Everything posted by ResidentialBusiness
-
Ring Pop’s new Pennsylvania factory will make 1.5 million lollipops a day—and Gen Alpha can’t get enough of them
When the Ring Pop factory in Scranton, Pennsylvania, unexpectedly shut down last summer because of a shaky floor, it abruptly halted production of tens of millions of the iconic oversized candy bauble lollipops that come attached to a cheap plastic ring meant to be worn on a finger. It was a shocking moment for an American candy brand whose enduring popularity spans at least five generations of consumers. “Everyone knows Ring Pop. All I have to do is put its shape in front of somebody and they know immediately what it is,” says Tony Jacobs, CEO of Ring Pop maker, Bazooka Candy Brands. After seven months, a new Ring Pop factory opened in Pennsylvania in March. New York-based Bazooka Candy Brands is doubling down on not only quickly closing the supply gap for Ring Pops triggered by the shuttered plant but has also set ambitious new production targets for the candy. “We should be able to fill up the pipeline by June,” Jacob says, adding that the new factory is expected to churn out nearly double the amount of Ring Pops made annually. Shut everything down Since 1977, the stickless lollipop has been made in a 30,000-square-foot plant in Scranton that cranked out as many as 280 million Ring Pops annually. A novelty confectionery, and among the most recognized hard candy brands in the market, Ring Pop has captivated generations of sweet treat seekers—from Gen Xers to Gen Alpha—for decades. Ring Pop, which sells for under $1 to about $1.50 a piece, was consistently growing sales over the last decade, with year-over-year brand sales up 7% at the end of last year. “That number doesn’t even fully include our ecommerce sales,” Jacobs says. On August 29, 2024, everything came to a grinding halt, except the ground beneath the Ring Pop’s Scranton plant. “I remember that day very clearly,” says Jacobs. “We’ve had movement in the ground under our factory and the floor had become unstable. It’s no secret that Scranton has a lot of mines and there are mine shafts under our factory. We decided we had to shut everything down until we knew exactly what was going on.” Jacobs says that it was a tough decision, “knowing the impact it would have on the company and the brand.” “In a lot of ways, Ring Pop is our flagship product. But it was also an easy decision because it was a question about safety,” he says. But the factory closure also created a supply crunch that slowed down Ring Pop’s momentum. “I can tell you right now that it’s been painful not having a facility.” “Historically, we have outstripped the candy confectionery sales growth for our brands by how we innovate and market our candy products,” says Jacobs. “Right now, we’re not outpacing the category because we haven’t had supply.” According to the National Confectioners Association, total confectionery sales in the U.S. reached $54 billion in 2024. A little over half of sales were driven by purchases of chocolate products (52%) and 40% by candy (excluding gum). In 2024, overall chocolate sales reached $28.1 billion, up from $25.9 billion in 2023, while non-chocolate candy sales reached $21.7 billion last year, up from $19.2 billion in 2023. ‘We’re about edible entertainment’ With Ring Pop, especially, both the brand and consumers—including a few celebrities like Drake, Joe Jonas, and Sophie Turner—have leaned into its quirkiness to create viral moments in a way that’s given the affordable lollipop a multi-generation appeal. “Everything that we do is around not just hand-to-mouth candy. There’s a lot of great candy out there, but we’re about ‘edible entertainment,’” Jacobs says. “That’s play value, and viral value that really helps define our portfolio of candy brands.” “To have a product that’s been around for 48 years, that’s over the top, that people want to engage with and talk about, and it’s become a kind of social currency, is even more important,” he says. “We see Ring Pop packs at kids’ birthday parties and at bridal showers.” Bazooka Candy Brands’s other candy products include Push Pop, Juicy Pop, Bazooka Bubble Gum, and Baby Bottle Pop candy. Another current market trend in Ring Pop’s favor is that, “a younger demographic, Gen Z and Millennials, are a little bit more interested in non-chocolate options. It’s just their taste and preference,” said Christopher Gindlesperger, spokesperson with the National Confectioners Associations. A prime example of that is the explosion in popularity of squishy, chewy gummy candies. Last year, peelable gummy candies went viral and retailers scrambled to source and stock them after TikTokers couldn’t get enough of tiny mango-shaped gummy candies that you could, indeed, peel like a real mango fruit to reveal an inner gummy pulp candy and an edible gummy outer peel. Bazooka Brands says for Ring Pop, its biggest fans currently are even younger. They’re Gen Alpha. “While we don’t have exact figures on the breakdown of Ring Pop purchasers by generation, we do know that the brand over-indexes with households that have kids ages six to 12, making Gen Alpha the primary consumers,” says Becky Silberfarb, the company’s vice president of brand marketing for the Americas. Jacobs expects Ring Pop to fully close its supply gap and reestablish its brand dominance in the market within six months. The comeback plan begins with a move into the new factory. The company last week inaugurated a 120,000-square-foot factory in Moosic, Pennsylvania, about seven miles from the Scranton plant. The new plant, with just over 100 employees, will produce up to 1.5 million Ring Pops a day. “Our business has been growing. We need more manufacturing and more product,” says Jacobs. “Once we have our full production lines up and running efficiently, we should be getting close to 400 million Ring Pops made annually out of the new facility,” he says. View the full article
-
How working parents can maximize their tax refund
With tax season fast approaching, it’s the perfect time for parents to take advantage of valuable tax deductions and credits that can reduce their tax bill or increase their refund. Lisa Greene-Lewis, a tax expert with over 20 years of experience, has made it her mission to break down complex tax laws in a way that’s accessible and actionable for families. As a trusted voice in the industry—featured on programs like The Ellen Show and The Steve Harvey Show—Lisa shares her insights on the most important tax breaks parents should know about. This conversation has been edited and condensed for clarity. What are the top tax breaks parents should take advantage of before filing? Navigating tax season as a parent can feel overwhelming, but there are several valuable tax deductions and credits designed to ease the financial burden of raising children. Understanding these benefits can help you maximize your refund and keep more money in your pocket. One of the most well-known tax benefits for parents is the Child Tax Credit, which provides up to $2,000 per child under the age of 17. Even if you don’t owe taxes, you may still be eligible for a refundable portion of up to $1,700. For parents who rely on childcare to work or search for a job, the Child and Dependent Care Credit can help offset costs. You can claim up to $1,050 for one child or up to $2,100 for two or more children under 13. Even summer day camps and sports camps qualify—though overnight camps do not. If your child has a disability, there is no age limit for this credit. If you’re working and earning an income, you may also qualify for the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), which can provide a significant boost to your refund. The amount depends on your income and number of children, with families of three or more kids eligible for up to $7,830 in 2024. Many eligible taxpayers miss out on this benefit, so it’s important to check if you qualify. For parents with college-aged children, there are additional tax credits to help with higher education costs. The American Opportunity Tax Credit offers up to $2,500 per dependent child for the first four years of college, if they are pursuing a degree and enrolled at least half-time. If your child is taking courses beyond the first four years of college—whether for a degree or simply to improve job skills—you may still qualify for the Lifetime Learning Credit, which provides up to $2,000 per return. Additionally, if you’re paying student loan interest for your child, you may be able to deduct up to $2,000 per tax return. It’s important to note that only the person claiming the child as a dependent can take advantage of these education-related tax benefits. If your child files their own taxes and claims these credits, you won’t be able to do so. A conversation between parents and students is key to determining who should claim these benefits. Finally, if you are a single parent who provides more than half of your household’s financial support, filing as Head of Household can increase your standard deduction to $21,900—significantly higher than the $14,600 deduction for those filing as single. Make sure to review your eligibility each year and consult a tax professional if needed to ensure you’re maximizing your benefits. Are there any last-minute moves families can make to lower their taxable income or increase their refund? First, gather all your documents in one place before you begin—this helps ensure you don’t overlook any important deductions or credits. One surprisingly common mistake is entering incorrect Social Security numbers, so double-check that you have the accurate numbers for yourself and any dependents. This is especially important for claiming valuable tax benefits like the Child Tax Credit, Earned Income Tax Credit, and the Child and Dependent Care Credit. Don’t forget about opportunities to reduce your taxable income. You can still make a 2024 contribution to your IRA—up to $7,000 (or $8,000 if you’re 50 or older)—until the April 15 deadline, and you may be able to deduct these contributions. Similarly, if you have a High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP), you can contribute up to $4,150 to a Health Savings Account (HSA) if you’re on a self-only plan, or up to $8,300 for a family plan, with potential tax deductions available. What steps should families take now to prepare for next year’s tax season? One of the most effective is maximizing contributions to a 401(k) plan. In 2025, you can contribute up to $23,500—or $30,500 if you’re 50 or older. Plus, thanks to the Secure Act 2.0, individuals aged 60 to 63 can contribute even more, up to $34,750. Not only do these contributions lower your taxable income, but they may also make you eligible for the Retirement Savings Contribution Credit, which offers up to $1,000 for single filers and up to $2,000 for those married filing jointly. This credit is essentially free money for prioritizing your retirement savings. Beyond retirement planning, parents can also find tax savings in everyday expenses. Keeping receipts for qualifying expenses—such as sending your child to summer camp—can help maximize available deductions or credits. Additionally, if you’re able to itemize your deductions, now is a great time to declutter and donate to a 501(c)(3) charitable organization. These donations can be deducted, offering financial benefits while supporting causes you care about. View the full article
