to take 5.5 million Americans through a tumultuous night, zooming into districts with 10M+ data points from 16 years of electoral data, with real-time updates of 16,356 geographies across the U.S. Code and Theory was also tapped by Microsoft last year to develop immersive product landing pages for one of its most important releases in recent history: the Microsoft Copilot+ PC. Rather than build a traditional promotional website, the firm created dynamically generated pages across 52 markets worldwide, tailoring these AI demos to a user’s own interests and inputs. 8. SquarespaceFor using AI to build custom websites even faster For all of the promise of generative AI, it hasn’t offered a lot to the average person. But for Squarespace users looking to construct beautiful websites as fast as possible, the company’s Blueprint AI tool made the task even easier. Through natural language—just answering a few questions about their business—users can have Squarespace build them a custom site with a modern layout, customized fonts, and interchangeable colors. It will even fill the site with stock imagery and generated copy. Of course, Squarespace might not get the design perfectly to your liking, but each component is easily updated through the graphic interface. After a few years of stock ups and downs, Squarespace was acquired by private equity firm Permira last year. Blueprint AI is an innovation modernizing the company’s design tools. It improves on Squarespace’s templated approach to website building and pushes it a step further in speedy, simple UX that courted 25% of users to try it last year across 200 countries. 9. QuiltFor building a heat pump that anyone can use It’s so small that you barely notice it. Unlike your traditional space heater or window A/C unit, the Quilt heat pump almost disappears onto a wall—despite replacing both of these products in one. As the smallest and most efficient multi-zone heat pump on the market, the units are a mere 8 inches tall and can heat or cool a room automatically with the assistance of predictive algorithms. Quilt makes convenience a core feature: The company handles everything from sales to installation, pairing customers with an installer. That convenience is catching on. After launching the heat pump in the Redwood City area in May, Quilt quickly sold out of its 2024 inventory. In 2025, it plans to spread to five major markets including L.A. While the product promises to save customers energy and money, the carbon impact alone might make the upgrade worthwhile: Over the next 15 years, Quilt’s most ambitious targets project cutting the CO2 equivalent of the state of California up to 10 times over. 10. SkipFor making it easier to move Skip may very well sell you your first exoskeleton. After spinning out of Google X in 2023, the robotics company developed what it dubs an “e-bike for hiking” called Mo/Go (which is short for “mountain goat.”) It’s a pair of robotic bracers that move along with your stride, relieving half the effort of each step. But while most robots look like robots, Skip teamed with the outdoor gear company Arc’teryx to integrate Mo/Go into a pair of pants. The pants made their debut in August 2024 through a climbing clinic in Squamish, Canada, and since then, Skip spent the latter half of the year validating and refining both the fit and the algorithms behind the design through hundreds of testers who’ve rented samples, more than half of whom reported “loving” the experience. After fulfilling its $4,500 preorders that start shipping in fall 2025, Skip plans to put Mo/Go on sale inside Arc’teryx stores and eventually expand its purview to serve people with movement challenges from strokes or Parkinson’s disease. In other words, while Mo/Go is being designed for hikers hoping to get a leg up on the trail, the performance machine is being developed to eventually benefit everyone who just wants to move with more ease. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The 10 most innovative data science companies of 2025
In the midst of an artificial intelligence boom that’s reshaping almost every facet of the business world, companies are competing in an arms race to build the best and brightest models and fully embrace the nascent technology, whether that’s as a product or service for customers or as an integral component of their organizations’ processes. This has raised the profile and pursuit of data science: After all, as Airbyte CEO and co-founder Michel Tricot succinctly put it, “no data, no AI.” But this arms race could have many winners at its finish line. Indeed, this year’s honorees all have something in common beyond their creative use of data in a world increasingly dependent on it: namely, a keen understanding of how to employ data science to make a positive impact on the world around them, building a successful business in the process. They include Unstructured, which helps organizations from Fortune 10 companies to the U.S, military transform raw data into the fuel for AI applications; Chainalysis, a blockchain intelligence group that’s become the go-to agency for financial institutions and law enforcement countering crypto crime; Norstella, which harnesses big data to help biopharmaceutical companies develop thousands of life-saving drugs through accelerated planning and AI-assisted decision-making; Makersite, which employs AI to help manufacturers embrace data-driven transparent supply chains in pursuit of ethical consumption; and Satelytics, which analyzes satellite-based geospatial data in search of methane leaks so energy companies can reduce emissions. Vacuuming up data to build an in-house AI agent is one thing, but using that data to substantially improve the lives of consumers is another thing entirely – and these companies all earned a spot on our list because of it. 1. UnstructuredFor broadening the scope of corporate data that can inform AI Unstructured’s goal is to help businesses unlock and leverage their unstructured data, making it accessible as the foundation for AI-powered solutions. With the majority of enterprise information trapped in disparate formats that are hard to analyze and integrate—so much so that developers and data scientists spend more than 75% of their time simply preparing data for ingestion—Unstructured automates the transformation of raw data into AI-friendly formats, enabling organizations to utilize it for RAG (retrieval-augmented generation, which uses supplemental data to improve results) and fine-tuning large language models. Its solution extracts unstructured data from databases, converts more than 30 file types into LLM-ready formats, and loads the results into vector databases for RAG applications. By continuously providing real-time, up-to-date data, Unstructured’s platform ensures that LLMs are tailored to specific organizational knowledge. In 2024, the company launched its commercial SaaS API and enterprise platform, a move that quickly attracted over 10,000 customers. It’s now parlaying its advancement of business AI into serving as an open-source tools hub for the technology community. It’s also playing a critical role in national security by partnering with U.S. military organizations, including the Air Force, Space Force, and Special Operations Command. Read more about Unstructured, honored as No. 24 on Fast Company’s list of the World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies of 2025. 2. ChainalysisFor bringing transparency to the crypto industry Chainalysis’ blockchain data platform targets trust and transparency in the crypto industry. Its compliance software helps crypto companies fulfill anti-money-laundering and other legal requirements while its investigative software helps government agencies regulate the industry. In 2024, Chainalysis screened more than 250 million transfers and $4 trillion in transactions, identifying 6,500 unique entities and collaborating with more than 1,300 customers worldwide. It helped recover more than $11 billion in illicit funds and track nearly $25 billion in criminal transactions. The company is on track to take in an estimated $250 million revenue (up nearly 30% over the previous year). It has partnered with government agencies, financial institutions, and cybersecurity firms in more than 70 countries and more than 250 law enforcement agencies worldwide. Chainalys has also introduced key upgrades to its Crypto Investigations Solution, enabling agencies to instantly assess blockchain addresses and trace complex crypto transactions. In 2024, the company scored a pivotal win when a U.S. district court judge ruled that its blockchain forensics were admissible as substantive evidence, establishing a critical legal precedent and affirming the reliability of its analytics for prosecutors and regulators. Read more about Chainalysis, honored as No. 36 on Fast Company’s list of the World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies of 2025. 3. AirbyteFor simplifying large-scale data integration for AI-centric projects In a world dominated by AI, it’s difficult to overstate how critical data management is to the foundations of a functional system. As Airbyte CEO Michel Tricot notes, “no data, no AI.” The company makes it easy for organizations to move data from any source to any destination so businesses can unlock the potential of that data. In 2024, Airbyte’s technology helped organizations fuel AI-driven initiatives using existing data pipelines through support for eight vector databases, RAG transformations (which improve response accuracy and relevance), and unstructured data management. The launch of Airbyte Marketplace, featuring more than 400 certified data connectors, further simplified integration by enabling instant deployment or customization. With an open-source model fostering community-driven innovation, Airbyte has used AI to help a robust community of 20,000 data engineers develop 10,000+ user-built custom data connectors. The company’s initiatives drove a fourfold increase in revenue in 2024. Airbyte has become the most widely adopted data movement platform globally with more than 170,000 deployments across 7,000 active companies, including Siemens and Peloton. 4. NorstellaFor fostering faster drug discovery by analyzing billions of data points Norstella’s goal is to help major pharmaceutical and life sciences companies navigate the complex path to developing lifesaving treatments. That, in turn, makes it easier and faster to get life-changing therapies into the hands of the patients who need them. Launched in 2024, its NorstellaLinQ platform integrates over 74 billion data points—including insights from hundreds of medication launches, tens of thousands of clinical trials across 185 countries, and 500,000 investigations—to combine real-world data with proprietary clinical, regulatory, and commercial intelligence. The result is sharper decision-making and accelerated clinical trial planning to facilitate faster drug development. The company also launched Citeline SmartSolutions, a suite of AI-enabled products that uses Norstella’s trove of data to address challenges in clinical trial design. The platform saves customers time and money by optimizing trial predictability, reducing costly amendments, and streamlining investigator selection. Norstella’s integration of real-world insights and diversity data further enhances trial design, ensuring more inclusive, accurate studies. Norstella’s impact is already evident: In the past year, the company has helped bring over 50 new drugs to market. It is now assisting major pharmaceutical and biotech companies that have more than 23,000 drugs in their pipelines. 5. MakersiteFor helping companies design and build more sustainable and cost-effective products Makersite’s goal is to streamline product development with data-driven supply chain transparency, enabling companies to design and manufacture more sustainable and cost-effective products. By combining the world’s largest manufacturing data foundation with proprietary algorithms, the company claims to deliver real-time lifecycle assessments 100 times faster than the best available alternatives. Its user-friendly dashboard guides designers and engineers to better data-driven decisions early in development. In 2024, the company launched new tools that enhance the solution’s flexibility and granularity. In-workflow plugins improve sustainability and cost estimates by using proprietary data instead of industry averages, and an AI-powered eco-design dashboard has already helped engineers reduce product and packaging lifecycle impacts by up to 58%. Makersite also expanded its data platform, integrating environmental database providers like Carbon Minds to enhance insights about chemicals and plastics and using generative AI to deliver more precise data for mechanical and chemical supply chains. Makersite doubled year-over-year revenue in 2024 as the company saw 20% growth in enterprise customers. Its highest-profile win was with Microsoft, which used the company’s unique methodology to identify carbon hotspots in the Surface Pro 10’s supply chain and reduce the device’s carbon footprint by 28% versus the previous model. The improvement vividly demonstrated how Makersite can help customers align design excellence with ethical consumption. 6. AnacondaFor expanding AI’s reach to the masses with its premier Python platform. In 2024, Anaconda solidified its role as the world’s leading platform for specialized deployments of Python—the most popular data science programming language—by offering data scientists, developers, and enterprises better and more sophisticated tools. Its distribution platform, trusted by 93% of Fortune 500 companies and 45 million users, introduced innovations that scaled Python’s impact across industries by simplifying workflows and democratizing advanced analytics. Key features included Python in Excel, allowing non-programmers to create AI-powered code generation and effortless data visualizations without external installations. Anaconda also launched the AI Navigator, a curated library of 200+ pre-trained models for natural language processing, code generation and more. The desktop app offered enterprise-grade security and local AI deployment, enabling users to harness generative AI while safeguarding sensitive data. Additionally, the enhanced Anaconda Assistant and Code & Toolbox streamlined coding, debugging, and data visualization, making Python workflows more accessible. By tapping into Python’s 839% growth in enterprise usage and quadrupling to over 1 million organizations since 2022, Anaconda has helped to fuel the language’s reach, reflecting the company’s commitment to push the boundaries of data science in a rapidly evolving tech landscape. 7. SatelyticsFor detecting methane leaks with satellite-based geospatial analytics Satelytics is a geospatial analytics platform that uses multispectral and hyperspectral imagery from satellites, drones, aircraft, and fixed cameras to deliver actionable insights for the natural gas industry. By analyzing this data, Satelytics can rapidly pinpoint problems like methane leaks with remarkable detail and deliver alerts within hours, minimizing costs and operational disruptions. In 2024, Duke Energy used Satelytics’ AI-powered platform to detect leaks as small as 1 kg/hr with pinpoint accuracy; the deployment identified 433 methane plumes alone during its first scan of Charlotte, North Carolina. The project’s success led the energy company to expand the program across five states and to laud Satelytics as a key driver in its efforts to drastically reduce methane emissions.Satelytics’ applications extend beyond energy; the company is also advancing land management through a collaboration with Envu’s RangeView tool. By analyzing invasive species like cheatgrass and medusahead and employing high-resolution imagery and AI-powered insights, Satelytics helps ranchers and landowners precisely tackle infestations, reducing manual labor and restoring rangeland productivity. It is another demonstration of how the company’s offerings can address critical environmental and operational challenges while driving efficiency and sustainability. 9. EarthDailyFor using big data to help the mining industry improve its sustainability. While calls for sustainability from an industry like mining might seem inherently hypocritical, harnessing renewable energy still requires using rare-earth materials that must be mined. To that end, at least one technology company is applying data science to encourage mining company sustainability while enhancing efficiency, safety, and transparency. In 2024, Descartes Labs, a provider of AI tools for geospatial data analysis that was recently acquired by EarthDaily, expanded the company’s novel data collection and analysis tools to include mineral exploration and operational safety. Marigold, its cloud-hosted mineral exploration platform, features hyperspectral processing, The technique enables precise mineral composition analysis that accelerates ore discovery while minimizing unnecessary drilling. Iris, the company’s other flagship product, leverages interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) to monitor ground deformation with millimeter-scale accuracy. Its automated alerts can help operators prevent disasters and better comply with environmental regulations. Descartes Labs will continue to integrate its newly acquired geospatial analytics and data science capabilities to help customers optimize resource use while minimizing environmental impact and community risk. 10. NominalFor building a data platform for mission-critical testing and evaluation Nominal’s data platform is purpose-built for testing and evaluation within mission-critical sectors such as aerospace, defense, and advanced technology. While hardware companies have previously wrestled with complex, messy data pipelines and multiple analysis tools, Nominal integrates real-time data processing, advanced analytics, and collaborative tools to unify the testing lifecycle. The company’s platform ingests and synchronizes complex datasets, validates systems in real time, and diagnoses root causes by using comparative analysis, environmental context-aware analytics, and other tools. It can be deployed on anything from cloud servers to ruggedized laptops. In 2024, Nominal developed a unified platform to enable seamless synchronization, organization, and analysis of high-scale, multi-format data with dynamic tools for visualization, anomaly detection, and root cause analysis. It also raised $27.5 million in Series A funding from General Catalyst, Founders Fund, and other investors. Its offerings, which have been used to accelerate test campaigns for autonomous drones, optimize jet engines at military test facilities, and analyze spacecraft reentry data for the U.S. Air Force, Varda Space Industries, and others, continue to transform testing and evaluation. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The most innovative companies in consumer electronics for 2025