-
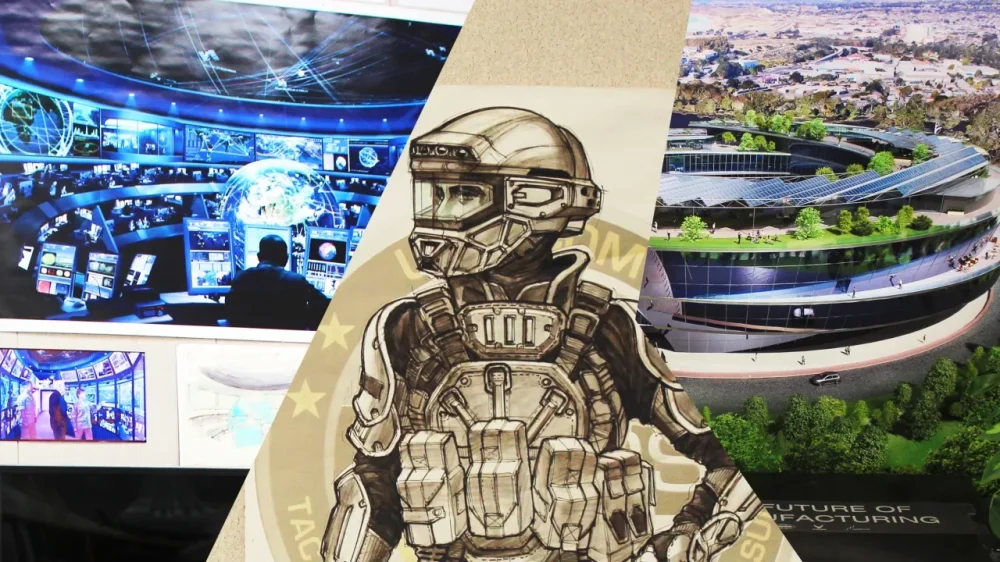
How this former Disney Imagineer is shaping the next generation of defense technology
The way Bran Ferren sees it, the future of warfare depends as much on creativity as it does on raw firepower. The former head of research and development at Walt Disney Imagineering—the elite R&D arm responsible for the entertainment empire’s “secret sauce”—the 72-year-old Ferren has spent decades building a reputation for fusing art, design, and storytelling with serious technical and engineering know-how in pursuit of novel innovations and experiences. This pioneering approach to “creative technology” is the heart and soul of Applied Minds, the company Ferren cofounded 25 years ago to help clients from the Pentagon to Fortune 500 companies envision and test breakthrough technologies before they even realize they need them, from rapidly prototyping advanced robotics and vehicles to designing futuristic command centers and immersive simulators. If you can imagine it, chances are the artists and engineers at Applied Minds can make it a reality. Now, with the United States gearing up for its next big war, Ferren and Applied Minds’s unique brand of prototyping has never been more important. In a defense sector often constrained by bureaucracy and incremental improvements, the company’s ability to think outside conventional silos and pull insights from unexpected fields—whether theme park design, Hollywood special effects, or commercial tech—offers a much-needed jolt of creative problem-solving and gives Applied Minds an edge in a defense landscape that increasingly demands speed and creativity over incremental improvements. “We’ve turned into, for lack of a better word, an imagineering resource for hire,” says Ferren in a recent interview with Fast Company. The son of two artists, Ferren grew up “surrounded by people doing art and technology,” whether it was uncle Roy Ferren, the director of flight test for North American Aviation (now part of Boeing), or uncle Stanley Tonkel, the prolific Columbia Records recording engineer who helped produce tracks for famous musicians from Miles Davis to Frank Sinatra. Ferren’s early career encompasses a constellation of creative endeavors. In the 1970s and 1980s, he cofounded Associates & Ferren, a design and special effects firm that quickly rose to prominence for its work in film, theater, and high-tech installations. The company contributed to several Hollywood productions, providing innovative visual effects for movies including Altered States (1980), Little Shop of Horrors (1986), and Star Trek V: The Final Frontier (1989), as well as special effects for Broadway plays like the Sherlock Holmes mystery The Crucifer of Blood and major concert performances by Paul McCartney, Pink Floyd, R.E.M., and Depeche Mode, among others. Ferren distinguished himself by marrying the theatrical and the technological; among his more unusual projects includes orchestrating a nationwide tour of the Bill of Rights to mark the bicentennial of the document, a task that involved designing and building a special transportation vehicle from the ground up to house the fragile artifact as well as a traveling exhibit space to accompany it. “I really love doing new things that I’ve never done before and that other people haven’t done before . . . theater, film, rock ’n’ roll touring. These were all early venues where you had the opportunity to do that,” Ferren says. His expertise in blending technology with storytelling caught the attention of Disney, leading to the acquisition of his company in 1993 and his installation as head of R&D at Walt Disney Imagineering, which is responsible for master planning all of the company’s far-reaching creative endeavors, including theme parks. “Theme parks are story driven,” Ferren says. “It’s about bringing you into those stories.” Ferren’s group was also responsible for prototyping and demonstrating next-generation products for Disney executives to provide insight into the technological trends shaping the entertainment industry, including desktop gaming consoles, ebooks, and on-demand digital video delivery. Ferren likens the role of Imagineering at Disney as “the defined job of what ARPA or DARPA is for the defense community,” which is “to prevent surprise,” he explains. “Imagineering was my home, but also from my perspective, my job was: How do I help bridge between different worlds, such as Silicon Valley and such as Hollywood, who often have very compatible goals, but speak different languages?” he adds. Always in search of the next big thing, Ferren left Disney in 2000 to cofound Applied Minds with computer scientist Danny Hillis, whom Ferren had previously recruited to Disney as a fellow in 1996, and entrepreneur Doug Carlston. Since then, the company has worked with major players across virtually every industry you can think of, from automakers General Motors and Ford and agricultural giant John Deere to geographic information systems pioneer Esri and defense primes like Boeing, as well as every branch of the U.S. armed forces. (The company declined to share the total value of its contracts but stated that it’s roughly an even split between military commercial clients). In the process, Applied Minds has notched more than 1,000 patents that encompass everything from full-color and enhanced 3D night vision devices, customizable instrument control panels, immersive display environments, centralized controls for autonomous vehicles, modular vehicles, and even portable systems for communicating underground—the latter of which is of particular interest to the U.S. military ahead of a future conflict. Applied Minds made a splash from the get-go. In what might be the company’s most significant early innovation, Ferren and Hillis would end up playing a pivotal role in the development of “pinch-to-zoom” technology, the now-ubiquitous multi-touch gesture interface used on smartphones, tablets, and other touchscreen-based devices. (The pair’s 2005 patent was at the center of a high-profile 2013 lawsuit which saw consumer electronics juggernaut Apple accuse competitor Samsung of infringing on its own patents, including pinch-to-zoom, which the former had popularized with the launch of the iPhone in 2007; Apple’s lawsuit was invalidated based on Ferren and Hillis’s existing claim to the technology.) Applied Minds also established deep roots in the defense world. Among its most notable projects are the Photographic Landing Augmentation System for Helicopters (PHLASH), developed in 2007 to help prevent brownouts during dicey helicopter landings in the deserts of the Global War on Terror, and the U.S. Army’s Expeditionary Lab, a mobile workplace designed to help soldiers engineer technical fixes on the fly while deployed overseas. The company has provided the Pentagon with prototypes for advanced combat vehicles, sophisticated cockpit interfaces for the military’s upcoming sixth-generation fighter jets, next-generation workstations to streamline operations, immersive simulators to improve training, and new approaches to data visualization that look like they’re ripped straight out of a science fiction movie; it even participated in the Pentagon’s ill-fated effort to build a real-world “Iron Man suit” to protect troops engaged in high-intensity combat. Among Applied Minds’s latest victories is a critical fix for the U.S. Air Force’s next-generation KC-46 Pegasus tanker, considered a critical aerial refueling capability for extending the range of tactical and transport aircraft amid a high-intensity future conflict. Unlike traditional tankers, which feature a boom operator positioned at the tail with a direct line of sight of a target aircraft for the delicate dance of lining up the refueling boom, the KC-46 instead transmits digital imagery from the so-called Remote Vision System (RVS) to operators at a high-tech Aerial Refueling Operator Station nestled in the body of the aircraft. But initial testing had revealed that the RVS feed was marred by image distortion, inconsistent lighting, and depth perception issues that made it consistently unreliable during refueling operations. Without an accurate picture of the outside world to work from, operators simply can’t do their job, rendering the KC-46’s core mission of keeping other aircraft fueled and ready to fight effectively moot. At the behest of Boeing, the prime defense contractor on the system, Applied Minds eventually rolled out a fix in the form of the RVS 2.0, which features enhanced cameras and a full-color high-definition display to improve depth perception and counteract glare and shadow. “Now, you’d say, ‘Clearly the U.S. Air Force Research Lab and Boeing and Rockwell Collins were working on this, they don’t need a few more engineers and computer scientists to solve things. . . . Why would we have expertise in this?’” Ferren says. “It’s because we actually come from the film business, so some of us have expertise on how you make good looking images.” Bran Ferren While Applied Minds operates in the defense technology space, it doesn’t function like a traditional defense contractor. Instead of competing for massive military contracts or manufacturing hardware at scale, the company has positioned itself as an elite think tank and prototyping powerhouse, working on a project-by-project basis and helping organizations rapidly develop creative solutions to complex technical challenges. This approach allows the company to remain agile, moving between industries while maintaining a small, highly specialized team of engineers, designers, and technologists. Indeed, those skills Ferren honed as head of R&D at Disney Imagineering—architecting immersive, intuitive experiences—translate surprisingly well to a military context. To wit: One of the Applied Minds’s specialties is the development of military command centers, those high-intensity spaces where critical information and life-or-death choices collide. The company has designed installations including the U.S. European Command (EUCOM) Command Center in Stuttgart, Germany; and the U.S. Air Force (now U.S. Space Force) Joint Space Operations Center at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California; in 2023, the Naval Postgraduate School Foundation contracted the company to help develop its Naval Innovation Center to serve as a central node for R&D for the Navy and Marine Corps. As it turns out, designing a cutting-edge military operations center isn’t so different from creating an immersive theme park attraction for Disney: You’re shaping the user experience, guiding decision-making, and ensuring everything works intuitively under pressure And it’s not just the military interested in building such spaces: Fast Company has learned that Applied Minds is currently engaged in work to design a Monitoring, Analysis, Restoration Center (MARC) for Virginia-based energy company Dominion Energy to help deal with extreme weather events and a “customer engagement center” for Amazon Kuiper Government Solutions, the tech subsidiary focused on boosting broadband connectivity through a sprawling satellite constellation in orbit. But these command centers aren’t just about functional utility, but creating environments that are themselves conducive to collaboration and innovation. After all, the company’s core philosophy is focused on helping other organizations “develop creative concepts to solve problems,” as Ferren puts it—which, in turn, means helping other organizations become more organically innovative themselves. Applied Minds doesn’t just exist to build cool shit, but to empower organizations traditionally stymied by their own institutional limits (like, say, rigid R&D pipelines and other bureaucratic hurdles) to embrace creative technology and foster their own long-term innovation ecosystem. “The throughline is storytelling and how you do it in different forms: how is that an enabler to a whole variety of other innovations in technology, in organizations, and such?” Ferren says. “And then how do you create both virtual and dimensional spaces that are capable of doing that better. I mean, the story is the play. The theater is the venue when both of them work.” Nearly a decade after the Air Force first discovered issues with the RVS, the system is still proving a headache for the service: As of March 2024, the second iteration of the system was still behind schedule due to unspecified “supply chain issues” among various Boeing subcontractors, according to Defense News. But to Ferren, the project was particularly illustrative of Applied Minds’s vision: to develop fresh solutions to serious challenges through the careful marriage of creativity and technology. “This was a technically hard problem, but it didn’t require a brute force technical solution,” It required a different way of doing it, and so we were able to come in orthogonally,” Ferren says of the RVS 2.0 project. “So rather than being focused on what the technical requirements are in the details, we come in and say, ‘You know, there are different techniques that can be used to do this.’ And we built proof of concepts, and we’re able to demonstrate it for them.” Applied Minds’s unique blend of storytelling, design, and engineering has positioned the company as an indispensable force in the future of national security. And in an era of rapidly evolving threats, the U.S. military appears increasingly inclined to rely on tech outfits who understand both the art and science of problem-solving, who can take inspiration from theme parks and film production as readily as they can from aerospace engineering to find novel solutions to the most pressing challenges facing the nation. Ferren and his team have spent decades proving that the best solutions often come from unexpected places. As the challenges of modern warfare grow increasingly complex, so too does the need for Applied Minds’s brand of creative innovation. If the future of defense belongs to those who can imagine—and build—the impossible, then Applied Minds is already leading the way. View the full article
-
6 big mistakes job seekers commonly make
If you have been on the job market recently, you know how challenging it can be. Lots of tech companies, for example, are pulling back on hiring. Federal workers are being laid off by the thousands. And some types of jobs are simply not as available as they once were. Particularly in short supply are those prized white-collar positions paying $94,000 or more. So, any serious job seeker must sharpen their skills to land a job. You can increase the likelihood of a successful search by avoiding the following six big job search mistakes: Mistake No. 1: Applying for too many jobs The first mistake is applying for too many jobs and, as a result, not giving enough time to any one application. Some individuals send in applications for 100, 200, or even 400 jobs. That is far too many. Statistics reveal that job seekers who apply for 21 to 80 jobs have about a 30% chance of receiving a job offer, while candidates who apply for more than 81 jobs have only a 20% chance of receiving an offer. More applications typically get worse results. To get that next big job, focus on applications where you’re a decent fit, and give more attention to each one. Mistake No. 2: not customizing your résumé The second (and very common) mistake is sending every company the same generic résumé. Contrary to popular belief, most hiring companies do scrutinize résumés. After the interview, it’s the second-most-important vehicle for assessing a candidate. Providing boilerplate won’t often get you the job. Focus your work history and the bullet points under each job you’ve held. Align this material with the job you’re applying for. For example, don’t put down that you “optimized supply chain operations” if you are applying for a leadership role. Instead, say you “led a supply chain team.” Avoid jargon and technical language that might be misunderstood. Be sure to include only relevant work experience. If you have waited on tables at your university or worked in a donut shop, leave it out unless you’re applying for a service- or people-focused job. Mistake No. 3: Not tapping into your network A third job search mistake is overlooking your network. A LinkedIn study shows that 70% of job seekers get their jobs through successful networking. Don’t go it alone. Ask those you know for leads and introductions. Successful networking is usually a multistep process. “Most of the time, success is not through your first-degree network but through your second- or third-degree network,” writes career coach Sarah Felice on LinkedIn. “This means you have to have a lot of conversations, coffee meetups, Zoom meetings, and phone calls.” If you are interested in a position in a particular industry, approach an acquaintance who is knowledgeable about that field. Ask them to connect you to relevant people. If you’re interested in moving up within your company, do your research and find out which department head you should talk to. Introduce yourself with a well-written letter. Such steps may take time, but they will be much more likely to get results. Mistake No. 4: Poor interview prep To ace the interview, you’ve got to research the company and the job, prepare a script to guide you, and develop answers to possible questions. The knowledge you gain as you prepare will enable you to align your background with the company’s culture and the job. It will also help you ask intelligent questions and show that you take the company and the job seriously. An interview script will provide an all-important guide for you. It doesn’t have to be memorized or delivered verbatim. It simply will remind you how you want to open the conversation, what your message is, how you are going to develop your message, and how you will close the conversation. Without a script to guide you, you won’t come across as clear-minded and confident. (For more discussion of how and why to prepare a script for your job interviews, see my book, The Job Seekers Script.) Mistake No. 5: Using weak language Be mindful of the words you use throughout the interview process. Eliminate anything that has negative overtones. That includes phrases like “I can’t,” “I don’t,” “I’m not sure,” or “I don’t know.” Eliminate filler words like um, ah, and you know. Avoid overly casual speech like “You guys.” And don’t judge the questions by saying things like, “That’s a good question.” You’re there to answer questions, not evaluate them. Apologetic language, such as “I’m sorry,” also tests poorly. You may think you are being thoughtful when you apologize, but doing so can make you sound weak. Mistake No. 6: Not following up The final job search mistake to avoid is not following up after your interview or a conversation with someone you networked with. Write a note of thanks—an email or an actual written note—and do so promptly. People appreciate that thoughtfulness, and often it will make all the difference if someone is deliberating about hiring you. View the full article