While smartphones are still the indisputable center of our digital lives, this year’s most innovative consumer electronics companies aim to improve life beyond the touchscreen. A lot of that involves advancement in wearable computing. EssilorLuxottica, for instance, has come up with a winning formula for smart glasses in both the Meta Ray-Bans and its Nuance Audio hearing aids, which pack just enough technology to avoid looking uncool. Apple is approaching things from the opposite direction, using its Vision Pro to show what mixed reality can look like when no expense is spared. Bose’s Ultra Open Earbuds, meanwhile, lead a burgeoning category of hearables that let in outside sound instead of tuning you out, with a comfy design that clips to the side of the ear. And when Bose gave up on making earbuds for sleep, a new startup called Ozlo picked up the slack, licensing Bose’s design for tiny sleep buds and building out new features such as Bluetooth audio and sleep detection. Elsewhere on the wellness front, smart ring pioneer Oura is extending its lead in the category with more comfortable band design, better battery life, and significantly more accurate sensors. Not every innovation was wearable, though. On the home tech front, Open Home Foundation is building a more empowering smart home platform focused on offline control and privacy, with an Alexa alternative that works without internet. Sony is pushing brighter TVs that come closer to what creators envisioned, and GE Appliances has figured out how to bring a real barbecue smoker indoors. Meanwhile, ESR’s cooling phone chargers work more efficiently and preserve long-term battery health, and Swarovski Optik’s AX Visio binoculars promise to augment your next birding trip with offline wildlife identification. As with the innovations in wearables, it’s another way you’ll be able to leave the phone in your pocket for a while longer. 1. EssilorLuxotticaFor making smart glasses cool Big tech companies have fixated on augmented reality as the next frontier for wearable tech, but you’d probably never want to wear their bulky headsets in public. Thinking from the opposite direction, the eyewear giant EssilorLuxottica wanted to combine its stylish sunglasses with a minimal amount of technology. It found a partner in Meta, which had floated a similar idea back in 2017, and the two companies started collaborating on what would eventually become the Ray-Ban Meta line. Meta brought the technology, which includes a camera, speakers, and integrated AI assistant, while EssilorLuxottica focused on a design that would work within the confines of stylish frames. The latest version arrived in the fall of 2023, and the line expanded this year with new styles and custom frame-and-lens combos along with additional AI features from Meta. (The AI features continue to roll out: Meta just added AI video capability and real-time language translation functionality.) EssilorLuxottica says the new models sold more in their first nine months than the originals did in two years, and they’re the top-selling product in 60% of Ray-Ban stores in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. The company recently announced that it’s sold 2 million units of the glasses since October 2023 and is gearing up to produce 10 million every year by the end of 2026. Meta and EssilorLuxottica have also extended their partnership into the next decade. That’s not to say that EssilorLuxottica is tying its tech fate exclusively to Meta. In 2022, it established a smart eyewear lab with Politecnico di Milano, the same year that it acquired Nuance Hearing. The company previewed the first product from the latter effort, a set of glasses with integrated hearing aids, in 2024. They received FDA clearance in February, and they’re planned to ship by the end of Q1. The glasses amplify sounds in front of the wearer using beamforming technology to make conversations easier and eliminate distractions from ambient noises. And they come, naturally, in two stylish frames. Read more about EssilorLuxottica, honored as No. 8 on Fast Company’s list of the World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies of 2025. 2. BoseFor engineering a pair of earbuds that don’t tune you out Not every earbud wearer wants to be disconnected from the outside world, so Bose came up with a clever new design to let the sound in. The Bose Ultra Open Earbuds clip to the side of your ear and project sound into the ear canal. This keeps the inner ear free of any uncomfortable intrusions and lets wearers hear what’s happening around them without having to rely on external microphones and special transparency modes. Open earbuds are an area of increasing interest for audio brands, though none has put quite the same emphasis on all-day comfort. New models from Monster, Nothing, and Earfun are larger and rest over the ears, while Sony’s latest LinkBuds Open earbuds rest inside the ear, with a hole to let outside sound through. Some open-ear headphones, such as Shokz’s bone conduction models, even wrap around the back of the head. While Bose’s unique design is starting to draw more direct imitations—most notably from Anker’s Soundcore C30i buds—reviews give a clear nod to the Ultra Open Earbuds for comfort and sound quality, carving out a leadership position in a growing category. 3. GE AppliancesFor bringing the barbecue indoors Too many smart kitchen appliances promise to make cooking simpler, only to add new layers of complication. GE Appliances’ Profile Smart Indoor Smoker offers something more tangible, allowing you to eat delicious smoked meat without having to step outside. At 16-by-17-by-20 inches, the $1,000 device is compact enough to fit on a countertop but large enough to contain a few racks of ribs or an entire brisket when split among top and bottom racks. It uses real wood pellets for smoke, which then passes through a filtration system akin to a catalytic converter to avoid smoking up the house. A companion app lets you tweak temperatures and monitor the meat’s doneness through internal probes. This is the only product of its kind, and it enables a type of cuisine that would otherwise require an outdoor appliance. Reviews have praised the product, albeit with reservations about what it means for barbecue as a hobby. Tasting the results, Texas Monthly called them both “delicious” and “sacrilegious.” 4. OzloFor dreaming up a well-designed pair of sleep earbuds When Bose discontinued its svelte Sleepbuds in 2023, a group of former employees decided to carry the torch, licensing Bose’s IP to make earbuds to help people sleep better. Ozlo’s Sleepbuds, which launched in October 2024, have the same comfy design as their predecessors, so they’re compact and squishy enough even for side sleepers, and they can play a night’s worth of ambient sound to mask a partner’s snores or other outside sounds. But Ozlo’s version does a lot more than Bose’s original. It supports Bluetooth audio from a phone and detects when you’ve fallen asleep, so it can switch from a podcast or audiobook over to its own ambient sounds. The earbuds case also has its own built-in sensors for light, noise, and temperature, so they can report on outside disturbances that might be affecting your sleep. Ozlo’s not stopping there. In October, the company raised $12 million to develop a second-generation model. It’s also trying to gain FDA clearance for tinnitus therapy, as it believes its earbuds are already helpful for the 10% of Americans suffering from it. 5. AppleFor turning small breakthroughs into a bigger, visionary one Apple’s Vision Pro is the perfect example of how the company’s smaller innovations tend to snowball over time. Yes, the product itself is a spare-no-expense luxury—a $3,500 headset whose visual fidelity and ability to see through to the real world far exceed that of any competitor—and it’s clearly aimed at bleeding-edge early adopters and app developers right now. But it also taps into frameworks and features that were years in the making on other Apple products. For instance, it builds on Apple’s existing ARKit framework, allowing developers of augmented reality iPhone apps to reuse many of the assets, and it uses the same Quick Look technology to pin virtual objects persistently in the real world. It also builds on content-sharing feature Sidecar to bring a Mac display into virtual space and SharePlay to experience apps with faraway friends. In February, Apple announced that it was bringing its Apple Intelligence AI features to the headset. Meanwhile, the hardware provides a starting point for Apple to build new kinds of content partnerships. (One intriguing possibility: Apple is in talks with Real Madrid to offer virtual seats at live matches.) Apple hasn’t revealed sales figures for the Vision Pro, but rumors suggest the company is working on more affordable variants. Its steady iterations will ensure that it has plenty of apps and content waiting when that happens. 6. OuraFor making a more practical smart ring, especially for women Oura didn’t need to reinvent the wheel for its fourth-generation health-tracking ring. Instead, it made significant refinements to extend its lead in the category it helped pioneer. The Oura Ring 4 uses recessed sensors instead of raised sensor bumps to improve comfort, and it packs additional signal pathways—more than twice as many as the previous model—to improve accuracy. It also comes in more sizes than before, has longer battery life, and adds new features, such as daytime stress tracking. The company has been positioning its device to give women, in particular, more insight into their health. It now tracks 30 different markers, including the new Fertile Window, which estimates fertile days, chance of conception at that time, and detected day of ovulation, giving women more information about their chances of getting pregnant throughout their cycle. In addition, it now offers a Pregnancy Insights report that tracks gestational age and provides weekly updates about physiological changes. Smart rings are a category of growing interest, with Samsung entering the fray this year, but Oura is in a strong position. The company announced in June that it’s sold more than 2.5 million rings and that 59% of its wearers identify as female. That’s a shift from a year ago, when most wearers were men. It also raised $200 million in a Series D round in December. 7. ESRFor tackling wireless charging’s silent battery killer Wireless phone charging is convenient, but it tends to generate heat, which can hinder the charging process and harm the battery’s long-term health. ESR’s CryoBoost tech aims to solve the problem by putting a fan and cooling ducts around the charger, activating them automatically when an iPhone is placed on top. ESR first introduced CryoBoost in 2022, and this year it unveiled a new open duct design that further improves charging efficiency while reducing noise. It also supports the Qi2 wireless magnetic charging standard, which Android phones will be able to use in the future. ESR says the new design reduces phone temperatures while charging by about 10 degrees Fahrenheit compared to conventional wireless chargers. While ESR doesn’t break out CyroBoost sales in particular, the company is on the rise as an accessory maker, with 92% annual revenue growth in 2024, total revenues of $290 million, and 17 million products sold. 8. Swarovski OptikFor lowering one of birding’s barriers Big tech companies are racing to bring augmented reality into everyday life, but Swarovski Optik has a much narrower use case in mind. Its AX Visio binoculars, which launched in 2024, can identify thousands of birds around the world though an onboard database that works without an internet connection. They can also identify mammals, dragonflies, and butterflies in Europe and North America. The binoculars also have a smart way of sharing discoveries with fellow observers: You can mark them in the viewfinder, then hand the binoculars over, and they’ll point the other person in the direction of the finding. Meanwhile, a companion app logs the exact location of those discoveries for future reference. The concept is impressive on its own, but Swarovski also sees AX Visio as a platform for future augmentations. It offers an API for developers to bolt on new capabilities and even has two unassigned spots on its function wheel to allow for additional feature expansions. The binoculars are pricey at $4,800, but in the long run they could change how birders and other budding nature enthusiasts interact with the hobby. 9. Sony ElectronicsFor making a bold bet on TV brightness Unlike most flagship TVs, which use OLED display technology, Sony’s top-shelf Bravia 9 TV uses Mini-LED. TV makers typically view Mini-LED as a step downward, because it can’t achieve the same deep black levels as OLED, but Sony has come up with a new backlighting system that reduces the blooming of Mini-LED while achieving much higher peak brightness levels. For Sony, the shift isn’t just about winning the tech spec war. It’s also a top purveyor of mastering monitors for movie and TV studios, and last year it introduced a model that supports significantly higher brightness across the entire screen. As editors take advantage of these new monitors, the hope is that TVs like the Bravia 9 will bring what you see at home even closer to what creators intended. 10. Open Home FoundationFor building a more sustainable—and privacy-focused—smart home system Home Assistant has long been the platform of choice for DIY smart home enthusiasts who value privacy and control, but now it’s on a stronger footing than ever. This year, its backers formed a new nonprofit called the Open Home Foundation to shepherd the project, and it’s taken some big steps to make the platform more approachable to newbies. You can now buy Home Assistant’s simple smart home device on Amazon, for instance. A privacy-focused voice assistant device to rival Amazon’s Echo and Google’s Nest debuted in December. (The group also established a “Wake Word Collective” to help train the voice assistant, which will work entirely offline.) Home Assistant has been cleaning things up on the software side as well, with a redesigned smart home dashboard, Apple CarPlay support, and an overhauled Music Assistant for controlling music from streaming services or a local file collection. It’s still primarily a platform for geeks, but it’s getting easier for anyone to adopt. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The most innovative companies in consumer and household goods of 2025