-
How Helsinki ditched coal in just 2 years
A few years ago, if you turned on the heat in an apartment in Helsinki, the energy typically came from coal. But the city’s power company shut down one coal plant in 2023, and the remaining one closed this week—four years earlier than a target set by the national government. “Within two years, we have completely phased out coal,” says Olli Sirkka, CEO of Helen, the power company, which is a subsidiary of the city. The city has one of the world’s biggest district heating systems, with a network of underground pipes filled with hot water that deliver heat to buildings. It takes a huge amount of energy to run. One large chunk of that now comes from wind power, which has more than doubled in Finland since 2020. Helsinki is now building the world’s largest heat pump, which will send heat to 30,000 homes when it starts running in 2026. At the site of one of the closed coal plants, the city is also building a new facility that will capture heat from the Baltic Sea. Some of the energy also now comes from wood pellets, which Helsinki is using temporarily as it transitions completely away from combustion. (Wood helped replace natural gas from Russia after the invasion of Ukraine, but isn’t a good long-term solution. Burning it still produces CO2, it puts pressure on forests, and it’s more expensive than other alternatives; Finland plans to phase it out completely by 2040.) Helsinki also uses some hydro and nuclear power, and as much waste heat as possible. That includes capturing heat from local data centers and wastewater. Though the coal plants shut down quickly, the push to close them started more than a decade ago. In 2015, a campaign called Coal Free Helsinki convinced the city council to commit to closing the first coal plant. “I think activists played a really big role,” says Amanda Pasanen, who previously studied the coal phaseout and is now a city councilmember. “It was very much due to public pressure that they decided to quit coal burning.” At that point, it still wasn’t clear how it could happen. “Then, it was considered a completely impossible goal,” says Sirkka. “It was only maybe four years ago there was a solid decision that this has to happen. And then it started to roll really, really fast.” The steep drop in the cost of wind power, thanks to technological advancements and scaled-up production, was key. “Wind power decreased electricity prices so much that it’s actually a very good business case to replace coal with electricity,” he says. On the day we talked, it was windy enough that electricity prices in Finland had dropped to zero. (Finland is a fairly windy place and well suited for the technology; while it also has some solar power, it’s so far north that it isn’t sunny in the winter, and solar can’t really be used to power heating.) The power company continually monitors energy sources, shifting from one source to another to optimize costs. The city’s layout, with the district heating system, helped make the switch easier than if every single building had to be retrofitted with different technology. “It’s easier to implement these environment-friendly solutions in a centralized system where you have district heating and where you can use your economies of scale,” says Helsinki Mayor Juhana Vartiainen. Other factors also pushed the company to act quickly. The EU’s emissions trading system increased the price of coal as carbon prices rose over time. In 2019, Finland passed a national law to phase out coal by 2029 as part of its climate plan. Changes in national tax policy made coal more expensive and clean power cheaper. In 2021, Helsinki decided to speed up its own plan to become carbon neutral, moving the target date from 2035 to 2030. “There is broad political consensus on the issue [of climate action],” says Vartiainen, noting that when he took office in 2021, there was nearly unanimous agreement that Helsinki should move faster on its already-ambitious plans to cut emissions. Yet even with that political mandate, it wasn’t guaranteed that the change would happen quite as quickly as it did. “It’s been quite surprising,” Vartiainen says, “to see how fast this shift to electricity has taken place.” View the full article
-
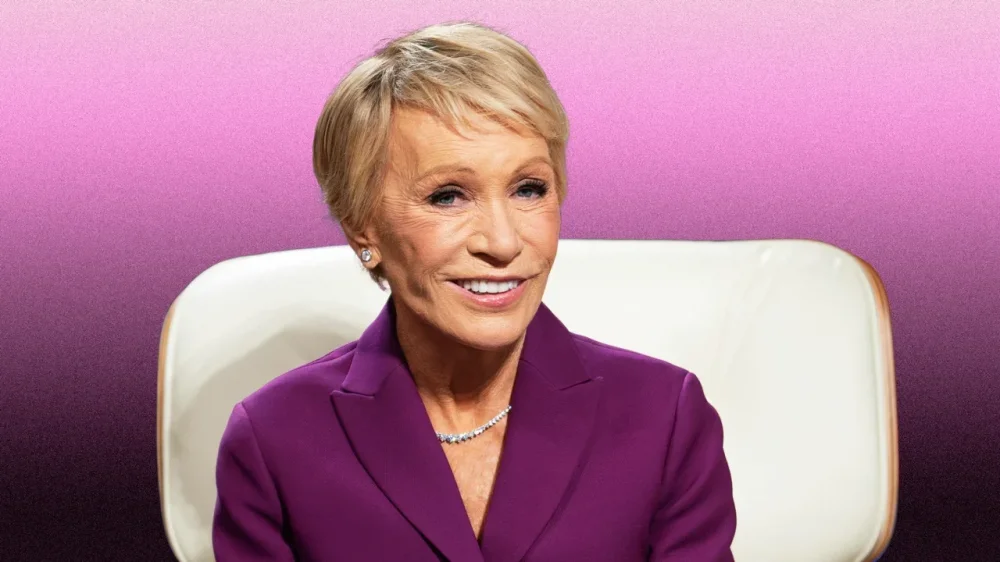
Barbara Corcoran’s unconventional financial advice rejects the idea of ‘saving for the future’
Barbara Corcoran is one of Shark Tank’s longest-running sharks, with an estimated net worth of approximately $100 million. But she’s also one of 10 kids from a working-class family. By age 23, she’d held more than 20 jobs. By 52, she sold her real estate company for $66 million. Corcoran knows how to build wealth. Her financial strategies are bold and unconventional. They buck traditional financial wisdom and—full disclosure—they can be also risky. But could they help you build wealth? 1. Don’t Bother Saving Money “I’ve never saved a dime my whole life,” Corcoran told CNBC Make It in 2023. Rather than letting her money sit idly in a bank account, Corcoran immediately identifies the best way to spend anything she earns, often investing it into something with the potential to grow her wealth. Of course, investing all your earnings is risky. No one knows when an unexpected expense or income loss is coming and you’ll need to live on your savings. But consider the root of Corcoran’s advice: How much money can you safely risk investing in yourself or a business venture you believe in? How much money could you reasonably put into a stock or other fund with the potential to grow at a higher rate than your savings account? 2. Be The Highest Bidder—On Valuable Assets “I am always willing to overspend on any property that’s good,” Corcoran said in an interview. Overspending on anything might sound counterintuitive, but Corcoran is specifically referencing quality assets with high growth potential. Corcoran especially believes in using this principle for real estate investments. She says that if you’re willing to spend more than anyone else on a property you know is quality and be patient, you will eventually make that extra money back and then some. 3. Put All Your Eggs in One Basket “One piece of advice people hear all the time, and I just don’t believe it, is ‘Diversify. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket,’” Corcoran told CNBC Make It. Diversification is investing in different areas so you don’t lose everything from a downturn in one area of the economy. In Spring 2025, you might hesitate to even put all your literal eggs in one basket, but Corcoran’s advice here is about investing in areas where you have expertise rather than diversifying just for the sake of it. Corcoran has historically focused all her money in real estate, where she can constantly leverage her knowledge and experience to evaluate current and potential investments. Corcoran isn’t alone in this view. Warren Buffett famously called diversification “protection against ignorance.” His late Berkshire Hathaway cochair Charlie Munger also referred to the practice as “diworsification.” Both investors made billions by focusing their investments in industries where they were already experts. Focused investments can lead to outsize returns—but also outsize losses, so the expertise piece of Corcoran’s advice is vital. Don’t just toss all your money into one thing you don’t understand,” she said. “Stick to what you know.” View the full article
-
How AI is steering the media toward a ‘close enough’ standard
The nonstop cavalcade of announcements in the AI world has created a kind of reality distortion field. There is so much buzz, and even more money, circulating in the industry that it feels almost sacrilegious to doubt that AI will make good on its promises to change the world. Deep research can do 1% of all knowledge work! Soon the internet will be designed for agents! Infinite Ghibli! And then you remember AI screws things up. All. The. Time. Hallucinations—when a large language model essentially spits out information created out of whole cloth—have been an issue for generative AI since its inception. And they are doggedly persistent: Despite advances in model size and sophistication, serious errors still occur, even in so-called advanced reasoning or thinking models. Hallucinations appear to be inherent to generative technology, a by-product of AI’s seemingly magical quality of creating new content out of thin air. They’re both a feature and a bug at the same time. In journalism, accuracy isn’t optional—and that’s exactly where AI stumbles. Just ask Bloomberg, which has already hit turbulence with its AI-generated summaries. The outlet began publishing AI-generated bullet points for some news stories back in January this year, and it’s already had to correct more than 30 of them, according to The New York Times. The intern that just doesn’t get it AI is occasionally described as an incredibly productive intern, since it knows pretty much everything and has superhuman ability to create content. But if you had to issue 30-plus corrections for an intern’s work in three months, you’d probably tell that intern to start looking at a different career path. Bloomberg is hardly the first publication to run head-first into hallucinations. But the fact that the problem is still happening, more than two years after ChatGPT debuted, pinpoints a primary tension when AI is applied to media: To create novel audience experiences at scale, you need to let the generative technology create content on the fly. But because AI often gets things wrong, you also need to check its output with “humans in the loop.” You can’t do both. The typical approach thus far is to slap a disclaimer onto the content. The Washington Post’s Ask the Post AI is a good example, warning users that the feature is an “experiment” and encouraging users to “Please verify by consulting the provided articles.” Many other publications have similar disclaimers. It’s a strange world where a media company introduces a new feature with