The gadgets produced by this year’s most innovative companies in consumer and household goods are, in their small way, revolutionizing every room in the house. From standout kitchen devices and boundary-pushing wellness products to a more humane mousetrap, this year’s list offers something for every moment of the day. Starting at the front door, there’s Level, the leader in smart locks, which finally upgraded its “invisible” system to sync with smart home hubs like Apple Home and Google Home via a low-tech radio connection. For the kitchen, there’s Walmart, which debuted Bettergoods, its first new private label in 20 years with a lineup of 300 quality products, not just cheap knockoffs. Science—the startup incubator behind Dollar Shave Club and Liquid Death—launched Final Boss Sour, a “healthy” candy brand that gamifies sour gummies. Pour-over fiends were treated to brews from a first-of-its-kind coffee maker, xBloom. (Recyclable pods come with whole beans that are ground fresh for each cup, while a scannable code loads brewing instructions to yield coffee as a professional barista would prepare it.) Aerflo debuted the first-ever travel carbonator: For $0.49 a bottle, its handy bottle turns any water into bubbly on the go or from the home countertop. For the bathroom, Suri has, in just two years, succeeded in creating a sustainable electric toothbrush brand that commands brand loyalty. In the living room, Looking Glass—known for its retail holographic displays—released a 6-inch version for everyday consumers that transforms photos, Polaroids, even notebook sketches into stunning 3-D projections. For garages and dark corners, Goodnature, the world’s only B Corp-certified pest control company, saw soaring sales of its humane, toxin-free smart traps. And outside the home, Gob introduced the first-ever mycelium earplugs, already endorsed by Billie Eilish, as a sustainable, high-performance alternative to the 40 billion foam plugs thrown out annually. Overdrive Defense, meanwhile, ventured into a more controversial space with its fentanyl and drink-spike test kits. Designed in bright colors with flourishes like the “rock on” emoji hands, they aim to make a real dent in America’s drug overdose crisis. 1. WalmartFor creating a hit private food label that’s high-quality and low-priced In 2024, Walmart introduced Bettergoods as its first private food brand in 20 years. It became the fastest-growing private label in the category. Bettergoods is a line of 300 items including snacks, beverages, dairy, pasta, soups, and chocolate—all intended to reimagine grocery store-branded products as items that offer chef-driven, clean-label, often quirky bespoke goods at affordable prices, such as guacamole-flavored tortilla chips, vegan mozzarella, hot honey for less than three bucks, and bronze-cut Italian pasta for $1.97. In many ways, 2024 was private labels’ year. Half of retailers said they expected them to be the #1 driver of growth. These in-house lines also gave supermarket chains a way to compete with Trader Joe’s, the leader by a mile for private labels. While other retailers, such as Target, saw slower growth, Walmart’s efforts snagged a level of positive critical reception that’s generally not showered on its other house brands, such as Great Value. (One prominent food publication in December said that Bettergoods had the “absolute best” Greek yogurt available.) Call it a paradigm shift if the industry’s largest player is looking to transform the image of store-brand goods from cheap knockoffs to quality products worth seeking out in their own right. 2. SuriFor making electric toothbrush design sparkle Suri offers one product: a sustainable electric toothbrush that, in 2024, finally achieved a level of pop recognition unheard of in a category where many consumers couldn’t tell you what brand they’re using. At least a dozen media outlets chose the Red Dot award-winning brush to be the year’s top pick. Clocking in at half the size of regular electric toothbrushes, it was designed by dentists, is waterproof, and needs recharging less than once per month. The brush head is made from castor oil and starch, and Suri will recycle it for free when it’s time for you to get a new one. There’s even an optional UV case that Suri says can kill up to 99.9% of bacteria. Focusing its full energy on thoughtfully designing one single product, available in five color options, helped Suri to break past $30 million in sales within two years. Co-founders Gyve Safavi and Mark Rushmore believe that the key realization was that really no toothbrush maker prior to theirs had inspired any sense of brand loyalty—consumers simply bought one from the pharmacy or, worse, took the free one from their dentist. 3. LevelFor making tiny, powerful home lock technology wi-fi compatable Hard door keys are becoming yesterday’s technology. Level’s “invisible” design remains the market’s most discrete smart lock—so understatedly high-tech that it looks totally analog (no keypad or fingerprint scanner) and requires only a screwdriver to install. Until 2024, Level avoided wi-fi entirely so as not to affect the device’s yearlong battery life. Connectivity relied on Level’s standalone “bridge” that had to plug into a wall within 20 feet of the lock. Level finally dispensed with the bridge late last year by activating a feature—one dormant for two years, to the annoyance of online technophiles—that can sync its locks with Apple, Amazon, Google, Samsung, and other smart home hubs. It uses a low-tech radio connection (a protocol called Thread) that requires very minimal power, yet allows owners to access their locks through those hubs, via encrypted channels that double as a security firewall. The setup is considered an aesthetic improvement as well, since the Level Connect wi-fi bridge can disappear, a plus for a brand centered around making the least obtrusive, most elegant and secure home locks. 4. Overdrive DefenseFor empowering partygoers to test for fentanyl before they indulge The founders of acne patch maker Starface and emergency contraception brand Julie Care created Overdrive Defense in the hopes of getting society to take harm reduction and drug safety more seriously. In the fall of 2024, they unveiled two products: Fentanyl Test Kits and Drink Spike Defense, which tests for the three most common drink-spiking drugs. The drink tests can detect the presence of roofies, ketamine, or GHB in minutes. Fentanyl kits, developed with trusted drug-testing lab WHPM, come as a five-pack for $13 and are sensitive enough to detect as few as 15 nanograms of the substance in a milliliter sample size (roughly the same as finding a human cell in a 1/5 teaspoon of powder). Both can be purchased at CVS locations nationwide or ordered for delivery from GoPuff. Asserting that test kits resembling a “sterile medical brand” are unlikely to be used, and therefore ineffective in making a dent in America’s fentanyl overdose problem, Overdrive has stuck things like the “rock on” emoji hands on the opposite end of its electric-orange test spoons. The safest way to do hard drugs is to not do them all, but the company contends that this approach alienates individuals who partake regardless, and, in turn, represent a group ignored by many mainstream health companies. Overdrive says it is donating 1% of profits to harm-reduction programs, and has also launched billboard education campaigns in states where lawmakers have voted to criminalize the sale of fentanyl tests on the grounds they facilitate drug use. 5. GobFor designing regenerative foam earplugs Most earplugs for concerts are still the throwaway kind, and they’re usually petroleum-based and contain a known human carcinogen. Gob makes the first single-use pair from mycelium, the rootlike structure of fungus, rethinking hearing protection from the ground up. After their use, Gob’s earplugs biodegrade fully back into nutrients that feed the soil, wherever they’re left. And during use, their specially formatted mycelium foam dampens sound more evenly than traditional PVC, which has the downside of muffling certain frequencies more than others. This year, Gob’s USDA-certified, toxin- and microplastics-free earplugs became the wearable of choice for several performers who fill stadiums and, according to the brand, have collaborated directly with experts in material science. Billie Eilish is now partnering with the company and wore Gob earplugs on her most recent tour, as did the Lumineers. Annually, some 40 billion foam earplugs are produced around the world. Gob asserts that by replacing even a portion of them with its regenerative mycelium alternative, the carbon savings could reach hundreds of million pounds of CO2e per year. 6. GoodnatureFor building a better mousetrap The only B Corp-certified pest control company, Goodnature was started by a couple of New Zealander design students with a goal of helping biodiversity to thrive, rather than eliminating household pests with chemical pesticides. It produces biodegradable, smartphone-connected traps that are more humane and have quickly established a global reputation with consumers, companies, and governments. Its award-winning flagship product, a mousetrap equipped with the first infrared no-touch sensor, delivers a swift, clean kill by discharging a CO2 canister into an enclosed space and afterwards resets itself. Last year, Goodnature launched its newest battery-powered trap that can manage 100 uses per charge at U.S. retailers like Walmart, Ace Hardware, and Amazon. Toxin-free lures come in scents like PB&J, hazelnut, and “meat lovers,” depending on what animal the user needs to attract. Toward the end of 2024, manufacturing began at a production facility in Wellington. The company says that its pest-free footprint worldwide grew by an area the size of Paris. The brand teases that it’s 24 months away from large-scale trials of what it calls its “moonshot,” a biodegradable trap that can be deployed, tens of thousands at a time, in hard-to-reach landscapes, displacing the need for arial toxin drops. 7. xBloomFor engineering a coffee machine with the knowledge of a barista Perfecting a café-caliber pour over is usually a job best left to a well-trained barista. Over the past decade, though, countertop coffeemakers have been outfitted with all sorts of fancy features that help home brewers come pretty close. But all lack a seemingly critical feature: the professional themselves. Now, respected coffee equipment maker xBloom has introduced the Studio to address that. Joining the growing field of all-in-one home coffeemakers last April, the Studio packs a high-end burr grinder, scale, and pour-over arm dripper, as others do, into a snazzy integrated unit retailing for $499. But the impressive aspect is how xBloom is partnering with the industry’s top roasteries—Black & White Coffee, Proud Mary, Sey, Onyx, Counter Culture, Sightglass—to deliver the coffee beans in what it dubs “xPods.” Made from recyclable kraft paper, the pods are single-serving canisters of not ground coffee, but a handful of fresh beans. They double as the machine’s brewing cones, have filters already inside, and include a recipe tap card that, when touched against the machine, dials in that specific coffee so it brews exactly how the roastery itself would have prepared it—ideal grind size, perfect water temperature, exacting brew speed. Think of it as like the machine being possessed by a new coffee pro each time, the expert who also sourced and roasted that day’s coffee beans. 8. ScienceFor incubating gonzo brands including gamified sour candy In 2024, Science bequeathed another madcap brand to the world, on the heels of other retail hits it had incubated (including billion-dollar brands Liquid Death and Dollar Shave Club). This one was Final Boss Sour, a line of video game-themed gummy snacks. Science says that its reason for disrupting gummies revolved around the category’s options marketing the shape they take (bears? worms? strips?), not their flavor intensity. With Final Boss Sour, Science took route two, adding a 16-bit video game nostalgia element, built on the idea that the consumer decides which “boss” to face: 1 for the least sour gummies, and 3 for the most mouth-puckering. Allegedly a 4 is in the works. Meanwhile, the founders point out that the product itself isn’t even candy. It is, in fact, very quietly healthful, made by mixing pure dried fruit (one of three berry types and mango pieces) with intense sour flavoring, no added sugars or artificial flavors. After Final Boss Sour was brought to market, the Science team spent 2024 taunting consumers with villains like Arachnothorn, Jawslicer, and the unknown “Final Boss,” who for now is a storm cloud and question mark. Their work hyping the brand on TikTok and YouTube, with the help of co-founder and viral video maker London Lazerson, drove more than 275 million impressions so far on social media in a matter of months and collecting some $3 million in seed funding. 9. AerfloFor taking carbonation to go Sparkling water is (still) having its moment, but for all the customization at fizz fanatics’ fingertips, it took until 2024 before anyone created a portable bottle that carbonates water on the fly with the press of a button. This first-ever travel carbonator—the Aerflo Aer1 System—launched in August for under a hundred bucks, works on countertops too, and even screws onto a standard-mouth Hydro Flask, converting it into a makeshift bubble-maker. CO2 capsule replacement is circular; consumers ship their empty canisters back to Aerflo’s facility in New Jersey, postage paid, and Aerflo inspects, cleans, and refills them. The math works out to roughly $0.49 per bottle, making Aerflo less expensive than most other bottled sparkling waters. The device is handier than such soda makers as SodaStream and Aarke but equally customizable, Aerflo says. All this is done at near-zero waste, since in addition to refillable canisters, the other single-use materials are either recyclable or biodegradable. The company raised $10 million around the Aer1’s release, and the carbonator is now sold direct to consumer, by outdoor retailers like Huckberry and Uncrate, and even on fashion sites like Editorialist and Goop. 10. Looking GlassFor bringing holograms home Looking Glass has been pioneering 3D imaging since its team of holographic hackers first occupied a Brooklyn storefront in 2014. Over the past decade, it has pivoted from volumetric printing to 3-dimensional LED cubes to holographic displays: Loro Piano implemented the technology to let customers see how clothes fit without the hassle of changing into them, while Cartier is letting people try on earrings and watches without physically being inside stores. But a successful Kickstarter this past year marked the brand’s biggest pivot yet, into into home use. The Looking Glass Go, a 6-inch display that retails for $300, instantly transforms photos and artwork—iPhone pics snapped at a party, old Polaroids, computer drawings, even notebook sketches—into “memories” that can be viewed physically as 3D projections. A detachable “frame” can be added to give it the semblance of staring at a classic wood-framed photo sitting on a bookshelf. As a bonus, users can talk to ChatGPT-powered 3D characters if they so desire—gimmicky, but probably a sign of what’s to come, and one that doesn’t require purchasing a $3,500 pair of augmented reality goggles. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The 10 most innovative computing companies of 2025
The heated race to develop and deploy new large language models and AI products has seen innovation surge—and revenue soar—at companies supporting AI infrastructure. This year’s Most Innovative Companies in computing include TSMC; the Taiwan-based fabricator’s N3P chip offers the smallest, most densely packed transistor size yet, while the company Chip-on-Wafer-on-Substrate (CoWoS) packaging technology is integral to AI accelerator chips, including Nvidia’s Blackwell GPU. Lambda Labs’ new 1-Click service provides on-demand, self-serve GPU clusters for large-scale model training without long-term contracts. SambaNova Systems takes another tack with its SambaNova Cloud, an “AI inference” service. Powered by the company’s specialized RDU (reconfigurable dataflow unit) processor, the service makes running AI workloads (as opposed to AI model training) faster and more efficient than on GPU-powered systems. Commercial data centers are also transforming to meet the demands of AI and high-performance computing applications. Aligned Data Centers has rolled out next-generation liquid-cooling systems, which use far less water and energy than air cooling, across its operations. Oxide Computer’s hyperscale cloud computers combine compute, storage, and networking elements in a single plug-and-play package, allowing security-sensitive customers to run their own private cloud server within a data center. And Sima.ai introduced novel multi-modal AI chips for edge computing; they can analyze inputs from text, computer-vision images, and audio for use in self-driving vehicles, robotics, smart retail, healthcare, and other applications. Apart from AI, some of the most exciting technology developments took place in quantum computing, with companies large and small taking different approaches to building utility-scale systems. They included trapped-ion specialist Quantinuum and “neutral atom”-focused startup Atom Computing. Following its 2023 unveiling of two of the largest quantum computers ever made, IBM expanded and upgraded its cloud quantum service and its open-source Qiskit quantum software platform in 2024. 1. IBMFor growing the quantum computing ecosystem with partners that can broaden access to a large developer community After its breakthroughs in quantum computing hardware at the end of 2023, Big Blue moved to cement its place as a leader in the quantum ecosystem in 2024, supporting a growing community of developers with software tools and access to computing resources. In December of 2023, IBM debuted the IBM Quantum Heron, a 156-superconducting-qubit system that demonstrated the company’s highest performance metrics to date, offering 16 times better performance and a 25-fold increase in speed over its 2022 quantum systems. It also unveiled its IBM Quantum System Two, a next-generation modular architecture that it hopes to scale in ever larger configurations. In September, IBM expanded its Quantum Data Center in Poughkeepsie, New York, which operates the most utility-scale quantum computers at a single location. And in October, the company opened its first global quantum data center outside the U.S., in Ehningen, Germany. Aiming to build a critical mass of quantum developers to support the ecosystem, IBM also upgraded its quantum software toolkit Qiskit with user-friendly features in April, and released an open-source benchmarking tool called Benchpress for comparing the performance of different kinds of quantum hardware and software. The same month, IBM delivered its first quantum computer on a university campus, at the Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Troy, New York. This November, at its first-ever Quantum Developer Conference , IBM announced that revisions to the Heron system have made it possible to run much bigger quantum “routines,” involving up to 5,000 two-qubit gates, a scale that the company says can deliver real scientific discoveries and push toward “quantum advantage” (solving problems that aren’t feasible with classical computers). IBM says that some 600,000 people have registered to use its quantum systems. 2. Lambda LabsFor accelerating AI development by sharing GPUs with everyone AI breakthroughs have traditionally relied on access to lots of GPUs–capacity that has been available mostly through expensive, long-term contracts with long wait times for service. Lambda Labs, which provides computing to support deep-learning applications, aims to change that. In 2024, it launched 1-Click Clusters, a service that provides AI startups and engineers with the first on-demand, self-serve GPU clusters for AI model training. With 1-Click Clusters, users of any size can get on-demand access to state-of-the-art Nvidia H100 Tensor Core GPUs and GH200 Superchips in a public cloud, enabling large-scale model training without having to lock in long-term contracts. Lambda Labs’ AI Cloud is used by companies and research institutions that include Intel, Microsoft, Amazon, Stanford, Harvard, Caltech, and the Department of Defense. In August, the company announced a partnership with SK Telecom to expand cloud services in South Korea. In December, the company announced the launch of Lambda Inference API, which claims to be the lowest-cost service of its kind on the market, allowing enterprise customers to deploy AI models and applications for end users without having to procure compute power themselves. In February, Lambda Labs raised a $320 million Series C venture round. The company ended 2024 with more than 10,000 customers. 3. TSMCFor pushing transistor density to the limit. Again. TSMC is the world’s leading dedicated semiconductor foundry and manufacturer of logic semiconductors, accounting for 28% of global semiconductor output value (excluding memory) as of 2023. With the chips it produces already powering everything from artificial intelligence and smartphones to automobiles, the company continues to deliver breakthroughs. For AI, transistor density is critical for continued gains in performance and efficiency, and TSMC’s has been relentlessly minimizing. In Q4 2023, TSMC launched its state-of-the-art 3 nm (nanometer) process, which provided an 18% speed improvement and 32% power reduction over earlier 5 nm technology. In 2024, it released an upgrade, the N3P, which offers an additional 4% speed improvement and 9% power reduction. The company expects a majority of its customers’ designs to utilize N3P, which is backward-compatible with its predecessor but provides higher performance efficiency and lower cost. TSMC is also a major supplier of so-called “CoWoS” Chip-on-Wafer-on-Substrate packaging technologies to designers of AI accelerator chips. NVIDIA’s Blackwell GPU, launched in March 2024, makes use of CoWoS to encase multiple chips together in a single package. Benefits include reducing the distance data must travel between chips, minimizing signal delay and power loss, and enhancing overall system efficiency when running large language models. TSMC had record 2024 annual revenue of $87.8 billion, a 33.9% increase over 2023. 4. SambaNova SystemsFor chips that could deliver exponential AI application gains SambaNova Systems’ platform, designed for enterprise and government use, combines AI chips with Samba-1, an open-source large language model similar to OpenAI’s GPT-4. The heart of SambaNova Systems’ technology is its own fast, specialized processor called an RDU (reconfigurable dataflow unit) that optimizes data flow and acceleration for large language models and complex AI tasks. With a focus on applying versus training AI, the company is betting that faster, more efficient systems with lower power consumption will shift real-time applications toward RDUs, which it claims deliver 10x the speed of GPUs at 1/10th the cost. In 2024, SambaNova added Accenture, Analog Devices, NetApp, Aramco, SoftBank, and Los Alamos National Laboratory to its customer list and expanded a partnership with the RIKEN Center for Computational Science. In September, it announced SambaNova Cloud, the world’s fastest “AI inference service” powered by its SN40L AI chip. And in November, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), known for running the world’s most powerful supercomputers, announced that it had deployed SambaNova Suite to assist its research with secure and energy-efficient AI. 5. Aligned Data CentersFor finding a next-gen approach to cooling its data centers Data centers supporting AI consume around 4% of U.S. electricity, a share expected to double by the end of the decade. Core to this energy demand are cooling systems, which account for at least 40% of energy consumption. In 2024, Aligned Data Centers—which builds adaptive data centers for hyperscale and enterprise customers—rolled out DeltaFlow, a next-generation liquid cooling technology for emerging applications in AI and HPC (high-performance computing). DeltaFlow is a closed-loop water system that directly cools computer chips (“direct-to-chip”) by circulating chilled water through cold plates attached to the components, dissipating heat through a heat exchanger within a single cooling distribution unit (CDU) that integrates seamlessly with existing data center infrastructure. Aligned has over 5,000MW of data centers in the planning and design phase or under construction. In March 2024, Blackstone loaned the company $600 million to finance the build of Aligned’s newest and largest data center, in West Jordan, Utah. It will join campuses in Chicago, Dallas, Phoenix, Salt Lake City, and Northern Virginia, with five more domestic locations in development. Aligned’s acquisition of Sao Paulo-based Odata last year expanded its footprint throughout Latin America. It has also invested in QScale, a Canadian operator of sustainable AI and HPC data centers. 6. SiMa.aiFor helping industrial robots, self-driving machines, and other machines run AI applications on their own hardware A burgeoning subsector of AI hardware is focused on so-called AI-at-the-edge technology, which enables local standalone processing of AI workloads in a wide range of real-world applications, including industrial robotics and autonomous vehicles. The edge AI hardware market is projected to grow from $24.2 billion in 2024 to $54.7 billion by 2029, according to research firm MarketsandMarkets. Silicon Valley semiconductor startup Sima.ai is a leading developer of embedded machine learning system-on-chip (MLSoC) solutions. After securing $70 million in funding in April, in September the company announced Modalix, the first edge-computing chips targeted at multi-modal AI. The new SoCs, which process text, computer-vision images, and audio, can run cutting-edge reasoning models like Meta’s Llama 2-7B. Energy efficiency is critical in edge applications, and Sima.ai’s chips have demonstrated up to 85% greater efficiency compared to leading competitors. Sima is targeting the embedded edge market, the computing layer that sits between the cloud and personal devices, and is pursuing applications in healthcare, smart retail, self-driving vehicles, government, and robotics. 7. Oxide Computer CompanyFor giving customers control over their computing clouds In 2024, San Francisco Bay Area startup Oxide Computer began commercial sales of its plug-and-play hyperscale cloud computers for private data centers. Designed for customers in government, financial services, and e-commerce who want high-performance computing capabilities along with the security of local control, Oxide’s systems make the transition to the private cloud as easy as possible. Its server racks include 32 compute sleds with more than 2,000 CPU cores, with integrated storage and networking elements, in a single plug-and-play package. Each rack is also equipped with DC power busbars, which are more efficient than standard AC connection. Compared to traditional rack servers, they improve per-watt usage by 70% and energy efficiency as much as 35%, Oxide’s computers are delivered with all the software needed to run full cloud computing services and require no assembly, allowing users to get up and running in a matter of hours compared to months for deploying in a data center. Oxide, which cites Shopify as a major ecommerce customer, has raised $78M to date. In November, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory selected Oxide’s hyperscale cloud system for its supercomputing center in California, providing scientific users with access to virtual machines that can help optimize demanding applications while maintaining the on-premises security necessary for their workloads. 8. NextSiliconFor creating chips that respond to real-time computing needs Tel Aviv chipmaker NextSilicon has faced formidable rivals like Nvidia and AMD. But with its innovative Maverick-2 chip, it is targeting the high-performance computing (HPC) niche where it sees less competition and a better fit for its parallel processing technology. Unlike fixed GPUs designed for AI and machine-learning workloads, the Maverick-2—manufactured by TSMC using a 5 nm process—is an “Intelligent Compute Accelerator” that uses advanced algorithms to dynamically reconfigure hardware based on real-time application needs. The algorithm instantly designs a temporary, dedicated chip in the hardware to run the specific software. NextSilicon says the chip offers four times the performance-per-watt of GPUs and 20 times the performance-per-watt of CPUs, while cutting operating costs by more than 50%. NextSilicon plans to build on the adoption of the company’s Maverick-1 chips by government agencies and academia. Launched in October, the Maverick-2 is already shipping to dozens of customers, including Sandia National Laboratories, the U.S. Department of Energy, and organizations in financial services, energy, manufacturing, and life sciences. 9. QuantinuumFor bringing quantum computing to the financial sector Quantinuum takes a different approach to quantum computing than many other companies advancing the technology. While IBM and other leaders in quantum have focused on superconducting qubits as their basic processing unit, trapped ions—charged atomic particles that are confined and manipulated using electromagnetic fields—offer a rival approach with advantages including longer coherence time and high qubit fidelity. In June 2024, UK and Colorado-based Quantinuum unveiled the industry’s largest-ever “trapped ion” quantum computer, with 56 trapped-ion qubits. In a May publication in Science Advances, researchers from Quantinuum, the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, and JPMorgan Chase reported using Quantinuum’s processors to achieve a quantum algorithmic speedup in a benchmark called the quantum approximate optimization algorithm, which has potential applications in logistics, telecommunications, financial modeling, and materials science. The company has been collaborating with JP Morgan Chase, one of its earliest users, on quantum technology for the financial industry since 2020. In 2024, Quantinuum also partnered with HSBC, the first international bank to offer tokenized physical gold. The companies trialed the first application of quantum-secure protection against a “store now, decrypt-later” (SNDL) attack, in which digital assets protected by today’s encryption are stored with the intention of being decrypted by future quantum computers. 10. Atom ComputingFor harnessing light to build high-performance qubits Berkeley and Boulder-based quantum computing startup Atom Computing takes a less-common approach to creating qubits—the basic unit of quantum information—using pulses of light to manipulate neutral atoms. Neutral atoms, which can be tightly packed in arrays, enable all qubits to connect with each other and can provide higher performance than fixed-qubit approaches. In September, Microsoft and Atom announced they would accelerate development of fault-tolerant quantum supercomputers that can solve impactful problems, and that Atom Computing’s neutral-atom hardware would be integrated with the Azure Quantum compute platform. This November, Microsoft and Atom announced rapid progress, setting a record for “entanglement” by creating a quantum connection among 24 logical qubits made from neutral atoms. Entangled qubits, which interact with one another through what Einstein called “spooky action at a distance,” is central to quantum computing’s promise. Even as Microsoft unveils its own cutting-edge quantum hardware, such as its recent Majorna 1 chip that it claims creates a new state of matter, it is working toward 2025 delivery of commercial on-premises quantum systems based on Atom’s technology, with a software stack that allows usability at a range of skill levels. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The most innovative companies in business services for 2025
These 10 companies provide vital services for businesses at every life cycle stage, from birth to death. Whether facilitating communications with customers, scaling operations, or reducing friction in the marketplace, honorees in the business services category of this year’s most innovative companies help companies grow and thrive—or even perform last rites when that moment finally arrives. In an increasingly post-literate world, companies continue to turn to video to communicate with key stakeholders, and two of this year’s business services honorees help enterprises produce streamable content more efficiently. As part of its ongoing efforts to infuse its products with AI-powered capabilities, Adobe released a new tool that transforms still images into video in less than two minutes, guided only by text prompts. Another honoree, HeyGen, launched a streaming avatar that enhances real-time interactions, creating more useful chatbots and tutors. Several of the honorees on this year’s list provide tech solutions that can help organizations scale. It’s been three decades since companies began reinventing themselves to remain competitive in the emerging digital world; now they face a similar challenge to harness the power of artificial intelligence. Working closely with Nvidia, Dell Technologies created its AI Factory to help companies navigate their AI transformations without ceding control of sensitive data. Six-year-old Lightrun launched a new debugger that is the first AI-powered tool of its kind, automating the entire debugging process and freeing developers from the endless tedium of troubleshooting. Smartling‘s new AI-powered toolkit reduces translation turnaround times while delivering accurate results for companies engaged in global commerce. As the cannabis industry continues to boom, LeafLink introduced a first-of-its-kind platform that guarantees payments to brands based on retailer sell-through, improving cash flow for companies that are often operating on challenging margins. Pattern (the only repeat honoree from last year’s business services list) introduced a new service that helps ecommerce companies navigate the tricky “middle mile” of the fulfillment process. And SimpleClosure takes the top spot in the category for addressing a challenge no founder ever likes to contemplate: closing a business. 