a label that effectively says, “You can’t rely on this.” Providing accurate information isn’t a secondary feature of journalism—it’s the whole point. This contradiction is one of the strangest manifestations of the application of AI in media. Moving to a “close enough” world How did this happen? Arguably, media companies were forced into it. When ChatGPT and other large language models first began summarizing content, we were so blown away by their mastery of language that we weren’t as concerned about the fine print: “ChatGPT can make mistakes. Check important info.” And it turns out that for most users that was good enough. Even though generative AI often gets facts wrong, chatbots have seen explosive user growth. “Close enough” appears to be what the world is settling on. It’s not a standard anyone sought out, but the media is slowly adopting it as more publications launch generative experiences with similar disclaimers. There’s an “If you can’t beat ’em, join ’em” aspect to this, certainly: As more people turn to AI search engines and chatbots for information, media companies feel pressure to either sign licensing deals to have their content included, or match those AI experiences with their own chatbots. Accuracy? There’s a disclaimer for that. One notable holdout, however, is the BBC. So far, the BBC hasn’t signed any deals with AI companies, and it’s been a leader in pointing out the inaccuracies that AI portals create, publishing its own research on the topic earlier this year. It was also the BBC that ultimately convinced Apple to dial back its shoddy notification summaries on the iPhone, which were garbling news to the point of making up entirely false narratives. In a world where it’s looking increasingly fashionable for media companies to take licensing money, the BBC is architecting a more proactive approach. Somewhere along the way—whether out of financial self-interest or falling into Big Tech’s reality distortion field—many media companies began to buy into the idea that hallucinations were either not that big a problem or something that will inevitably be solved. After all, “Today is the worst this technology will ever be.” Think of pollution and coal plants. It’s an ugly side effect, but one that doesn’t stop the business from thriving. That’s how hallucinations function in AI: clearly flawed, occasionally harmful, yet tolerated—because the growth and money keep coming. But those false outputs are deadly to an industry whose primary product is accurate information. Journalists should not sit back and expect Silicon Valley to simply solve hallucinations on its own, and the BBC is showing there’s a path to being part of the solution without evangelizing or ignoring the problem. After all, “Check important info” is supposed to be the media’s job. View the full article
-
Minister hits back at Trump claims UK is ‘very happy’ with tariffs
Government aiming for better trade deal with US after 10% rate applied to Britain View the full article
-
Understanding the social biome and how everyday communication adds up
Andy Merolla is a professor in the Department of Communication at the University of California, Santa Barbara. Jeffrey Hall is a professor in the Department of Communication Studies and the director of the Relationships and Technology Lab at the University of Kanas. What’s the big idea? Individually, most day-to-day interactions may seem trivial, but they add up to an important personal and societal opportunity. We all engage in our own unique ecosystem of everyday communication—our very own social biome. Meaningful engagement with others is critical to health and wellbeing, but we live in a time when any kind of engagement is dwindling. So, even if we don’t get every moment “just right,” it’s worth prioritizing human contact and kindness so that we can cultivate happiness within and around us. Below, coauthors Andy Merolla and Jeffrey Hall share five key insights from their new book, The Social Biome: How Everyday Communication Connects and Shapes Us. Listen to the audio version—read by Merolla—in the Next Big Idea App. 1. We all inhabit unique communication ecosystems that define us. We come to know ourselves and others through communication. This includes the full range of daily face-to-face and mediated interactions, from passing hellos and office chit-chat to heated conflicts and heart-to-hearts. But it’s hard to conceptualize all this interaction. We coined the term social biome to help people understand how our lives are lived out in everyday communication. A social biome is our ecosystem of day-to-day talk. It’s the totality of our moments of communication—in-person and digital—with loved ones, acquaintances, coworkers, neighbors, customers, clerks, and complete strangers. Our biomes include interactions we choose to engage in, those thrust upon us, and those we just happen to bounce in and out of. The term “biome” comes from biology and ecology to describe what life is like in specific regions, including its plants, wildlife, and climate. Every human has their own unique microbiome, composed of the trillions of bacteria, fungi, and viruses living in and on our bodies. These microbes shape our health and well-being in fascinating ways, and although our microbiome is subject to the choices we make, such as the foods we eat, it’s also shaped by innumerable factors beyond our control. This includes where we happen to be born and the spaces we live and work in. Our social biomes, too, are products of choices we make and many factors beyond our control. You can choose to be as kind as you can to those around you, but in many situations, you simply don’t get to choose who’s around you, nor how they communicate with you. When we start viewing our lives as lived out in social biomes, we recognize how consequential our moments of everyday interaction are for shaping our self-concept and worldview. We also understand the limits of what we can do. Any individual moment of interaction can seem inconsequential, but at scale, our habits of interaction are anything but. Respect, dignity, and trust, as well as hate, indifference, and disdain all play out in small moments of communication—small moments that, over time, accumulate, crystallize, and calcify into our view of the world around us as a generally welcoming or inherently intolerant place. Ultimately, a social biome perspective compels us to scrutinize how we spend our time and why, how we choose to treat others, and what adjustments we can make to social habits to make our lives—and the lives of those in our social biomes—healthier and happier. Moves as small as a text to let a friend know you were thinking about them, or pausing an extra beat to acknowledge a coworker you might usually ignore, can initiate new and, hopefully, enduring, routines of connection that can scale up and reverberate across people. 2. There is no such thing as “just right” when it comes to communication. It’s incredible how much people value good communication skills. In one survey, over 90% of parents said that good communication skills are essential for their kids to thrive. Compare that to the percentage citing math skills (79%) or science skills (just 58%). It’s not just parents. Corporations prize communication abilities in hiring. This makes sense, as research indicates that communication problems are at the root of billions in corporate losses each year. People instinctively know that if they could just communicate better, it would help to address a lot of problems they face. But what exactly is “better” when it comes to communication? It is a harder question to answer than you might think. Despite decades of research, simple definitions of good communication are hard to find. First off, consider how messy everyday communication is. Of the thousands of words we typically speak each day, we tend to communicate in six-word chunks that are chock full of vocal fillers like um and ah, hesitations, starts, stops, interruptions, and trail offs. Add to that the constant digital distractions that tax the cognitive processing abilities of even the most Zen among us, and you get a good sense of what everyday communication is like. It bears little resemblance to the polished turns of talk we see in a typical Netflix series. Further, many of us think about communication in the wrong way. We use the word “communication” as if it’s a singular entity. But it’s not. We all operate from different sets of assumptions about what good communication entails. We even differ in our view of what communication is for. The meaning of communication is always co-constructed between people, and those people might be operating from very different understandings of what demarcates the communicative good from the communicative bad. Many communication challenges result from our tendency to put too much pressure on ourselves (and others) to get communication “just right.” But “just right” is always dependent on the unique standards people apply, and those standards don’t always align between communicators. When we fully appreciate that there is no such thing as “just right,” we can feel freer to connect with others in ways that feel authentic, knowing there are many paths to good communication. 