1. SimpleClosureFor simplifying the onerous task of shutting down a startup Nearly half of all startups fail within their first five years. Loggerhead sea turtle hatchlings have a better chance of reaching the surf than founders do of celebrating their first anniversary. Israeli entrepreneurs Dori Yona and Nimrod Ram, serial founders who have navigated both successful exits and painful closings, launched SimpleClosure in 2023 to streamline the process of shuttering a business that fails, which more than half a million do each year. Leveraging fintech, legal tech, and AI, its platform automates much of the regulatory paperwork, final payroll distributions, and investor communications that traditionally take months and cost as much as $75,000 to execute—drudgery that can keep entrepreneurs from moving on. SimpleClosure, which has raised $5.5 million from investors, spent the past year developing its platform, creating a system of integrated technologies that reduces corporate dissolution time from months to days. Today, companies of all sizes, from mom-and-pop shops to venture-backed unicorns, are using SimpleClosure’s platform. (They pay a one-time fee based on the complexity of their structure.) Yona says companies only need to spend 10 or 15 minutes to onboard, uploading bank statements and HR data. The platform then ingests additional information from public state databases and delivers a personalized shutdown plan. Working on referrals from a range of top law firms, VCs, accounting firms, and partners like Stripe Atlas and Carta, SimpleClosure helped shutter more than 500 companies in 2024, ending the year with a run rate in the high seven figures. “Products grow when they are actually good and they solve customer pain points,” Yona says. “We’re building the TurboTax of shutting down.” Read more about SimpleClosure, honored as No. 47 on Fast Company’s list of the World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies of 2025. 2. Dell TechnologiesFor helping organizations integrate AI into their operations Over the past 30 years, businesses have invested trillions of dollars to undergo the digital transformation of their operations. While we are still in the early days of the subsequent AI transformation, 2024 global spending on AI infrastructure reached nearly $14 billion, a six-fold increase over the previous year. In May 2024, Dell launched its AI Factory, a new service designed to help businesses and organizations harness and scale their own AI initiatives. What differentiates Dell’s platform from many of its competitors is that it’s a hybrid solution: Rather than existing exclusively or primarily in the cloud, AI Factory integrates Dell’s on-premise AI servers, allowing companies to configure their AI infrastructure in ways that enable them to maintain more control over data. Dell co-developed its AI Factory with Nvidia, marrying Dell’s PowerEdge servers, storage, and networking with Nvidia’s powerful AI GPUs. Samsung SDS, McLaren Racing, and Elon Musk’s xAI are utilizing AI Factory, and AI platform Hugging Face named Dell its preferred on-premises infrastructure provider. The Dell AI Factory can reduce setup times by up to 86%, while enhancing privacy and reducing latency. From Q1 to Q2 2024, following the launch of AI Factory, Dell reported a jump in AI server sales from $1.7 billion to $3.1 billion, and at the end of 2024, it reported full-year sales of about $10 billion. The company’s overall 2024 revenue of $95.6 billion represented an 8% increase over the previous year. 3. AdobeFor bringing commercially safe generative-AI magic to video More than 90% of global businesses employ video in their marketing efforts. Average production costs range from $1,500 to $7,000 per video minute, putting a huge strain on annual budgets. In February 2024, as part of the ongoing expansion of its generative AI-powered Firefly platform, Adobe released a beta version of its new Video Model to the public. As is the case with Firefly Image—first released to the public in 2023; the latest version, Firefly Image 3, came out in April 2024—the Video Model is trained exclusively on licensed or public domain imagery. The new tool creates videos out of still images, guided by text prompts, in less than two minutes. Adobe has begun integrating its Video Model into Premiere Pro, which has a global user base of 30 million people, 47% of whom work for large companies. In addition to its Video Model, Adobe introduced a range of features to other key products in 2024, including a “distraction removal” tool that uses AI to excise unwanted elements from photos, an expansion to its Generative Workspace that creates high-resolution images more quickly and facilitates work involving multiple elements, and an AI assistant that provides a conversational interface to guide users through Adobe’s Experience Platform. 4. LeafLinkFor making B2B cannabis payments more mellow The legal cannabis industry continues to grow like, well, a weed, increasing from less than $1 billion a decade ago to about $40 billion today. Conservative estimates predict a total U.S. market of more than $76 billion by 2030. In 2016, LeafLink launched as a marketplace to connect brands with retailers and streamline the ordering process. Over the intervening years, the company has introduced increasingly sophisticated fintech tools to facilitate invoicing and expand payment options. In September 2024, LeafLink launched a first-of-its-kind payment option that guarantees payments to brands based on retailer sell-through, improving cash flow and reducing financial risks for both parties. Payment on Sell-Through (PoST) allows brands to receive automated payments upon the sale of their products, eliminating the cumbersome and time-consuming process of manual collections. Brands also benefit from detailed insights into product performance. More than 70 customers have integrated PoST into their operations. In November, the company introduced LeafLink Plus, a subscription-based platform that provides cannabis retailers detailed data insights into their inventory and operations. In July, LeafLink completed a $125 million funding round backed by CPMG, Nosara Capital, L2 Ventures, Thrive Capital, and Tiger Global. That same month, the company acquired Dama Financial, a fintech company focused on the cannabis industry, and then in November, LeafLink acquired one of its competitors, Leaf Trade. 5. HeyGenFor building a video bridge across the uncanny valley As businesses increasingly rely on videos to engage customers and communicate with employees, HeyGen provides an economical AI-powered platform that helps them create text-to-speech explainer-style videos featuring AI avatars and spokespeople. Building on the Interactive Avatar it released at the end of 2023, HeyGen launched its Streaming Avatar in July 2024, which enables real-time interactions that enhance the avatar’s usefulness as a chatbot or tutor. Like its predecessor, the Streaming Avatar can communicate in 175 languages, switching from one to another in mid-conversation. HeyGen’s 2024 advancements also introduced real-time video translation tools that preserve the speaker’s voice and style, as well as new integrations like PowerPoint-to-video conversion that streamline content creation. Even users of the free tier can now create a personalized “digital twin” avatar in a matter of minutes. HeyGen’s million-plus users number more than 40,000 monthly subscribers, and corporate customers have included McDonald’s, Salesforce, and the Weather Channel. The company’s pricing begins at $24 per month for individual creators, with business subscriptions starting at $89 per month. HeyGen reports it has doubled its annual recurring revenue to $35 million. In June, the company completed a $60 million funding round led by Benchmark, with participation from Thrive Capital, Bond, Conviction, and a number of individuals, including Dylan Field, CEO of Figma. 6. LightrunFor automating the debugging process for developers Founded in 2019, Lightrun is a developer-centric observability platform. What that means, in plain English, is that it allows software developers to monitor their applications while they are running, helping them to see how their code performs in real-time and making it easier to spot and fix problems quickly. In July 2024, Lightrun launched its Runtime Autonomous AI Debugger, the first generative-AI-powered tool of its kind. It automates the entire debugging process, from identifying bugs to specifying the precise line of code creating the issue. This frees up developers caught in the endless cycle of troubleshooting and reduces down time that can have serious consequences in all businesses but catastrophic ones in healthcare, finance, and public infrastructure. Lightrun says its new platform has improved mean time-to-repair rates by 70% across industries where it’s been deployed. The tool is being used by such heavyweights as Citibank, AT&T, Salesforce, Microsoft, UnitedHealth Group, and SAP. Lightrun says it grew its revenue by a factor of 4.5 in 2024. In July, the company completed an $18 million funding round led by GTM Capital with participation from previous investors Insight Partners and Glilot Capital Partners. 7. PatternFor helping online sellers navigate the middle mile You’re probably familiar with phrase “last mile” to describe the complicated—and expensive—final stages of delivering a package from distribution center to customer. But there’s also a “first mile” (from factory or origin to warehouse) and a “middle mile” (from warehouse to distribution center). In March 2024, Amazon introduced a new “inbound placement policy,” changing the rules and fee structure of managing shipping in a way that altered the economics of the middle mile and threatened to put a serious crimp in the margins of sellers. Previously, brands had shipped their product to the nearest Amazon fulfillment center, and Amazon then distributed product to other fulfillment centers closest to customers. But beginning in March, brands had to begin paying $0.27 to $1.58 per unit to ship to the closest Amazon fulfillment center or else figure out how to get its packages to a location closer to the final customer. Pattern saw an opportunity to save money for brands (and generate additional revenue for itself) by helping them get their goods to Amazon. The e-commerce accelerator is one of the most prolific shippers in the Amazon universe, with 1,400 employees in 22 countries and 14 global distribution centers. Its new middle-mile service allows brands to ship goods to one of Pattern’s warehouses. The company then harnesses trillions of data points to determine how to parcel out packages most efficiently to the optimal Amazon fulfillment center, charging brands about half what they’d have to pay Amazon. Pattern says it has been profitable since its founding in 2013, with five-year revenue growth of more than 270% and trailing 12-month revenue of nearly $1.8 billion. 8. SmartlingFor helping online stores and other websites eliminate language barriers The Translation Management Systems (TMS) sector is booming, growing at an estimated 17% annually. As e-commerce, digital content, and other companies expand globally, they have to translate media, product descriptions, marketing materials, and customer support in consumers’ native languages. This past year, Smartling introduced a series of innovations to solidify its position as a leader in the TMS space. The company’s AI-powered human translation tool combines AI, large language models, and human expertise to deliver faster translations at lower costs. And in May 2024, the company launched an AI Translation Toolkit that reduces turnaround times while still delivering accurate results. A new set of AI-powered quality assurance tools released in November streamline the production process, and a data access and visualization module (also released in November) allows clients direct access to their translation data so they can connect it with business intelligence tools like Tableau, Power BI, or Looker. Smartling’s revenue reached a reported $39.7 million in 2024, a 90% increase over 2023, with translation volumes up 30% year over year. Companies that use Smartling include Pinterest, Shopify, SurveyMonkey, Walgreens, InterContinental Hotels Group, and Accenture. 9. GigsFor helping businesses launch their own mobile phone networks Over the past quarter century, mobile cellular subscriptions have ballooned from about 300 million to more than 9 billion—meaning there are more mobile subscriptions than there are humans on the planet. To take advantage of our heightened connectivity, more and more companies (currently about 2,000) have become mobile virtual network operators, or MVNOs. MVNOs lease network capacity from operators like AT&T or T-Mobile and resell the services to consumers, offering branded phone plans that can include discounted rates and various other benefits and discounts. Gigs is not an MVNO, but since its founding in 2020, the telecom-as-a-service company has been making it easier for enterprises to create their own mobile networks with a platform that streamlines the process. In March 2024, Gigs launched a critical new component of its MVNO-in-a-box platform: Tax Engine analyzes the myriad tax requirements of different states and automatically calculates the tax burden to simplify billing. Another new product launched in 2024 integrates seamlessly into enterprise-level HR tools, making it easier for companies to create corporate phone plans that operate across more than 50 countries. In October 2024, Nubank—Latin America’s largest fintech bank, with more than 100 million customers—harnessed Gigs to launch its MVNO, called NuCel, which offers integrated services, such as global connectivity for travelers. In December, Gigs announced completion of a $73 million funding round led by Ribbit Capital. Other investors included Google’s Gradient Ventures and Y Combinator. 10. AletheaFor helping companies detect security risks from misinformation and disinformation campaigns Misinformation is a huge threat to business. Two years ago, a fake Eli Lilly Twitter account announced the company would begin providing free insulin, leading to a 4% drop in share price—more than $13 billion in market cap value. Starbucks, Pepsi, Blackrock, and Kay Jewelers are just a few of the companies that have suffered from misinformation campaigns in recent years. Lisa Kaplan, a fellow at George Mason University’s National Security Institute, founded Alethea in 2019 to combat disinformation and social media manipulation. The company’s flagship product is an AI-powered tool called Artemis that leverages advanced analytics and machine learning to detect misinformation threats in real time. The platform launched at the end of 2023, and last year it added the ability to detect threats across a wider array of sources, including niche social media platforms and extremist organizations. Artemis scans the open web, analyzing billions of data points across multiple languages to detect early signs of cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, and influence operations. The platform delivers its insights to company communications and security teams. A series of exclusive 2024 Alethea reports on Russian disinformation and influence operations prompted coverage in The New York Times, The Washington Post, Axios, and other prominent news outlets. Given the nature of its service, Alethea does not reveal specific customers, but it says it added four Fortune 200 companies last year. In April 2024, the company completed a $20 million funding round led by Google Ventures. Since then, it has hired executives from major companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Tesla, and over the last three years, it has sustained a better than 400% increase in annual recurring revenue. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
These 10 biotech companies are changing how we discover new drugs and treat complex diseases
This year’s list of biotech companies reflects the evolving impact of AI, a growing interest in cutting-edge research tools for single-cell analysis and spatial proteomics, and clinical advances for novel drug candidates that promise more convenient and effective treatment for conditions impacting millions of Americans. AlzPath’s highly sensitive blood test can detect signs of Alzheimer’s disease before symptoms develop—and in time to potentially benefit from new treatments. Genomic sequencing specialist GeneDx is helping parents discover and treat hundreds of rare diseases in newborns. 10x Genomics and Syncell streamline cutting-edge analytics for life science research, while Nabla Bio is using generative AI to design completely new antibodies. Protagonist Therapeutics is partnering with Janssen on an oral peptide for treating plaque psoriasis, aiming to expand the use of these powerful drugs beyond obesity. And Recursion is harnessing the largest supercomputer in pharma to power a drug discovery platform used by Big Pharma customers, while advancing multiple AI-based candidates of its own through clinical trials. 1. ALZpathFor using a simple blood test to diagnose Alzheimer’s at an earlier stage Earlier diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease is seen as increasingly important and worthwhile as a focus for new medications. Currently, AD is typically diagnosed via cognitive testing alongside expensive PET brain scans or invasive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) tests, which are costly and painful. But recently, a much less invasive blood test has demonstrated comparable accuracy to these methods. ALZpath has developed a proprietary antibody that, when utilized in blood-based tests, can detect tiny concentrations of the biomarker p-tau217, which has long been recognized as a reliable sign of Alzheimer’s but previously could not be identified via blood test. Concentrations of p-tau217 can signal the accumulation of proteins that cause Alzheimer’s years before the onset of cognitive symptoms, making ALZpath’s test an option for earlier diagnosis and treatment. In March 2024, Neurocode, a clinical laboratory that tests for neurological disorders, became the first U.S. lab to make the test available for clinical diagnostic use, clinical trials, and other research purposes. In June 2024, Roche licensed the ALZpath p-tau217 antibody to develop and commercialize an Alzheimer’s disease in-vitro diagnostic test. The Roche p-tau217-based test was recently granted Breakthrough Device designation by the FDA and will be commercialized as part of an ongoing collaboration between Roche and Eli Lilly. In 2024, ALZpath reached the milestone of obtaining over 50 active partners across pharma, diagnostics, and academia, and has seen a 130% increase in revenue from 2023. 2. GeneDXFor offering diverse newborn populations genomic screenings for rare diseases The average time for accurate diagnosis of a rare disease is about five years, but in some populations it may take up to a decade. GeneDx aims to shorten that diagnostic journey and get patients the care and treatments they need sooner. In 2024, the company—a leader in genome and exome testing for rare diseases—provided the large-scale sequencing and reporting for the largest study of its kind on genomic screening for rare diseases in newborns. A collaboration with Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York-Presbyterian, the New York State Department of Health, and Illumina, the GUARDIAN (Genomic Uniform-Screening Against Rare Diseases in All Newborns) study aims to screen 100,000 newborns in a diverse population for more than 450 actionable genetic conditions not currently included in standard newborn screenings. The study, which is open to babies born at New York-Presbyterian Hospitals, has sequenced more than 17,000 newborns to date. Preliminary results from the first 4,000 newborns, published in October 2024, found that 3.7% of newborns had one of these rare conditions, the majority of which would not have been picked up by traditional newborn screening. GeneDx has also partnered with the New York Center for Rare Diseases at Montefiore, PacBio, and Google Health to deliver genetic diagnoses for Bronx families living with rare diseases. The company’s customers today typically include clinical geneticists, genetic counselors, pediatric neurologists, developmental pediatricians, and neonatologists, but the goal is to make genomic newborn screening the standard of care nationwide and to have more general pediatricians use genomic screening as a first-line test for children with rare-disease symptoms. The company’s 2024 full-year revenue of $302.3 million was a 56% year-over-year increase over 2023. 3. 10x GenomicsFor bringing speed and efficiency to single-cell analysis In 2024, 10x Genomics worked to cement its status as “the single-cell analysis company,” making upgrades and additions to its portfolio of tools used by researchers in academia and industry to understand molecular activity in the three-dimensional space of cells and tissues. “Single-cell” analysis refers to the study of genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and cell-cell interactions at the level of the individual cell, as opposed to conventional methods that study bulk populations of many cells. This is important because many diseases, particularly cancer, are driven by changes in particular cells, not all cells; precision treatments require pinpointing those that really matter. In 2024, 10x Genomics launched 10 new products and capabilities across its single-cell and spatial platforms, including GEM-X, an innovative microfluidic chip design that allows for significantly improved sensitivity and efficiency compared to previous versions, enabling researchers to detect up to two times more genes for a more than twofold reduction in cost per cell analyzed. Another new product, the Visium HD Spatial Gene Expression Assay, enables users to layer cell-level gene-expression data on top of histology (tissue) images, with high-resolution, to pinpoint drug targets, for example. 10x’s tools are used in several major collaborative research efforts, including the Human Cell Atlas, the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, and NIH’s BRAIN Initiative Cell Census Network (BICCN) project. 4. Protagonist TherapeuticsFor expanding peptide-based therapies beyond obesity Protagonist Therapeutics makes novel drugs based on peptides—the building blocks of proteins, and the basis of drugs including insulin and obesity medications like Wegovy and Zepbound. Because peptides are potent, selective in their action, and safe, there is growing interest in their potential therapeutic applications in many areas. But it has been extremely difficult to deliver effective peptide treatments in oral form, because they break down rapidly in the gut. Protagonist’s lead drug candidate, Icotrokinra (JNJ-2113), is an oral peptide that was jointly discovered with scientists from Johnson & Johnson and saw positive topline results in two phase 3 clinical trials for treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. Three more phase 3 studies are ongoing, with results expected in Q2 2025. Additional preliminary results from a phase 2b study in ulcerative colitis are expected in Q1 2025. Protagonist’s other leading drug candidate, Rusfertide, is an injectable synthetic peptide that mimics the natural hormone hepcidin, which helps regulate how the body processes iron. In January 2024, Takeda and Protagonist announced a global license and collaboration agreement to develop and commercialize Rusfertide as a treatment for blood cancer polychthemia vera, which causes an overproduction of red blood cells. Protagonist reported over $259 million in license and collaboration revenue for the first half of 2024. Net income of nearly $177 million for the first half of 2024 was a significant turnaround from a net loss of $72.2 million in the same period in 2023. 5. RecursionFor mapping a path for AI-driven drug discovery Founded in 2013, Salt Lake City-based Recursion was a techbio company before there was such a thing. In 2024, it made big moves to stay at the forefront as research and discovery platform for biopharma customers and as a company with multiple clinical-stage therapies of its own. In January 2024, the company launched its LOWE (LLM-Orchestrated Workflow Engine) platform, which provides a natural language interface for complex drug discovery tasks. Powered by Recursion’s proprietary biological and chemical data, it can orchestrate experiments using the company’s automated wet laboratories. In May, a partnership with NVIDIA allowed the company to upgrade its “tech stack” with an on-premise supercomputer called BioHive-2, which ranked number 35 in the world in 2024 and is believed to be fastest computer in the biopharmaceutical space. In August, Recursion’s first neuroscience “phenomap”—which shows chemical and genetic alterations in neuronal cells—was optioned by Roche Genentech for $30 million as part of a fee structure that could exceed a total of $500 million across multiple maps. Recursion made steady in its own pipeline, too: In October 2024, the company announced the first patient dosed in its phase 2 clinical trial of REC-3964, a potential first-in-class, nonantibiotic treatment for recurrent Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection, and in December, the start of a phase 1/2 trial of REC-1245, a potential first-in-class therapy, called an RBM39 degrader, for certain solid tumors and lymphoma. In late November, Recursion completed the acquisition of a former rival in AI-driven drug development, Exscientia, bringing the company’s total number of in-house drugs in preclinical and clinical development to 10. 6. Basecamp ResearchFor recording Earth’s microbial biodiversity and sharing the benefits Less than 1% of the Earth’s genetic biodiversity has been recorded. But U.K.-based Basecamp Research is working to expand our knowledge of what’s out there. By conducting more than 125 research expeditions across five continents so far, the company has assembled what it bills as the world’s largest genomic database of biodiversity, comprising genetic sequences and protein data from microbes collected in volcanic vents, caves, oceans, jungles, and other extreme and remote ecosystems around the world. The Basecamp platform integrates environmental data like temperature, pH, and other chemical conditions alongside protein sequences, providing context for understanding protein function. It uses AI models to help customers in pharmaceuticals, materials science, consumer goods, and other areas by identifying and designing novel proteins for drugs, industrial enzymes, and biomaterials. The company licenses its platform to clients and has partnerships with more than 50 companies and research institutions, including Sanofi P&G, and U.K. chemicals company Johnson Matthey. Basecamp Research has also worked to ensure that the benefits of its discoveries are shared fairly with the communities whose native biodiversity feeds the platform, by tracing the source of proteins that clients use to develop products, and making royalty payments to these communities starting in the R&D phase. At the UN Biodiversity Conference in Montreal in August 2024, Basecamp announced a new, landmark bioprospecting deal with the nation of Cameroon, which in addition to royalty payments provides nonmonetary benefits including training of Cameroonian scientists and academics, sequencing equipment, data for soil and environmental monitoring, and education programs in the areas where the company collects samples. In October, the company raised a $60 million Series B. 7. Nabla BioFor harnessing AI to build truly novel antibodies from scratch So-called multipass membrane proteins, which comprise two-thirds of all cell surface proteins and play a major role in controlling cell behavior, represent some of the most promising targets for antibody drugs. But developing antibodies that recognize these proteins has been notoriously difficult. As of September 2023, only three multipass membrane proteins had been successfully targeted by antibodies. Nabla’s generative protein-design platform promises to unlock hundreds of these previously inaccessible targets, potentially doubling the number of disease-relevant drug targets the industry goes after. This fall, Nabla released a technical paper demonstrating the successful use of its AI platform to design several therapeutic antibodies “from scratch,” given just a target protein sequence and/or structure—the first evidence of computationally designed antibodies that can target a subset of these proteins called G protein-coupled receptors. On the promise of its platform, Nabla has inked more than $550 million in total deals with Big Pharma customers including AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, and Takeda. Since launching in 2021, the Cambridge, Massachusetts-based company has raised $37 million in venture funding, including a $26 million Series A round in January 2024. 8. DarwinHealthFor matching cancer patients with experimental treatments Today, overall cure rates for advanced lung, breast, and colon cancer are typically less than 50%. Finding a plan B for patients when standard-of-care therapy has failed comes down to high-stakes and time-consuming guesswork to navigate a maze of potential treatments. There are 250 FDA-approved cancer drugs and 200 different types of cancer—meaning, there are tens of thousands of possible drug-cancer combinations and billions more if you combine multiple drugs. DarwinHealth uses AI—its VIPER algorithm—to take experimentally measurable data from a patient’s tumor, such as gene expression profiles, and make predictions about which existing drugs are most likely to be effective against the “Tumor CheckPoint” proteins driving their particular type of cancer. In 2024, DarwinHealth introduced innovations across its platform, speeding its adoption in multiple clinical trials in rare and treatment-orphan malignancies (including renal carcinoma, gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, breast cancer, prostate cancer, and pancreatic carcinoma), and in drug development, where customers including BMS have used it analyze more than 1,500 oncology-related compounds. Trial results published in 2024 showed 100% accuracy of the DarwinOncoTarget tool at predicting response to drugs called HDAC6 inhibitors in breast cancer, and a 91% accuracy of DarwinOncoTreat at predicting response of multiple tumor types. Estimated revenue doubled from $4M in 2023 to $8 million in 2024, and biopharma partnerships increased from 3 to 8. 9. IO BiotechFor developing a one-two shot of immunotherapy for melanoma Copenhagen-based IO Biotech is developing novel dual-action cancer vaccines that harness the immune system by directly stimulating immune T cells as well as important immune-suppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment. Unlike mRNA vaccines that are personalized to each patient, IO’s peptide-based vaccines are “off-the-shelf,” meaning patients can start treatment more quickly. The treatment could offer an alternative with less potential for systemic toxicity than RNA-based cancer vaccines (one of which, from Moderna, is in phase 3 trials). IO’s lead candidate, IO102-IO103, for the initial treatment of advanced melanoma, has shown promising clinical efficacy and safety in phase 1/2 studies in combination with Keytruda, demonstrating an 80% overall response rate and 50% complete response rate. This data led to FDA Breakthrough designation and allowed the company to move directly into phase 3 trials. Phase 2 trials of IO102-IO103 in combination with Keytruda are also underway in lung and head and neck cancer patients with solid tumors. In December, IO Biotech entered a loan agreement of up to €57.5 million from the European Investment Bank, the long-term lending institution of the European Union, to fund further development and pre-commercialization work. 10. SyncellFor speeding up spatial proteomics discovery In 2024, life science tools startup Syncell launched its ultra-high-speed, real-time targeted microscopy-based illumination platform called Microscoop, which offers a new level of precision for researchers studying spatial proteomics—three-dimensional protein expression—in cancer and other diseases. Syncell’s Microscoop platform technology uses microscopy-guided photo-labeling to isolate proteins from disease-related regions of interest, followed by mass spectrometry analysis, to identify novel proteins that could serve as targets for new drugs. Syncell offers a complete system—including proprietary reagents that are used to prepare cell and tissue samples for labeling and analysis. The technology is applicable to a broad scope of biological problems, including the identification of new disease biomarkers and novel targets for drugs. It has already been used to enable the discovery of novel protein constituents in beta amyloids associated with Alzheimer’s disease, TDP-43 aggregates associated with ALS disease, a marker of triple negative breast cancer, and more. In December, the Taipei and Watertown, Massachusetts-based company raised a $15 million Series A financing round led by Taiwania Capital. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The most innovative companies in beauty for 2025