3. We’re living in an Age of Interiority. Time-use data, which tracks how people spend their daily lives, has shown that we spend less and less time socializing. This trend started long before the COVID-19 pandemic. Time spent alone has been increasing for at least three decades. Social changes, such as food delivery apps, online shopping, and self-checkout lines, make it possible to avoid human interaction for tasks that once required it. It’s becoming increasingly possible for people, especially highly resourced folks in the Global North, to live in ways that circumvent face-to-face interactions. We’re not just hanging out with friends less often; we’re able to orchestrate a more disconnected life that’s finely tailored to our own needs. If we remember that people within social biomes are interdependent, then we see that each person’s shift toward a more interior life limits opportunities for social connections. When it comes to belonging, we are all in it together. Disconnection, moreover, is self-reinforcing. When we become less comfortable interacting with people, even in mundane moments of everyday life, our social skills can atrophy. Social inertia sets in, making it increasingly energy-intensive to re-engage and build new relationships. The reason for this interior shift across society is not solely due to personal choices. The social world controls us as much as we control it, and innumerable structural factors are pulling and keeping people apart. Long work hours. Precarious economic conditions. Lacking access to reliable and high-quality child and eldercare. These factors deplete people and lead them to want nothing more than to retreat from the social world—often toward a screen where they get some semblance of control. On top of it, ongoing segregation and political sorting intensify divisions, so even when we connect with others, it’s most likely with like-minded others. There are both personal and societal costs when we live more interior lives. 4. Connection and restorative solitude are linked. Alone time is important. A well-connected and socially satisfying life requires contented solitude. Research shows that communicating with others, including highly enjoyable conversations, requires a lot of energy. To replenish that energy, we need to recharge, often in solitude. Importantly, though, satisfying interactions make our time alone feel better. In a study Jeff and I conducted a few years ago, we found that people’s overall satisfaction with their life was associated with their daily survey reports of how content they felt when alone—feeling contented while alone is most likely to occur following positive social interaction experiences. For many people, though, solitude isn’t contented or chosen. Instead, it’s inescapable. When we find ourselves alone but don’t want to be, it reflects the kind of disconnection and loneliness that former Surgeon General Vivek Murthy and many others have so admirably called attention to in recent years. Social connection is highly uneven. Some people are doing great—their days are full of enjoyable interaction, and their calendars are packed with fun social events. Meanwhile, many others don’t have reliable access to the rewarding interactions that facilitate vital feelings of belonging. This is again where a social biome perspective can be helpful because it reminds us that we can do our best to look out for other people around us, particularly folks who don’t have as many opportunities for social interaction and support. This includes acquaintances, neighbors, and people we work with. Our efforts to reach out can rekindle connections for people badly needing them. 5. Hope is an interpersonal phenomenon. If we’re in an Age of Interiority, we could just as easily contend that we’re in an Age of Hopelessness. People have lost faith in institutions and feel less trust in the people around them. People with marginalized identities feel under attack by people in positions of great power. Fears of climate change. The existential dread of AI. Pick your poison. But what exactly does it mean to feel hopeless or hopeful? In day-to-day conversation, we say things like we’re “holding out hope” or “trying not to get our hopes up.” Such comments suggest that hope is, at best, an intentional suspension of disbelief or, at worst, willful ignorance of the cold, hard reality of life. This view of hope—as a foolish illusion or dangerous obliviousness to the way things really are—is one held by some of history’s most famous philosophers. Hope was among the evils inside Pandora’s box. Over the past 70 years, however, social psychologists have offered a radically different view of hope tied to the way we think about and pursue goals. The late psychologist C. R. Snyder and his collaborators helped us see that many of our most important goals are linked to other people. These goals can be both big and small. When we see friends giving their full attention to one another or small acts of kindness between strangers, that is hope in action. People are choosing to prioritize their finite attention and energy on others. These are building blocks of connection and, over time, give us a sense of hope to pursue larger, more challenging goals. When we accept the idea that hope is communal and not just personal, we better appreciate how much is riding on our treatment of one another in everyday moments of talk. Small moments of acknowledgement and compassion aren’t the antidote to all the world’s ills, but it’s hard to envision a world of rebuilt trust and a better future for our kids if we don’t try to spread kindness and dignity, moment by moment, across our social biomes. This article originally appeared in Next Big Idea Club magazine and is reprinted with permission. View the full article
-
Public safety power shutoffs are ramping up. Here’s how to be prepared
Are you prepared for when the power goes out? To prevent massive wildfires in drought-prone, high-wind areas, electrical companies have begun preemptively shutting off electricity. These planned shutdowns are called public safety power shutoffs, abbreviated to PSPS, and they’re increasingly common. So far this year, we’ve seen them in Texas, New Mexico, and California. Unlike regular power failures, which on average last only about two hours while a piece of broken equipment is repaired, a PSPS lasts until weather conditions improve, which could be days. And these shutoffs come at a steep price. In 2010 alone, they cost California more than $13 billion. A 2019 analysis of shutoffs in Placer County, California, found that they harmed 70% of local businesses. I am a business school professor who studies how people pay for things, including during emergencies. As I point out in my new book The Power of Cash: Why Using Paper Money Is Good for You and Society, many people have abandoned paper money and switched to electronic payments such as credit cards and mobile apps. This can become a big problem during an emergency, since these systems need electricity to operate. The switch to electronic payments is making the world less resilient in the face of increasing numbers of major natural disasters. So if a public safety power shutoff strikes and you don’t have any cash, you may be doubly vulnerable. On the other hand, keeping cash can protect you—and not just you and your family but also local businesses and your community. After all, keeping the economy moving during shutoffs reduces the financial damage they cause. Why do they keep turning off the power, anyway? It’s all about risk. The world has experienced a number of very destructive wildfires recently. In 2025, large parts of Los Angeles burned to the ground, with more than 18,000 buildings destroyed or damaged. In 2023, wildfires in Hawaii killed more than 100 people. Massive wildfires have also occurred recently in South Korea, Portugal, and Australia. Governments, people whose houses burned, and insurance companies are all looking for someone to blame and pay for the damage. Climate change, which is increasing the world’s average temperatures and drying out trees and grass, is setting the conditions. Since Mother Nature cannot be sued, utilities make handy scapegoats with deep pockets. Electrical utilities are sued because their power lines, transformers, and other equipment often start blazes. So to prevent lawsuits as well as fires, power companies are increasingly turning off the power when the conditions are ripe for a catastrophic blaze. There’s no uniform set of standards for when to impose a shutdown, but in general power companies do it when there are hot, dry, and windy conditions. For example, a PSPS is triggered in Hawaii if there’s a drought, wind gusts are over 45 mph, and relative humidity is under 45%. Power shutoffs are a relatively new idea. They were proposed in California in 2008 and first allowed in 2012. Since then, power companies across the entire western U.S. from Texas to Hawaii have adopted these plans. Shutoff plans also stretch from southern border states such as Arizona to northern border states such as Idaho and Montana. Shutting off the power is a huge problem, since it causes massive disruption to communities. People depend on power to run medical equipment, work, and keep communities safe. Even people with a desperate need for electricity, such as those on medical life support, are not immune to a safety shutoff. How to prepare for a PSPS As the world warms, the chance of being caught in a preemptive power shutoff increases. What can you do to minimize the impact? Having solar panels won’t protect you: Utilities shut off customers with solar panels to block those panels from pushing power onto the grid, since the whole goal is to shut off the grid. The only way for you to still have power is to buy a battery storage system and a transfer switch, which allows you to take your system completely off the grid. But this is very expensive. Getting a portable generator is only a partial solution for a multiday shutoff, since most last only 6 to 18 hours on a single tank of gas. Plus, generators run very hot, which creates its own fire risk. Another way to minimize the impact of both a power shutoff and a wildfire is to create a small disaster relief kit, or “go bag.” Creating one is relatively inexpensive. It should contain key items such as water, your medicines, some shelf-stable food—and importantly, some cash. Even some government websites forget to mention this. It’s also important to use paper money before a shutoff happens. I have all too frequently seen gas station attendants, supermarket checkout clerks, and restaurant servers have no idea how to handle cash. Recently at my local supermarket, for example, I paid with a $20 bill. The cashier had to ask another employee which kinds of coins to use to make change. If people don’t know how to handle cash during normal times, it ceases to be useful during emergencies. As the world warms, public safety power shutoffs will occur more frequently. The shutoffs clearly highlight the trade-off between economic and social disruption versus preventing dangerous wildfires. These shutoffs show there are no easy solutions, only hard choices. There are a few sensible and easy steps to take to reduce the impact of these shutoffs. One is to understand that during one of the very moments you might really need to spend money, modern payment systems fail. Holding and frequently using old-fashioned cash is a simple and low-cost way to protect yourself and your family. Jay L. Zagorsky is an associate professor at the Questrom School of Business at Boston University. This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article. View the full article