The world is moving fast—so fast that many people feel like they can’t keep up. The beauty industry is meeting consumers where they are, slowing things down, looking to the past, and consulting nature for inspiration. Nostalgia and a desire to claw back more time, any time, were major drivers in beauty innovation over the past year. Arcaea worked with bioengineers to recreate the DNA of extinct flora from Borneo and extract its essence to create indulgent fragrances under the brand name Future Society. (The company also donates a portion of proceeds to stave off further extinctions on the island.) Delavie Sciences looked to the cosmos for a groundbreaking skincare product. Retro suncare brand Vacation channeled Gen X nostalgia (or, as the band LCD Soundsystem once put it, “borrowed nostalgia from the unremembered Eighties”) to revive the texture, color, and scent of Bain de Soleil’s out-of-production orange gelée, now reformulated with a higher SPF for modern sun worshippers. L’Oréal helped the 40% of women who color their hair at home save time by creating an application device that retains mixed formulas for future uses. Olive & June found a way to help nail buffs do gel manicures at home. Credo Beauty, meanwhile, developed ways to make beauty packaging more sustainable. Rōz, founded by celebrity hairstylist Mara Roszak, rolled out a nitrogen-propelled, VOC-free aerosol root lifting spray that gives loads of volume, without harming the environment. And some beauty companies paid specific attention to bringing back people’s smiles: Megababe joyfully took the stigma out of products aimed at the nether regions, E.l.f. Beauty brought its popular, affordable products to underserved markets (with a soundtrack), and Bubble Skincare became Gen Z’s lucky charms at college tailgates 1. VacationFor bringing back the Bain de Soleil tan Vacation isn’t just selling sunscreen—it’s selling nostalgia. Known for blending cutting-edge sun care with lifestyle-driven marketing, the Miami-based brand has turned what was once a chore (applying sun cream) into a luxury experience through the 2024 revival of a century-old cult classic: Orange Gelée, the iconic Bain De Soleil sun gel. Originally launched in 1920s France, Orange Gelée achieved iconic status by the 1970s but was discontinued in 2019, sparking a public outcry. Vacation seized the opportunity, forming the “Orange Gelée Revival Project,” which combined fan engagement, beauty expertise, and savvy storytelling. The team worked with a panel of diehard fans and modern experts to perfect a formula that preserved the gel’s original color and texture while meeting modern skincare standards. With 16,000 signups before launch, the SPF 30 sunscreen gel sold out in three days and became Vacation’s fastest-selling product ever—it sold 6 times more units in the first week of launch than its previous bestseller. Retailers including Ulta, Nordstrom, and Urban Outfitters quickly signed on, helping cement its success. This creative approach drives Vacation’s growth—the company reported $40 million in revenue in 2024—and fuels viral hits such as the Classic Whip Glow SPF 30, a shimmering rendition of Vacation’s best-selling, whipped cream-inspired Classic Whip SPF 30 Sunscreen Mousse. By combining heritage, innovation, and marketing prowess, Vacation proves sunscreen can be both protective and playful. 2. MegababeFor kicking taboo body issues in the butt When founder and body-acceptance advocate Katie Sturino first launched an anti-chafing stick in 2017, nobody really wanted to talk about what went on between a woman’s thighs, and yet the product was hit. Now seven years later, her brand, Megababe, is booming, with a constellation of products offering customers a humorous, effective way to address typically unspeakable bodily issues head-on. There’s the Bidet Bar, an in-shower cleansing bar launched in January 2024 designed specifically for one’s derrière, and Butt Stuff, a maximum-strength, FDA-approved hemorrhoid cream that came out in September 2024 September. And consumers can’t get enough. Megababe’s ever-expanding lineup now includes more than 30 products that reach heretofore unmentionable areas, from the Happy Pits Underarm Mask to Bust Dust Anti-Boob-Sweat Powder to Megaman Ball Deo, a cream-to-powder deodorant for male nether-regions launched last year. One stick of the OG product, Thigh Rescue, sells every 30 seconds, according to the company. The brand also released its first national marketing campaign in 2024, featuring Sports Illustrated cover model Hunter McGrady. It racked up 30 million impressions. Meanwhile, Megababe is considering the environment: One of the company’s Blade Bars, for example, contains as much product as two cans of shaving cream, for example, and all of the company’s deodorant containers are made with 100% post-consumer recycled materials. 3. Credo BeautyFor pumping out truly recyclable beauty products Credo Beauty, a retail and online marketplace of clean beauty brands with 15 brick and mortar retail shops in the U.S., focuses on the details of the many products it distributes, from patented ingredients to transformative packaging. It’s also a co-founder of Pact Collective, a not-for-profit focused on the responsible disposal of beauty packaging, as the industry generates 120 billion cosmetic packages annually, and in this role, Credo really helping rewrite the rules of sustainability. It’s a dirty little secret that most beauty packaging is notoriously hard to recycle due to its size, flexibility, or mixed materials. Pact is working to close the loop, creating collaborative solutions for hard-to-recycle materials. That starts with a revolutionary pump. Traditional pumps, with their metal springs and multi-material components, have historically been nearly impossible to recycle. Credo partnered with Pact to pilot a resin, called NewMatter™ , that’s made from 84% recycled materials sourced using beauty package empties from 140 companies and other ocean-bound plastics—and eliminated the pesky metal spring entirely. In 2024, Credo began using the NewMatter™ resin pumps in its own line of beauty products. They can be dropped off at any of Credo’s affiliate stores for true product circularity. Every 38 pumps diverts one pound of material from landfills or oceans, according to Pact Collective. To date, Credo has made more than 30,000 units of this pump, which has diverted close to 900 pounds of plastic waste — saving the equivalent of 8 cubic meters of landfill space. By 2025, Credo and Pact project they will manufacture a million of the pumps and roll them out to their 120 member brands, setting a bold and beautiful precedent for sustainable cosmetic packaging. 4. E.l.f. BeautyFor bringing prestige-worthy cosmetics to beauty deserts E.l.f is on a mission to make high-end beauty trends accessible and affordable. It does this, in part, by spotting trending beauty products in the so-called “prestige” market and then quickly developing appealing and effective ‘dupes’ that are priced for the masses. In 2024 alone, the brand was responsible for six of the year’s top 10 color cosmetics product launches, among them a $7 Camo Liquid Blush that took off on TikTok for being an effective substitute for a $23 Rare Beauty highly pigmented liquid blush. E.l.f. also democratizes beauty by working with mass market retailers. It has a widespread presence in drugstores, including CVS and Walgreens, and big box retailers Walmart and Target—both of which are turning over even more shelf space and display cases to E.l.f. in 2025. This November, the brand made its most aggressive move yet to find underserved beauty consumers: It launched in Dollar General stores, 80% of which are in rural markets with fewer than 20,000 people. These are places that have traditionally only had access to major legacy brands, that are in beauty deserts. All of this is aided by E.l.f.’s savvy approach to marketing. The brand had a breakout moment last year with its So Many Dicks campaign, which underscored the need for board diversity by highlighting the disproportionate number of Richards that hold board seats. The company also launched an entire music division to support its TikTok efforts. Its first act: dropping ‘Get Ready With Music, The Album,’ a collection of anthems that influencers and fans can use as a soundtrack for their GRWM videos. The company has had 24 consecutive quarters of net sales growth; for the nine months ended December 31, 2024, it grew revenue by 40% to $980.9 million. 5. Olive & JuneFor bringing the gel mani-pedi home Olive & June has been democratizing salon-quality nails, creating at-home polish solutions since 2019. This year, however, the DIY manicure company has raised even its own bar. After three years and 26 rounds of testing with more than 750 users, Olive & June unveiled its Gel Polish System in October 2024. It became the biggest launch day in Olive & June’s history, crushing its previous launch sales record by nearly 50%. If you’re thinking “press-on nails,” think again. And this isn’t just another gel kit, either. Designed to last up to 21 days, the system delivers salon-level shine that resists chips, lifts, and dullness—all without damaging your nails. The most impressive piece of this mani innovation isn’t the salon-quality LED light gel fixer or the silicone brush holder, but the Peel-Off Base Coat, a glycerin-rich barrier that makes removal idiot-proof, with no harsh acetone required. (For those who prefer a more traditional approach, the system also includes a salon-speed soak-off solution.) Priced at less than $2 per manicure, the system responds to a growing demand: 47% of gel users surveyed by Olive & June are now doing their nails at home more than in a salon. Available on Olive & June’s website and Target, the new gel mani, along with continued growth in overall sales—the company reported net sales revenue of approximately $92 million for 2024, led to an acquisition by Helen of Troy in December 2024 for $240 million. 6. RōzFor solving the aerosol dilemma when it comes to clean hairspray Founded by celebrity hairstylist Mara Roszak, Rōz is redefining haircare by blending professional-grade performance with clean, sustainable practices. Since its launch in 2021, the brand has built a reputation for creating intuitive, everyday products inspired by Roszak’s own kit (such as the popular Santa Lucia Styling Oil and Milk Hair Serum)—in eco-conscious packaging. Most products are delivered in easily recyclable aluminum and glass and offer refillable options whenever possible to help reduce waste. When plastic is necessary, the company ensures it contains at least 50% postconsumer recycled content, and all their paperboard packaging is FSC certified, promoting responsible forest management. Rōz outdid itself in the sustainability realm in 2024, with the release of the brand’s Root Lift Spray, a product that took three years to develop. It lifts hair at the root to give it volume, like many root sprays do, but the real innovation is its eco-valve and nitrogen propellant, which work together to deliver a consistent spray and precise application while allowing for twice as much formula per can compared to traditional aerosols, but without toxic VOCs or propellants that harm the environment and the ozone. Rōz’s focus on clean beauty hasn’t hindered its business growth. The brand expanded its retail footprint to 400 locations in 2024, including Nordstrom and Sephora, and more than 150 salons, up from just 40 salons in 2023. It also closed an oversubscribed seed round led by Silas Capital, with additional investment from notable celebrity backers like Lily Collins and Mila Kunis. 7. Delavie SciencesFor creating an anti-aging serum that’s out of this world In a discovery that sounds straight out of science fiction, NASA astronauts researched a resilient bacteria that survived on the outside of the International Space Station for 18 months, thriving despite exposure to harsh space radiation . When the organism was returned to Earth in 2022, researchers found that the bacteria had expressed genes to survive extreme conditions that are typically detrimental to any form of life. Newly launched company Delavie and its scientists saw the potential of these “extremophiles” and turned one of them into what they called bacillus lysate, the first biological cosmetic ingredient to be recognized as Certified Space Technology by the Space Foundation. Since its launch as the star ingredient in Delavie Sciences‘s Aeonia age-defying skincare line, this patented breakthrough has been shown to boost sunblock effectiveness, extending protection across UVA, UVB, HEV (blue light), and UVC rays. Dubbed an “SPF booster” for its ability to supercharge sunblock, bacillus lysate is not classified as sunscreen but delivers a new level of skin defense that includes reducing hyperpigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for melanin production, and lowering melanin levels. The organism is also a super-antioxidant that protects against UVA-induced free radicals, stimulates skin rejuvenation, and enhances moisture by increasing hyaluronic acid production by more than 200%. After just one use, Aeonia Age-Defying Serum showed improved radiance and hydration by 30%. The ingredient has been licensed for use in other beauty products. Delavie’s Aeonia line has expanded in the past to years to four total products, including the Aeonia Age Defying Serum, Aeonia Gentle Age Defying Serum, Aeonia Eye Refresh, and Aeonia Sculpting Cream, released in November. The brand will be debuting a sunscreen later this year. With a 61% revenue increase in 2024, Delavie is gearing up for a 155% revenue surge in 2025. It’s proof that highly effective skincare is sometimes of this world. 8. L’OréalFor making DIY hair color as easy as flipping a switch For decades, at-home hair coloring has been a messy, tricky process. Consumers often struggle with uneven application, stains, and difficulty reaching the back of the head. With 40% of women in the U.S. coloring their hair at home—and the global hair color sector estimated at nearly $27 billion—there was clearly demand for an easier, more efficient solution to covering those grays. Yet, despite the rise of DIY hair color, traditional kits often lead to inconsistent results, with 70% of users reporting dissatisfaction. So L’Oréal Groupe, a company with more than 100 years of experience in haircare, spent ten years developing Colorsonic, a revolutionary device designed to simplify at-home hair coloring. First unveiled at CES 2022 and released commercially in the summer of 2024 at Target, Colorsonic is a handheld, lightweight device that looks like a curling iron but uses leading-edge technology to mix and apply permanent hair color evenly, offering consumers a mess-free, precise solution to dying. The device’s custom mixer mechanism combines the exact amount of developer and formula in 20 shades, while its oscillating bristles move in a zigzag pattern to distribute color evenly across the hair. According to L’Oréal, Colorsonic covers 20,000 strands per minute, ensuring even results and 100% gray coverage in just five minutes. Plus, you can use it once for a full head and up to three times for root touch-ups without remixing the solution, making Colorsonic a practical, sustainable hair coloring option. No mess. No exploding bottles. No uneven color. Just easy DIY results. 9. ArcaeaFor harnessing the extinct past to create beauty products of the future What if your perfume could tell the story of an extinct world? The biotechnology company Arcaea, via its consumer brand Future Society, has turned that fantasy into reality. In 2023, the brand partnered with the Harvard Herbarium to access preserved specimens and sequenced DNA from the Shorea cuspidata, an ancient tree once thriving in Borneo, to create “Floating Forest.” Using cutting-edge bioengineering and the artistry of the world’s best perfumers, Arcaea resurrected the essence of this lost flora, blending science and artistry to craft a fragrance unlike anything on the market. And this ethereal perfume is more than just a high-end scent; it’s a step toward environmental responsibility. Partnering with the Borneo Project, Arcaea donates proceeds from the Floating Forest collection to support conservation efforts in Borneo, addressing habitat loss and promoting sustainable livelihoods, so there won’t be a need to make fragrances from the DNA of extinct plants in the future. In 2024, Future Society further advanced its goal to revolutionize the personal scent category by introducing the Optimal Habitat Fragrance Enhancing Primer. This groundbreaking product works with your skin’s unique biology to amplify a fragrance and extend its longevity for up to 24 hours, addressing common frustrations with fading scents. It does it by blending engineered ingredients that create the optimal skin pH for a fragrance of your choice to flourish for longer. The company is also currently working on a shampoo that “remembers” your hairstyle and sunscreen that strengthens your skin’s defenses against UV rays. With what the company reports to be the largest Series A funding in beauty history—thanks to infusions from big players in the beauty space like Chanel and Birchbox owner Viking Global Investors—and multiple patent applications across its technology platforms, Arcaea is proving that the beauty of the past can shape the future, one molecule at a time. 10. Bubble SkincareFor cracking the Gen Z beauty code with style and charm For Bubble, innovation isn’t just about skincare—it’s about staying in lockstep with Gen Z, a generation constantly rewriting the rules of self-expression. The modern, science-backed brand, which launched in 2020, has found success by listening closely to its 80k-plus “ambassador” community to craft skincare solutions that balance and hydrate young, vibrant skin. Every Bubble Skincare product, which is sold at behemoths like Ulta, Walmart, and CVS, undergoes a rigorous process: in-house formulation by an all-female product team, testing and oversight by the brand’s Dermatologist Advisory Board, and a thumbs-up from its community. If less than 90% approves, it’s back to the lab. But Bubble doesn’t stop at skincare. Its latest lip-care release, Juicy Secret, comes in the ultimate Gen Z accessory: purse charms that encase the beauty products, blending fun and function with customizable flair. And in fall 2024, Bubble followed its oldest Gen Z fans to college campuses with the “Face the Game Day” Tailgate Tour that lit up quads nationwide. The results? A 93% sales surge at Ulta stores, and 10 million unique impressions. With 3 million TikTok followers, Bubble is a brand that Gen Z refuses to outgrow. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article
-
The most innovative companies in automotive for 2025
You know the dream: electric vehicles that can drive straight from New York to Chicago without needing to top off the battery. Robotaxis at your beck and call. Amphibious cars. The promise of next-generation travel hasn’t fully materialized yet, but legions of companies around the world are focused on bringing the vision to life. This year’s list of the most innovative automotive companies recognizes both the upstarts and the incumbents advancing the next era in mobility. As the industry grapples with the larger questions of how to create viable solid-state batteries or commercialize robotaxi service, the companies listed here are focused on the incremental steps toward a fully autonomous future. The result is EV technology that makes the erstwhile novelty car more powerful, more affordable, and more ubiquitous. China’s largest car company, BYD, became the world’s second-biggest EV maker in 2024 due to the rollout of its ultra-affordable models such as the $11,000 Seagull as it grows its global footprint. Meanwhile, Southern California-based startup Rivian is disrupting the domestic EV industry with ultraefficient battery packs that can carry its pickup trucks and SUVs more than 400 miles on a full charge. Some companies, like Northbrook, Illinois-based UL Solutions, are focused on making batteries safer and more reliable, while others focus on what to do with the batteries once they reach the end of their life cycle. Mercedes-Benz, which returns to the list for the second consecutive year, became the first car manufacturer to close the loop with an in-house battery recycling plant in Kuppenheim, Germany. Of course, digital and connected features are becoming crucial to the user experience, and Nvidia, Qualcomm, and LG Electronics are racing to develop the computing power for faster processing and seamless service. But for now, keep your eyes peeled on the road for Waymo, which tops our list this year, as it rolls out commercial robotaxi service around the U.S. and possibly in a city near you. 1. WaymoFor making robotaxis part of the streetscape After 15 years, the original Google moonshot looks like it’s finally starting to reach escape velocity. Launched in 2009 as Google’s self-driving car unit, Waymo had its share of false starts before it began offering a limited version of its driverless ride-sharing service to customers in Phoenix in 2020. But in recent months, Waymo has emerged as the company ushering robotaxis out of the sci-fi realm and into reality. It’s paving the way for autonomous vehicles in five major U.S. cities, setting the bar for safety, transparency, and regulation for all other competitors, especially Tesla. And it’s making the general public comfortable with what now seems will be an inevitable part of the urban landscape. With wide-scale operations in San Francisco and Phoenix (and a limited rollout in Los Angeles), Waymo has been growing quickly—even with its emphasis on scaling responsibly. It is partnering with Uber and rolled out service in Austin in March, with plans to launch in Atlanta. Waymo also unveiled its Generation 6 automated driving system, an enhanced-technology suite designed handle tougher weather conditions. In October, the Waymo One taxi fleet reached 1 million autonomous miles driven. Waymo has made real what seemed unimaginable 15 years. It’s proven that Alphabet’s moonshot strategy can work. Read more about Waymo, honored as No. 1 on Fast Company’s list of the World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies of 2025. 2. BYDFor making EVs that are ultra-affordable, ultrafast, and even amphibious After almost 30 years as a battery supplier to mobile phone manufacturers, BYD has found explosive growth as an EV maker, catapulting over competitors to become a global juggernaut. The Warren Buffett-backed Chinese company shifted to building cars nearly two decades ago, applying its expertise in producing lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries to develop reliable, sub-$35,000 EVs. But the mid-2023 launch of BYD’s most affordable model—the four-figure Seagull compact car—ignited BYD’s exponential sales run. Boasting an all-electric range up to 252 miles, the Seagull became China’s top seller in August 2024 and solidified BYD’s status as the country’s largest automaker. But BYD isn’t focused only on affordability. Shipments of its first supercar, the $238,000 Yangwang U9, began in February. Today, BYD is running neck and neck with Tesla for the top spot among global EV makers and it is the undisputed champion of the plug-in hybrid sector, with 40% of that market. Last year, BYD delivered more than 3.8 million passenger vehicles in 2024—surpassing its full-year target of 3.6 million. The year also saw the company’s rapid expansion across Asia and into Mexico, South America, Europe, and Australia. In November, BYD produced its 10 millionth battery-powered vehicle, becoming the first automaker to reach that milestone, and announced a new Blade EV battery to power its future long-range EVs. The next-generation Blade technology is expected to increase driving range as well as battery life cycle. Whether BYD brings its cars to the U.S. is a question of geopolitics, but at least one top analyst says social media has helped spread the word among Gen Z and millennial shoppers, who are open to buying Chinese vehicles. “It’s only a matter of time before BYD is selling retail passenger vehicles in the U.S. market,” says Ed Kim, chief analyst at AutoPacific. “American consumers want them, and awareness of them is strong.” Read more about BYD, honored as No. 5 on Fast Company’s list of the World’s 50 Most Innovative Companies of 2025. 3. UL SolutionsFor developing cutting-edge automotive battery and energy storage testing EV batteries can catch fire or explode in the event of a collision, mechanical failure, or weather catastrophe, making battery safety crucial as more electric vehicles hit the road. Northbrook, Illinois-based safety science company UL Solutions has emerged as a key player in the space, conducting rigorous tests to determine how EV batteries handle a host of hazards, from thermal runaway to electric shock. The company launched an initial public offering in April 2024 at a roughly $7 billion valuation, and four months later, it opened a 90,000-square-foot advanced battery lab in Auburn Hills, Michigan. The company’s largest-ever laboratory investment puts performance and safety testing under one roof. The state-of-the-art lab is one of the most extensive electric and hybrid vehicle and industrial battery testing laboratories in the U.S., conducting electrical, mechanical, and environmental testing against standards and goals set by the International Electrotechnical Commission, United Nations, Society of Automotive Engineers, and others. The company grew revenue 7.2% to $2.9 billion in 2024, thanks to business from customers in more than 110 countries. It plans to construct a new Advanced Automotive and Battery Testing Center in South Korea to serve more customers across the Asia Pacific region and to add EV charger testing. 4. NvidiaFor powering the autonomous vehicle revolution Nvidia dominates the market for the semiconductors that power AI platforms in automotive and a range of other industries. Its GPUs are well-suited to the demands of AI model training, making Nvidia’s technology crucial to the creation and widespread adoption of self-driving cars. Top automakers from around the world (including BYD, Mercedes-Benz, Rivian, and Volvo) utilize the latest technologies from Nvidia (Drive AGX, Drive Orin, Drive Thor) to power their autonomous driving systems, and in early January 2024, Nvidia secured its pole position in the race to build better autonomous driving systems when it announced at CES that the world’s largest car manufacturer, Toyota, would be deploying its technology to build its next-generation vehicles. All this has put Nvidia on a tear, with revenue and market cap surging. In November, Nvidia replaced Intel on the Dow Jones Industrial Average. 5. Mercedes-BenzFor advancing battery chemistry and developing a recycling economy Mercedes-Benz is pulling ahead in the race to build a sophisticated battery economy. In October 2024, the automaker opened a state-of-the-art battery recycling factory in Kuppenheim, Germany. The factory—Europe’s first to house an integrated mechanical-hydrometallurgical process within a single plant—makes Mercedes the first automaker to close the ponderous battery recycling loop with its own in-house facility. Mercedes says the factory’s integrated process boasts a recovery rate of more than 96%, enabling a true circular economy of battery materials from old cars. The batteries come from test vehicles and production ramp-ups, as well as from returned vehicles from Mercedes-Benz. The plant will play a significant role in the battery life cycle, from shredding of battery modules to processing active battery materials to recovering scarce raw materials such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt. The downstream hydro-metallurgical process handles the “black mass,” the active materials that make up the electrodes of the battery cells. The factory, which began production in October 2024, is expected to generate enough material to produce more than 50,000 new battery modules annually. The knowledge gleaned from the project could help scale up production volumes in the medium- to long-term. Meanwhile, the automaker continues to roll out new EVs. In April, Mercedes-Benz launched an electric version of its rough-and-tumble G-Wagen truck, showing that electrification is possible for virtually any vehicle. 6. RivianFor disrupting the EV industry with ultraefficient battery packs It’s tough to start a car company. Just ask any of the fledgling EV companies that folded last year. The road has been rocky for Rivian, but the startup EV maker proved its staying power in June with the introduction of the second-generation R1S utility vehicle and R1T pickup truck. Together, the vehicles are challenging Tesla, General Motors, and other automakers thanks to their hearty, long-range power trains that are designed, engineered, and manufactured in-house. The second-generation battery packs offer up to 420 miles of range, while a new lithium iron phosphate-based battery pack can achieve an EPA-estimated 270 miles. Despite challenging sales, supply shortages, and layoffs, the company continues to plow ahead as a leader in the battery-electric sphere. In March, Rivian introduced a new midsize platform for smaller and more affordable vehicles, and followed that with the opening of its Rivian Adventure Network of DC fast chargers to all EVs. In October, the company announced that Volkswagen will invest $5.8 billion as part of a joint venture focused on developing vehicle software. In November, Rivian secured a $6.6 billion loan from the U.S. Department of Energy to revive its plans to build an EV factory in Stanton Springs, Georgia. 7. LG Vehicle SolutionFor bringing entertainment into the car LG is leading the lucrative race to bring entertainment into the car. In 2024, the South Korean juggernaut showed that it can adapt its expertise in consumer electronics for in-vehicle use, tailoring its user-friendly entertainment technology for automotive customers including Hyundai and Kia. In May, LG debuted a new infotainment platform with the launch of the Kia EV3 compact utility vehicle. The system brings LG Channels, an expansive network of entertainment, news and other content, into the car, eliminating complex app-based logins. The following month, the company rolled out its AlphaWare suite of customizable software to help automakers integrate advanced software and connectivity features across their lineups as seamlessly as possible. The comprehensive system addresses five key areas powering the vehicle, such as PlayWare for infotainment and VisionWare for safety. In November, LG presented its vision for the future of automotive interiors: a Digital Cockpit gamma featuring a 12.3-inch transparent OLED screen displaying real-time navigation, current speed, and points of interest, as well as a 14.2-inch retractable plastic OLED display embedded in the center console. A handy AI-based virtual assistant can detect driver fatigue, order a coffee from a shop nearby, and help you pay for the transaction through the screen’s built-in fingerprint-recognition sensor. 8. QualcommFor creating a scalable cloud-based platform for the automotive industry Qualcomm is expanding beyond mobile phones, transferring its expertise in chip technology to the automotive industry as cars become a new computing space. The system-on-chip technology that Qualcomm has honed for mobile phones is becoming crucial for the automotive industry as it evolves toward centralized computing. In October, the chipmaker announced a significant advance in automotive semiconductor technology with the launch of a scalable platform based on its fastest CPU. Qualcomm’s ultrafast Oryon CPU will power the latest version of its Snapdragon Digital Chassis, comprised of Snapdragon Cockpit Elite, which supports in-vehicle experiences like entertainment, and Snapdragon Ride Elite, which provides automated driving capabilities. The Snapdragon Digital Chassis can handle parallel AI workloads, such as processing data from multiple sensors and cameras to prevent a collision. It also allows different systems—such as infotainment and safety systems—to operate independently, which enables the car to process different types of data faster to make better-informed decisions. The cloud-connected platforms give customers like General Motors, Mercedes-Benz, Rivian, BMW, Ford, Honda, and Hyundai the flexibility to develop features such as customizable dashboards and over-the-air updates after the car has been purchased. In February, Qualcomm reported robust Q1 2025 growth, with automative bringing in $961 million, representing 61% year-over-year growth. 9. MichelinFor creating sustainable tires to support next-gen EVs Tires, perhaps the last part of a car to modernize, are finally undergoing a paradigm shift. Since 1960, cars have grown larger and heavier—increasing 21% in height, 14% in width, and 3% in length—putting more pressure on the tire, the humble component that supports the entire car. Now EVs, with their heavy batteries, are increasing weight by roughly 20%, an industrywide shift that necessitates more durable and more sustainable tires to support the extra heft. “Everything on electrification is pushing the market for bigger tires,” says Bruno de Feraudy, Michelin’s senior vice president of original equipment. Michelin’s Pilot Sport EV tires have been on the market since 2021, and at the 2024 Le Mans race in June, the company demonstrated a sustainable, track-oriented tire for the all-electric Porsche Cayman GT4 ePerformance race car. The motorsports tire at Le Mans is composed of 71% sustainable renewable and recycled raw materials, while the average tire uses 200 components that are difficult to recycle. These sustainable tires make greater use of rubber, recycled carbon black, oils such as sunflower oil and bio-sourced resins, silica from rice husks, and recycled steel. 10. Formula 1For pioneering the hybrid technology powering passenger cars Formula 1 has shot to the cultural forefront with the Netflix documentary Drive to Survive, now in its seventh season, but it’s also the world’s foremost test bed for the hybrid technology that trickles down into passenger cars. In June 2024, its governing body, the Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile (FIA), announced the racing series’s most ambitious plans for going carbon neutral. The regulations, which go into effect in 2026, call for each team to build a power unit that derives half its power from a V6 turbo engine and half from its battery and electric motor. FIA’s ever-changing regulations breed innovation by requiring teams to continually reengineer their cars and push technology to the limit. Each car competing in Formula 1, arguably the world’s most technically advanced sport, features thousands of sensors taking more than 1 million data points per second to optimize performance as the driver hurls the car up to 225 miles per hour. The sport has more eyes on it than ever, gaining momentum stateside with the recent addition of Grand Prix in Miami and Las Vegas. Explore the full 2025 list of Fast Company’s Most Innovative Companies, 609 organizations that are reshaping industries and culture. We’ve selected the companies making the biggest impact across 58 categories, including advertising, applied AI, biotech, retail, sustainability, and more. View the full article