-
BP chair Helge Lund to step down
Exit follows a bruising period for UK oil majorView the full article
-
can I suggest that my employee rethink her career, pimple patches at work, and more
This post was written by Alison Green and published on Ask a Manager. It’s four answers to four questions. Here we go… 1. Can I suggest that my employee rethink her career path? One of my direct reports, “Mindy,” has worked for my organization since college; she’s now 31. I joined the staff three years ago and enjoy her a lot as a person: she’s smart, has a wonderful attitude, is very diligent and organized, and brings her best to every project. The problem is that I don’t think she’s on the right career path. Right now Mindy does communications work. but the issue is that she’s not a very good writer, which is a fundamental skill for the job. We do a lot of writing and it has to be done well, and her pieces require lots of rewriting. After nearly a decade of writing projects, LOTS of coaching from me and her previous manager, plus related degrees, her work still needs endless rounds of revisions and is just overall not good enough. She wants so badly to do a good job and have a thriving career in this field, though! She has so much potential and I want her to succeed as a professional … but she flat-out doesn’t have some key fundamental skills needed. However, I think she’d be great at marketing. She’s very good at analyzing and planning, and marketing jobs don’t require the same need to constantly produce really high-level written pieces. I’ve worked in marketing in the past and her strengths would be huge assets for that type of work, and it’s a career that wouldn’t involve the skills that she hasn’t been able to develop. It’s not a job that exists at my organization, though. We have a good relationship and talk regularly in our check-ins about career growth. Is there a way I can diplomatically tell her that while I don’t think she’s suited for a career based around writing, I think she’d make an excellent marketer? I want to navigate this carefully with her so that she feels supported and respected, even if it means essentially telling her she should consider eventually finding a new job elsewhere. Bonus related question: I’m at the point where I’m going to outsource a large annual project Mindy is usually very involved with. The quality of her work is poor enough that it will be faster, much less stressful, and will turn out much better if we hire a consultant to do it. Is there a respectful way I can explain that she’s not going to be working on that project anymore because of the quality of her work? Should I even tell her that? I know I wouldn’t be doing her any favors by hiding the reason for hiring the consultant, and I’ve been consistent in addressing her work quality, but I have no idea how to approach that conversation. Yes, please tell her! In fact, you could use the outsourcing of the annual project as an opening into that conversation — first “here’s what I’m doing and why, and here’s what the issues were when you worked on this in the past” and then “I’ve been reflecting on where you’ve been struggling, and I want to be honest with you that while I know that you’ve been working extremely hard — and frankly you’re a pleasure to work with — I haven’t seen the level of writing that we need for this role. I see your strengths as more ABC, which I think would make you fantastic at projects like XYZ.” I do think there’s another question here, which is whether you’re going to be able to keep her on at all if she’s not able to work at the level that you need. Ideally, of course, you’d have this conversation, she’d reflect and come to agree, and she’d move in that direction on her own. But if she doesn’t, you’ll need to figure out whether the issues rise to the level of something that jeopardize her current job or not. (Based just on your short letter, it sounds like they may. If that’s the case, since it sounds like you have an excellent and supportive rapport with Mindy, I’d try to do it through a series of candid and supportive conversations that end in a mutual agreement that she will move on — but I’d also be thinking about how you’ll handle it if that mutual agreement doesn’t occur.) 2. Hickies revealed in the locker room This is more of a philosophical question than anything else. Is it okay to have visible hickies at work if they are normally covered by clothes and only seen when taking off your shirt in the locker room? Technically my coworkers might see that I have a sex life, although locker room etiquette is of course that everyone becomes invisible until their clothes go back on. Still: is this something to avoid? No one in a locker room should be paying any attention to the parts of your body that are revealed while you’re changing clothes. That said, there’s a difference between “should” and “will.” If part of your body is covered in what look very much like sex-related bruises … well, assume people may have thoughts about that, so proceed accordingly. They certainly shouldn’t say anything to you about it, but is that info you want your coworkers to have in their heads about you? If it’s a single small bruise, it’s almost certainly a non-issue, but I can imagine things that would be significantly more revealing than that. (For example, if your ass bears evidence that you’re into spanking, it’s better for everyone if you use a non-work gym that week.) Related: is it unprofessional to have hickeys at work? 3. Wearing pimple patches at work I want to get your take on wearing pimple patches at work. I have a new employee who is Gen Z who wears pimple patches on her face, sometimes multiples of them, at a time. Our workplace is corporate with a semi-strict dress code, but it often goes fairly ignored. For example: the dress code says no leggings, but people often wear them, including my boss. Also, the dress code says no sneakers but people often wear stylish sneakers. I wear pimple patches all the time, but wouldn’t wear them myself at work. We frequently conduct meetings via Zoom, and I feel like this comes across as unprofessional, but I could be off in terms of whether this is acceptable to another generation or other cultures. It really depends on the office, but the culture has definitely moved toward seeing pimple patches the same way as bandages (i.e., fine to wear at work). Particularly if they’re clear or flesh-colored, I’d mentally categorize them as bandages and ignore. If they’re brightly colored, it gets more into questions about your particular office culture (and if you’re unsure how it’s playing there, I might ask someone senior to you whose judgment you respect it feel out of sync in your particular office). 4. My boss keeps using WhatsApp, Signal, and texts to contact me I have a new boss (about two months) who pretty much never replies to emails. She’ll WhatsApp/Signal chat me instead. This is definitely not the culture, and I personally find it really annoying as I usually only use these apps for personal reasons or if there’s an urgent issue. She’ll also text me after hours / on weekends for not time-sensitive stuff. Sometimes it is actually urgent so I can’t mute her and check on my own schedule. Having to monitor three channels of communications with her is exhausting, especially as someone who’s trying to keep better work/life boundaries, and logistically annoying because if I’m trying to refer back to something, it’s not as easy as just searching one platform for the conversation. That said, she’s not aggressive or scary like some other bosses who text at all hours. Is there a way I can ask her to stick to email unless it’s time (or otherwise) sensitive, or as the lower in the hierarchy do I have to just accept her way as a new annoyance of my job? I am pretty senior in my organization but she is clearly above me in the hierarchy There are other issues with her management style which I don’t find to be the most strategic, but not to the level of my considering quitting over. Yes, you can say something! I’d frame it this way: “I don’t really use WhatsApp or Signal so I’ve been missing messages when you contact me there. Could we stick with email so I can be sure I see everything you send me?” And the next time she texts you after-hours, wait a while before responding (to reinforce that it’s not work time) and then say, “I’m going to move this to email so it’s with our work messages; I’m trying to keep work stuff off my phone. I’ll email about this shortly!” Do that enough and it might retrain her. View the full article
-
Knives out for Mike Waltz as Trump fires national security officials
Maga critics circle around hawkish foreign policy adviser who was at centre of ‘Signalgate’ fiascoView the full article
-
Trump chaos is alienating Republicans
Outside of the Maga ecosystem, bad economic news is starting to cut throughView the full article
-
How to make sense of Donald Trump’s tariffs
The new field of ‘geoeconomics’ offers a guide for the perplexedView the full article
-
Europe braces for flood of Chinese goods after US tariffs
EU officials ready emergency measures to prevent onslaught of discounted products in ‘economic nightmare’View the full article
-
Inflation fears add to pressure on Fed
Bets on surging import prices show concern that US economy is slowing sharply or even flirting with recessionView the full article
-
What comes next after South Korean president’s removal?
Ruling against Yoon Suk Yeol means election will be held in May amid highly polarised climateView the full article
-
South Korea’s president removed from office over martial law bid
Yoon Suk Yeol’s shortlived attempt to impose military rule triggered political crisisView the full article
-
Gas Prices Climb Nationwide, Driven by Refinery Maintenance and Seasonal Factors
The national average price for a gallon of regular gasoline jumped more than 10 cents over the past week, reaching $3.26, according to AAA. This marks the first time since September that prices have hit this level, reflecting typical seasonal shifts. Despite the increase, prices remain below last year’s national average of $3.54 for the same period. AAA attributes the rise to several contributing factors, including ongoing refinery maintenance and the transition to more expensive summer-blend gasoline. One month ago, the national average stood at $3.09. Supply and Demand Trends Data from the Energy Information Administration (EIA) shows a decrease in gasoline demand, falling from 8.64 million barrels per day to 8.49 million barrels per day over the past week. During the same period, total domestic gasoline supply dropped from 239.1 million barrels to 237.6 million barrels. However, gasoline production rose, averaging 9.3 million barrels per day. On the crude oil side, West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude rose by 51 cents at the close of Wednesday’s formal trading session, settling at $71.71 per barrel. The EIA reported a 6.2 million barrel increase in crude oil inventories from the previous week, bringing the total to 439.8 million barrels. Despite the increase, inventories are still about 4% below the five-year average for this time of year. EV Charging Costs Hold Steady For electric vehicle owners, the national average cost per kilowatt hour of electricity at public EV charging stations remained unchanged from the previous week at 34 cents. State-by-State Price Comparisons California remains the most expensive market for gasoline, with an average price of $4.91 per gallon, followed by Hawaii ($4.52), Washington ($4.30), Nevada ($3.99), and Oregon ($3.93). Rounding out the top ten are Alaska ($3.53), Illinois ($3.52), Arizona ($3.42), Idaho ($3.38), and Pennsylvania ($3.37). The least expensive markets for gasoline are Mississippi ($2.74), Tennessee ($2.80), Oklahoma ($2.81), Louisiana ($2.82), and Alabama ($2.85). Also among the lowest are Texas, Arkansas, and Kansas (each at $2.87), South Carolina ($2.87), and Kentucky ($2.89). In terms of EV charging, Hawaii continues to lead with the highest average cost at 56 cents per kilowatt hour, followed by West Virginia (46 cents), Montana (44 cents), Tennessee (42 cents), and South Carolina (42 cents). Other high-cost states include Idaho, Alaska, Kentucky, Louisiana, and New Hampshire, all ranging between 40 and 42 cents. The states with the lowest EV charging rates are Kansas (22 cents), Missouri (25 cents), Iowa and North Dakota (26 cents each), and Nebraska and Delaware (27 cents each). Texas, Washington, DC, Utah, and Maryland all report an average of 30 cents per kilowatt hour. This article, "Gas Prices Climb Nationwide, Driven by Refinery Maintenance and Seasonal Factors" was first published on Small Business Trends View the full article
-
Gas Prices Climb Nationwide, Driven by Refinery Maintenance and Seasonal Factors
The national average price for a gallon of regular gasoline jumped more than 10 cents over the past week, reaching $3.26, according to AAA. This marks the first time since September that prices have hit this level, reflecting typical seasonal shifts. Despite the increase, prices remain below last year’s national average of $3.54 for the same period. AAA attributes the rise to several contributing factors, including ongoing refinery maintenance and the transition to more expensive summer-blend gasoline. One month ago, the national average stood at $3.09. Supply and Demand Trends Data from the Energy Information Administration (EIA) shows a decrease in gasoline demand, falling from 8.64 million barrels per day to 8.49 million barrels per day over the past week. During the same period, total domestic gasoline supply dropped from 239.1 million barrels to 237.6 million barrels. However, gasoline production rose, averaging 9.3 million barrels per day. On the crude oil side, West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude rose by 51 cents at the close of Wednesday’s formal trading session, settling at $71.71 per barrel. The EIA reported a 6.2 million barrel increase in crude oil inventories from the previous week, bringing the total to 439.8 million barrels. Despite the increase, inventories are still about 4% below the five-year average for this time of year. EV Charging Costs Hold Steady For electric vehicle owners, the national average cost per kilowatt hour of electricity at public EV charging stations remained unchanged from the previous week at 34 cents. State-by-State Price Comparisons California remains the most expensive market for gasoline, with an average price of $4.91 per gallon, followed by Hawaii ($4.52), Washington ($4.30), Nevada ($3.99), and Oregon ($3.93). Rounding out the top ten are Alaska ($3.53), Illinois ($3.52), Arizona ($3.42), Idaho ($3.38), and Pennsylvania ($3.37). The least expensive markets for gasoline are Mississippi ($2.74), Tennessee ($2.80), Oklahoma ($2.81), Louisiana ($2.82), and Alabama ($2.85). Also among the lowest are Texas, Arkansas, and Kansas (each at $2.87), South Carolina ($2.87), and Kentucky ($2.89). In terms of EV charging, Hawaii continues to lead with the highest average cost at 56 cents per kilowatt hour, followed by West Virginia (46 cents), Montana (44 cents), Tennessee (42 cents), and South Carolina (42 cents). Other high-cost states include Idaho, Alaska, Kentucky, Louisiana, and New Hampshire, all ranging between 40 and 42 cents. The states with the lowest EV charging rates are Kansas (22 cents), Missouri (25 cents), Iowa and North Dakota (26 cents each), and Nebraska and Delaware (27 cents each). Texas, Washington, DC, Utah, and Maryland all report an average of 30 cents per kilowatt hour. This article, "Gas Prices Climb Nationwide, Driven by Refinery Maintenance and Seasonal Factors" was first published on Small Business Trends View the full article
-
Three key factors as banks manage CRE risk in 2025
As the risk of a recession rises, commercial real estate loans remain a major concern for banks and industry participants. One observer asked: "Is '25 the year where sellers start to capitulate, call a loser a loser, and move on?" View the full article
-
Leading Thoughts for April 3, 2025
IDEAS shared have the power to expand perspectives, change thinking, and move lives. Here are two ideas for the curious mind to engage with: I. Richard S. Tedlow on speaking truth to power: “The fantasy that if you get rid of the messenger, you can render the message untrue is a powerful one.” Source: Denial: Why Business Leaders Fail to Look Facts in the Face—and What to Do About It II. Todd Henry on the passion fallacy: “Instead of asking ‘What would bring me enjoyment?’ which is how many people think about following their passion, we should instead ask ‘What work am I willing to suffer for today?’ Great work requires suffering for something beyond yourself. It’s created when you bend your life around a mission and spend yourself on something you deem worthy of your best effort. What is your worthwhile cause?” Source: Die Empty: Unleash Your Best Work Every Day * * * Look for these ideas every Thursday on the Leading Blog. Find more ideas on the LeadingThoughts index. * * * Follow us on Instagram and X for additional leadership and personal development ideas. View the full article
-
Trump floats China tariff relief in exchange for TikTok sale approval
US president suggests he is open to horse-trading a day after imposing severe import levies on Chinese goodsView the full article
-
Build a smarter SEO content strategy by Digital Marketing Depot
A great piece of content doesn’t just rank—it drives the right traffic, at the right time, with the right message. In Your Content Marketing Blueprint from MoreVisibility, you’ll get a practical blueprint for building a smarter content strategy rooted in search behavior. What’s inside: A framework to align your content with real search intent A method for using keyword data to uncover content gaps A Help / Hub / Hero structure to serve every stage of the funnel Tips for using AI to streamline content creation—without losing quality Whether you’re auditing existing pages or planning net-new content, this guide helps you focus on what actually works. Visit Digital Marketing to get your copy today. View the full article